IWR-1-endoPotent Wnt signaling inhibitor CAS# 1127442-82-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 1127442-82-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 90488854 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C25H19N3O3 | M.Wt | 409.44 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | endo-IWR 1; IWR-1-endo | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 46 mg/mL (112.35 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
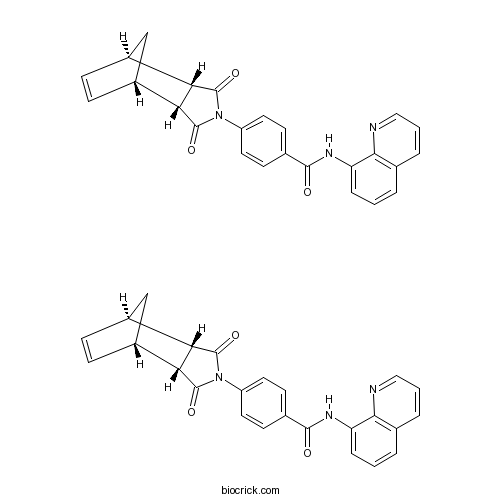
| Chemical Name | 4-[(1S,2R,6S,7R)-3,5-dioxo-4-azatricyclo[5.2.1.02,6]dec-8-en-4-yl]-N-quinolin-8-ylbenzamide | ||
| SMILES | C1C2C=CC1C3C2C(=O)N(C3=O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(=O)NC5=CC=CC6=C5N=CC=C6.C1C2C=CC1C3C2C(=O)N(C3=O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(=O)NC5=CC=CC6=C5N=CC=C6 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MFEADGGBEDIZRE-MGIYQXMMSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/2C25H19N3O3/c2*29-23(27-19-5-1-3-14-4-2-12-26-22(14)19)15-8-10-18(11-9-15)28-24(30)20-16-6-7-17(13-16)21(20)25(28)31/h2*1-12,16-17,20-21H,13H2,(H,27,29)/t2*16-,17+,20-,21+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Inhibitor of Wnt signaling. Induces an increase in Axin2 protein levels; promotes β-catenin phosphorylation by stabilizing Axin-scaffolded destruction complexes. Negative control exo-IWR available. |

IWR-1-endo Dilution Calculator

IWR-1-endo Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4424 mL | 12.2118 mL | 24.4236 mL | 48.8472 mL | 61.059 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4885 mL | 2.4424 mL | 4.8847 mL | 9.7694 mL | 12.2118 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2442 mL | 1.2212 mL | 2.4424 mL | 4.8847 mL | 6.1059 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0488 mL | 0.2442 mL | 0.4885 mL | 0.9769 mL | 1.2212 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0244 mL | 0.1221 mL | 0.2442 mL | 0.4885 mL | 0.6106 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IWR-1-endo is a small molecule inhibitor of Wnt Response with IC50 value of 180nM [1].
IWR-1-endo is a small molecule antagonists of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway screened out from a diverse synthetic chemical library. It acts as an inhibitor of Wnt response. IWR-1-endo can inhibit the activity of Wnt1, 2 and 3. In cultured cells, IWR-1-endo inhibits Wnt-induced β-catenin accumulation which is a downstream event of Lrp6 and Dvl2. It is proved that IWR-1-endo promote β-catenin destruction through promoting stability of Axin-scaffolded destruction complexes in the DLD-1 colorectal cancer (CRC) cell line. IWR-1-endo is also shown to inhibit tailfin regeneration and epithelial stem cell self-renewal in zebrafish. These two processes are both dependent on Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Furthermore, IWR-1-endo can block aberrant cell growth supported by hyperactivation of Wnt/β-catenin resulting from Apc loss [1].
References:
[1] Chen B, Dodge ME, Tang W, Lu J, Ma Z, Fan CW, Wei S, Hao W, Kilgore J, Williams NS, Roth MG, Amatruda JF, Chen C, Lum L. Small molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signaling in tissue regeneration and cancer. Nat Chem Biol. 2009 Feb;5(2):100-7.
- Oleonuezhenide
Catalog No.:BCN6011
CAS No.:112693-21-7
- Erigeside C
Catalog No.:BCN6010
CAS No.:112667-09-1
- Fragransin A2
Catalog No.:BCN6008
CAS No.:112652-46-7
- 1,7-Dihydroxyacridone
Catalog No.:BCN7275
CAS No.:112649-95-3
- BR-Xanthone A
Catalog No.:BCN6007
CAS No.:112649-48-6
- Garcinone E
Catalog No.:BCN3604
CAS No.:112649-21-5
- U-73122
Catalog No.:BCC5199
CAS No.:112648-68-7
- Dicyclanil
Catalog No.:BCC8938
CAS No.:112636-83-6
- Iso-mogroside V
Catalog No.:BCN3047
CAS No.:1126032-65-2
- 4-Allylpyrocatechol
Catalog No.:BCN6009
CAS No.:1126-61-0
- SKLB610
Catalog No.:BCC3647
CAS No.:1125780-41-7
- A 804598
Catalog No.:BCC6198
CAS No.:1125758-85-1
- exo-IWR 1
Catalog No.:BCC7823
CAS No.:1127442-87-8
- Galanin (1-15) (porcine, rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5762
CAS No.:112747-70-3
- Clemastanin B
Catalog No.:BCC8152
CAS No.:112747-98-5
- Osthenone
Catalog No.:BCN4731
CAS No.:112789-90-9
- Letrozole
Catalog No.:BCC1063
CAS No.:112809-51-5
- Gatifloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC1064
CAS No.:112811-59-3
- 1-Cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCC8465
CAS No.:112811-71-9
- 1-Cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8464
CAS No.:112811-72-0
- Dynole 34-2
Catalog No.:BCC7891
CAS No.:1128165-88-7
- Methyllycaconitine citrate
Catalog No.:BCC6897
CAS No.:112825-05-5
- 24R-Calcipotriol
Catalog No.:BCC1304
CAS No.:112827-99-3
- (24R)-MC 976
Catalog No.:BCC1289
CAS No.:112828-09-8
Intermedin protects HUVECs from ischemia reperfusion injury via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway.[Pubmed:30931679]
Ren Fail. 2019 Nov;41(1):159-166.
Intermedin (IMD) is a member of the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) superfamily and a pro-angiogenic factor. In the present study, we identified activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway by IMD. Adding CoCl2 HUVECs was used to establish an in vitro model. The migration of HUVECs was measured by wound healing assays and transwell migration assays. Capillary formation was measured using tube formation assays. Immunocytochemistry (ICC) analysis was used to evaluate VEGF and RAMP2 expression in HUVECs. The relevant signaling molecules were detected with western blot. Our study shows that IMD could promote H/R impaired HUVECs migration and tube formation in vitro. On the other hand, inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling led to the suppression of this promotion of migration and tube formation. This result suggests that Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is correlated to IMD induced angiogenesis. Analysis of results from ICC assays indicated that IMD works through increasing levels of VEGF and RAMP2. Meanwhile, the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling specific inhibitor IWR-1-endo was shown to down-regulate VEGF and RAMP2 expression. Western blot results further confirmed the signaling mechanism by which IMD promotes angiogenesis. Thus, Wnt/beta-catenin signaling plays an important role in IMD induced neovascularization. The data further suggest that the PI3K axis contributes positively downstream.
EGFL7 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis through increasing CKS2 expression by activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling.[Pubmed:30129142]
J Cell Biochem. 2018 Dec;119(12):10327-10337.
Epidermal growth factor-like domain multiple 7 (EGFL7) is an important sport stimulating factor and motility related factors significantly enhanced the tumor cell metastasis and overexpressed in many cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), associated with tumorigenesis. However, the molecular mechanism by which EGFL7 regulates HCC cell proliferation and apoptosis and the correlation between EGFL7 and cyclin-dependent kinases regulatory subunit 2 (CKS2), which is essential for biological function, have not fully explained. In this study, EGFL7 and CKS2 expression in patients with HCC was measured by real-time polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry. After HCC cells respectively transfected with pLKO.1-EGFL7-shRNA, pLVX-Puro-EGFL7 recombined vector or CKS2 small interfering RNA, cell counting kit-8 and flow cytometry was performed to examine the cell proliferation and apoptosis, respectively, and the expression of beta-catenin, CKS2, CDK2, and cleaved caspase-3 was measured by Western blot analysis. We found that EGFL7 and CKS2 were overexpressed in HCC tissues and a positive correlation was found between them. EGFL7 knockdown markedly inhibited proliferation and promoted apoptosis of HCC cells, along with decreased expression of CKS2 and CDK2, but increased cleaved caspase-3 expression, while EGFL7 overexpression showed an opposite effect. EGFL7 silencing in nude mice also showed decreased tumor growth and altered protein expression similar to its effect in HCC cells in vitro. Importantly, CKS2 silencing significantly inhibited EGFL7-induced HCC cell proliferation and protein expression, and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway inhibitor IWR-1-endo significantly inhibited CKS2 expression in HCC cells. Taken together, EGFL7 promotes HCC cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis through increasing CKS2 expression by activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling.
Efflux inhibition by IWR-1-endo confers sensitivity to doxorubicin effects in osteosarcoma cells.[Pubmed:29412166]
Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;150:141-149.
Osteosarcoma is the most common bone tumor that affects children and young adults. Despite advances in the use of combination chemotherapy regimens, response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in osteosarcoma remains a key determinant of patient outcome. Recently, highly potent small molecule inhibitors of canonical Wnt signaling through the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)-family enzymes, tankyrases 1 & 2 (Tnks1/2), have been considered as possible chemotherapy sensitizing agents. The goal of this study was to determine the ability of the highly specific Tnks1/2 inhibitor IWR-1-endo to sensitize chemotherapy-resistant osteosarcoma to doxorubicin. We found that IWR-1-endo significantly inhibited cellular efflux, as measured by cellular retention of Calcein AM and doxorubicin. In a model of doxorubicin resistant osteosarcoma, pre-treatment with IWR-1-endo strongly sensitized to doxorubicin. This sensitization reduced the doxorubicin IC50 in doxorubicin-resistant cells, but not in chemotherapy naive cells and caused doxorubicin-treated cells to accumulate at the G2/M checkpoint. Further, we found that sensitization with IWR-1-endo produced increased gammaH2AX foci formation, indicating increased DNA damage by doxorubicin. Taken together, our findings show that IWR-1-endo increases cellular responses to doxorubicin, by blocking efflux transport in a drug-resistant model of osteosarcoma.
LNGFR targets the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and promotes the osteogenic differentiation in rat ectomesenchymal stem cells.[Pubmed:28887537]
Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 8;7(1):11021.
Considerable evidence has shown that the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway is involved in osteogenic differentiation in various stem cells. However, the role of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in regulating the osteogenic differentiation of rat ectomesenchymal stem cells (EMSCs), which are considered to be the progenitors of dental mesenchymal stem cells, remains unknown. In this study, we demonstrated that nuclear beta-catenin was upregulated during EMSC osteogenic differentiation. The Wnt signalling inhibitor IWR-1-endo inhibited EMSC osteogenic differentiation, while the Wnt signalling agonist SKL2001 promoted it. Moreover, nuclear beta-catenin was further upregulated by the overexpression of low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor (LNGFR) during EMSC osteogenic differentiation. Further experiments demonstrated that LNGFR overexpression enhanced EMSC osteogenic differentiation, while LNGFR silencing decreased it. Additionally, IWR-1-endo attenuated LNGFR-enhanced EMSC osteogenic differentiation. Collectively, our data reveal that LNGFR targets the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and positively regulates EMSC osteogenic differentiation, suggesting that Wnt/beta-catenin pathway may be involved in the development of teeth and that the targeting Wnt/beta-catenin pathway may have great potential for applications in dental tissue engineering regeneration.
SOST silencing promotes proliferation and invasion and reduces apoptosis of retinoblastoma cells by activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway.[Pubmed:28485721]
Gene Ther. 2017 Jul;24(7):399-407.
This study aimed to investigate the effects of SOST and the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway on the proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of human retinoblastoma cells. Fifty-five retinoblastoma and 21 normal retinal tissue samples were collected as the case group and control group, respectively. HXO-RB44 and SO-RB50 cells were selected and assigned into blank, negative control (NC), siRNA 1, siRNA 2, siRNA 3, IWR-1-endo 1, IWR-1-endo 2 and IWR-1-endo 3 groups. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was applied to detect the expression of SOST, Wnt-1, and beta-catenin in the collected tissue samples. MTT assay, flow cytometry, transwell assay and the starch test were employed to determine the cell proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, invasion and migration after transfection. The qRT-PCR and western blotting were also used to detect the mRNA and protein expressions of SOST, Wnt-1, beta-catenin, C-myc, Cyclin D1, MMP-2 and MMP-9. The tumor formation in nude mice was conducted to evaluate the effects of SOST on the growth of a transplanted tumor. Compared with normal retinal tissues, the retinoblastoma tissues exhibited a downregulation of SOST but an upregulation of Wnt-1 and beta-catenin. The proliferation, invasion and migration of HXO-RB44 and SO-RB50 cells in the SOST-siRNA group were significantly higher than the cells in the blank and NC groups. The expressions of Wnt-1, beta-catenin, C-myc, Cyclin D1, MMP-2 and MMP-9 in the three SOST-siRNA groups were elevated, but the SOST decreased when compared with the blank and NC groups. SOST silencing promoted the growth of transplanted tumors in nude mice. These findings indicate that SOST silencing promotes the proliferation, invasion and migration, and decreases the apoptosis of human retinoblastoma cells by activating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway.
Structure-activity relationship studies of small-molecule inhibitors of Wnt response.[Pubmed:19410457]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Jul 15;19(14):3825-7.
Suppression of oncogenic Wnt-mediated signaling holds promise as an anti-cancer therapeutic strategy. We previously reported a novel class of small molecules (IWR-1/2, inhibitors of Wnt response) that antagonize Wnt signaling by stabilizing the Axin destruction complex. Herein, we present the results of structure-activity relationship studies of these compounds.


