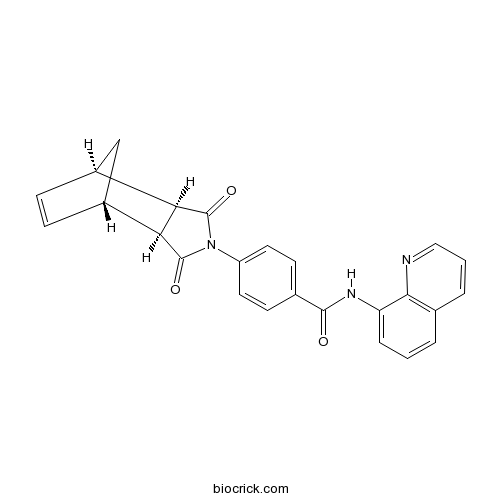
exo-IWR 1CAS# 1127442-87-8 |
- glucagon receptor antagonists 3
Catalog No.:BCC1595
CAS No.:202917-17-7
- glucagon receptor antagonists 2
Catalog No.:BCC1594
CAS No.:202917-18-8
- glucagon receptor antagonists 1
Catalog No.:BCC1593
CAS No.:503559-84-0
- MK 0893
Catalog No.:BCC1752
CAS No.:870823-12-4
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 1127442-87-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 1163034 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C25H19N3O3 | M.Wt | 409.44 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
| SMILES | C1C2C=CC1C3C2C(=O)N(C3=O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(=O)NC5=CC=CC6=C5N=CC=C6 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZGSXEXBYLJIOGF-BTYSMDAFSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H19N3O3/c29-23(27-19-5-1-3-14-4-2-12-26-22(14)19)15-8-10-18(11-9-15)28-24(30)20-16-6-7-17(13-16)21(20)25(28)31/h1-12,16-17,20-21H,13H2,(H,27,29)/t16-,17+,20+,21- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Negative control for endo-IWR 1. 25-fold less active than endo-IWR 1; exhibits decreased activity against the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. |

exo-IWR 1 Dilution Calculator

exo-IWR 1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4424 mL | 12.2118 mL | 24.4236 mL | 48.8472 mL | 61.059 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4885 mL | 2.4424 mL | 4.8847 mL | 9.7694 mL | 12.2118 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2442 mL | 1.2212 mL | 2.4424 mL | 4.8847 mL | 6.1059 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0488 mL | 0.2442 mL | 0.4885 mL | 0.9769 mL | 1.2212 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0244 mL | 0.1221 mL | 0.2442 mL | 0.4885 mL | 0.6106 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- IWR-1-endo
Catalog No.:BCC5102
CAS No.:1127442-82-3
- Oleonuezhenide
Catalog No.:BCN6011
CAS No.:112693-21-7
- Erigeside C
Catalog No.:BCN6010
CAS No.:112667-09-1
- Fragransin A2
Catalog No.:BCN6008
CAS No.:112652-46-7
- 1,7-Dihydroxyacridone
Catalog No.:BCN7275
CAS No.:112649-95-3
- BR-Xanthone A
Catalog No.:BCN6007
CAS No.:112649-48-6
- Garcinone E
Catalog No.:BCN3604
CAS No.:112649-21-5
- U-73122
Catalog No.:BCC5199
CAS No.:112648-68-7
- Dicyclanil
Catalog No.:BCC8938
CAS No.:112636-83-6
- Iso-mogroside V
Catalog No.:BCN3047
CAS No.:1126032-65-2
- 4-Allylpyrocatechol
Catalog No.:BCN6009
CAS No.:1126-61-0
- SKLB610
Catalog No.:BCC3647
CAS No.:1125780-41-7
- Galanin (1-15) (porcine, rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5762
CAS No.:112747-70-3
- Clemastanin B
Catalog No.:BCC8152
CAS No.:112747-98-5
- Osthenone
Catalog No.:BCN4731
CAS No.:112789-90-9
- Letrozole
Catalog No.:BCC1063
CAS No.:112809-51-5
- Gatifloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC1064
CAS No.:112811-59-3
- 1-Cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCC8465
CAS No.:112811-71-9
- 1-Cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8464
CAS No.:112811-72-0
- Dynole 34-2
Catalog No.:BCC7891
CAS No.:1128165-88-7
- Methyllycaconitine citrate
Catalog No.:BCC6897
CAS No.:112825-05-5
- 24R-Calcipotriol
Catalog No.:BCC1304
CAS No.:112827-99-3
- (24R)-MC 976
Catalog No.:BCC1289
CAS No.:112828-09-8
- (24S)-MC 976
Catalog No.:BCC1291
CAS No.:112849-14-6
Neuropathy of type 1 diabetes in the Arab world: A systematic review and meta-analysis.[Pubmed:28384559]
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017 May;127:172-180.
AIMS: Although type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a common disease in the Arab nations, there is no data available on the prevalence of peripheral neuropathy (PN) among T1D subjects in Arab countries. The aim of this study is to analyze the prevalence of PN in T1D subjects via published literature and to draw attention to the dearth of the published work in this serious complication of T1D. METHODS: A meta-analysis was performed on studies representing different Arab countries with a total number of 2243 T1D subjects. RESULTS: The pooled prevalence of PN among T1D subjects in the Arab region was estimated as 18% with 95% confidence intervals (CI): 0.09-0.34. The PN prevalence was significantly higher in the >16-yr age group, with 59.1% (95% CI: 0.45-0.72) compared to 9.5% (95% CI: 0.05-0.19) in the <16-yr age group. Furthermore, the PN prevalence was significantly higher in the group with more than 10-yr T1D, 35% (95% CI: 0.15-0.62) than in the group with less than 10-yr T1D, 9.4% (95% CI: 0.04-0.21). CONCLUSION: In Arab countries, PN is common in adults and children with T1D, but prevalence varies widely. Older age Arab people (>16years) with T1D are affected more with PN than younger age Arab people (<16years). PN is more frequently present in Arab subjects with a longer duration of T1D diabetes than in those with shorter duration.
Very low-dose fluvastatin-valsartan combination decreases parameters of inflammation and oxidative stress in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.[Pubmed:28384560]
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017 May;127:181-186.
AIMS: Previously we revealed the effectiveness of a new therapeutic approach with a short-term, very-low dose fluvastatin-valsartan combination on the improvement of arterial function in type 1 diabetes mellitus patients (T1DM). In this study we explored whether this approach influences inflammation and oxidative stress and explored any association of these effects with arterial function improvement. METHODS: This was a supplementary analysis of the two previous double blind randomized studies (included 44 T1DM patients). Treatment group received very-low dose fluvastatin-valsartan, the control group received placebo. Blood samples were collected and inflammation parameters: high-sensitivity CRP (hsCRP), interleukin 6 (IL-6), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and oxidative stress parameter total antioxidant status (TAS) were measured. RESULTS: Treatment decreased hsCRP values (by 56.5%, P<0.05) and IL-6 values (by 33.6%, P<0.05) and increased TAS values (by 21.1%; P<0.05) after 30days of treatment. High sensitivity CRP and TAS remained decreased 3months after treatment discontinuation. Importantly, the anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative action significantly correlated with arterial function improvement. CONCLUSIONS: The approach consisting of short-term (30days) treatment with a very low-dose fluvastatin-valsartan combination acts anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative in T1DM patients. These observations along with the improvement of arterial function support the assumption that this approach could have an important clinical benefit in T1DM patients.
No significant difference between chiari malformation type 1.5 and type I.[Pubmed:28384597]
Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017 Jun;157:34-39.
OBJECTIVE: Chiari malformation Type 1.5 (CM 1.5) was defined as the association of Chiari malformation Type I (CM I) and brainstem herniation. The objective was to demonstrate the difference of clinical features and surgical outcomes between CM 1.5 and CM I. PATIENTS AND METHODS: All CM 1.5 and CM I adult patients who underwent posterior fossa decompression with duraplasty at our institution between 2006 and 2010 were retrospectively reviewed. Clinical characteristics, imaging features, and long-term outcomes were compared between CM 1.5 and CM I patients. RESULTS: A total of 142 adult patients were enrolled, including 27 CM 1.5 and 115 CM I patients. The average follow-up period was 102 months. Age at diagnosis was significantly younger in CM 1.5 group than CM I group (p=0.039). And the degree of tonsillar herniation was significantly more severe in CM 1.5 group than CM I group (p<0.001). There was no significant difference in other clinical and imaging characteristics. Moreover, improvement of symptoms was observed in 21 CM 1.5 patients (77.8%) and 94 CM I patients (81.7%), and no significant difference was detected (p=0.637). There was no significant difference in the resolution of syringomyelia between CM 1.5 (72.7%) and CM I (76.5%) patients, either (p=0. 710). CONCLUSIONS: Although CM 1.5 patients presented with brainstem herniation and more severe tonsillar herniation, other clinical and imaging features and surgical outcomes were similar with CM I patients. We think CM 1.5 is just a subtype of CM I, rather than a unique type of Chiari malformations.
Poly-(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-1 Promotes Prothrombin Gene Transcription and Produces Des-Gamma-Carboxy Prothrombin in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.[Pubmed:28384634]
Digestion. 2017;95(3):242-251.
BACKGROUND AND AIM: Although des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin (DCP) is a well-known tumor marker for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the mechanism of DCP production is unclear. This study aimed to investigate the mechanism how DCP is produced in HCC cells. METHODS: Levels of mRNA and DCP were analyzed by real-time polymerase chain reaction and electro-chemiluminescence immunoassay respectively. Secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) expression vectors including deletion mutants of the prothrombin gene promoter were constructed for reporter gene assay. The transcription factors bound to DNA fragments were analyzed by mass spectrometry. An electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) was performed using a biotin end-labeled DNA. RESULTS: The prothrombin mRNA levels in all 5 DCP producing cell lines were appreciably high. However, those in 2 DCP non-producing cell lines were below detectable levels. A SEAP vector with -2985 to +27 showed a very high transcription activity in DCP-producing Huh-1 cells. However, transcription abruptly decreased when the vector with -2955 to +27 was transfected, and then remained at the similar levels with larger deletion mutants, indicating the existence of a cis-element at -2985 to -2955 (31-bp). Mass spectrometry analysis identified the protein that bound to the 31-bp DNA as poly-(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1). Knockdown of the PARP-1 gene by small interfering RNA in Huh-1 cells induced marked inhibition of prothrombin gene transcription. The EMSA clearly showed that PARP-1 specifically binds to the 31-bp DNA fragment in the prothrombin gene promoter. CONCLUSIONS: Our data suggest that PARP-1 activates prothrombin gene transcription and that the excessive prothrombin gene transcription induces DCP production in DCP-producing HCC cells.
Structure-activity relationship studies of small-molecule inhibitors of Wnt response.[Pubmed:19410457]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Jul 15;19(14):3825-7.
Suppression of oncogenic Wnt-mediated signaling holds promise as an anti-cancer therapeutic strategy. We previously reported a novel class of small molecules (IWR-1/2, inhibitors of Wnt response) that antagonize Wnt signaling by stabilizing the Axin destruction complex. Herein, we present the results of structure-activity relationship studies of these compounds.


