SCH 28080H+,K+-ATPase inhibitor CAS# 76081-98-6 |
- MLN8237 (Alisertib)
Catalog No.:BCC2166
CAS No.:1028486-01-2
- VX-680 (MK-0457,Tozasertib)
Catalog No.:BCC2167
CAS No.:639089-54-6
- Reversine
Catalog No.:BCC1892
CAS No.:656820-32-5
- AZD1152
Catalog No.:BCC1393
CAS No.:722543-31-9
- XL228
Catalog No.:BCC2058
CAS No.:898280-07-4
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 76081-98-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 108137 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H15N3O | M.Wt | 277.33 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 10 mM in ethanol and to 25 mM in DMSO | ||
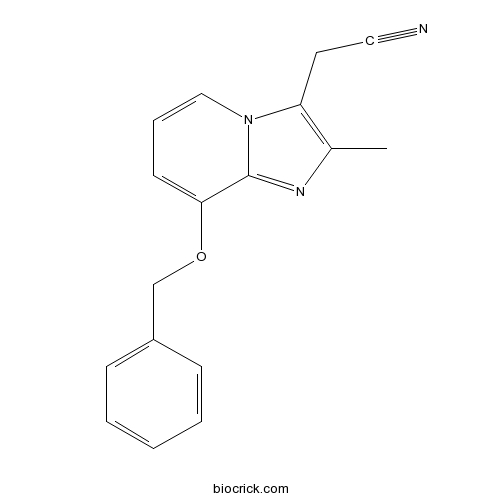
| Chemical Name | 2-(2-methyl-8-phenylmethoxyimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)acetonitrile | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(N2C=CC=C(C2=N1)OCC3=CC=CC=C3)CC#N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PYKJFEPAUKAXNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H15N3O/c1-13-15(9-10-18)20-11-5-8-16(17(20)19-13)21-12-14-6-3-2-4-7-14/h2-8,11H,9,12H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent inhibitor of H+,K+-ATPase (IC50 = 20 nM); binds to the K+ recognition site and is competitive with respect to K+. Inhibits gastric acid secretion in vitro and in vivo. |

SCH 28080 Dilution Calculator

SCH 28080 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6058 mL | 18.0291 mL | 36.0581 mL | 72.1163 mL | 90.1453 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7212 mL | 3.6058 mL | 7.2116 mL | 14.4233 mL | 18.0291 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3606 mL | 1.8029 mL | 3.6058 mL | 7.2116 mL | 9.0145 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0721 mL | 0.3606 mL | 0.7212 mL | 1.4423 mL | 1.8029 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0361 mL | 0.1803 mL | 0.3606 mL | 0.7212 mL | 0.9015 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Artocarpin
Catalog No.:BCN4309
CAS No.:7608-44-8
- Myricoside
Catalog No.:BCC8342
CAS No.:76076-04-5
- 1-Dehydro-6-gingerdione
Catalog No.:BCN3265
CAS No.:76060-35-0
- Broussonin C
Catalog No.:BCN4588
CAS No.:76045-49-3
- 3-Epikatonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4308
CAS No.:76035-62-6
- Lanatin
Catalog No.:BCC8194
CAS No.:76026-24-9
- H-DL-Nva-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3303
CAS No.:760-78-1
- Conopharyngine
Catalog No.:BCN3975
CAS No.:76-98-2
- Mepenzolate Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC3809
CAS No.:76-90-4
- Trityl Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC2805
CAS No.:76-83-5
- Tephrosin
Catalog No.:BCN4742
CAS No.:76-80-2
- Quassin
Catalog No.:BCN4315
CAS No.:76-78-8
- Enalapril maleate
Catalog No.:BCC8955
CAS No.:76095-16-4
- Hederacoside D
Catalog No.:BCN2330
CAS No.:760961-03-3
- Solithromycin
Catalog No.:BCC6446
CAS No.:760981-83-7
- Phaseollidin hydrate
Catalog No.:BCN3962
CAS No.:76122-57-1
- 7-Hydroxy-DPAT hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC6756
CAS No.:76135-30-3
- 8-Hydroxy-DPAT hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC6681
CAS No.:76135-31-4
- Glucosylvitexin
Catalog No.:BCN5929
CAS No.:76135-82-5
- Ipragliflozin
Catalog No.:BCC5137
CAS No.:761423-87-4
- ALK inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC1339
CAS No.:761436-81-1
- TAE226 (NVP-TAE226)
Catalog No.:BCC3885
CAS No.:761437-28-9
- ALK inhibitor 2
Catalog No.:BCC1340
CAS No.:761438-38-4
- TAE684 (NVP-TAE684)
Catalog No.:BCC3660
CAS No.:761439-42-3
Sch-28080 depletes intracellular ATP selectively in mIMCD-3 cells.[Pubmed:11029278]
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2000 Nov;279(5):C1319-26.
Two H(+)-K(+)-ATPase isoforms are present in kidney: the gastric, highly sensitive to Sch-28080, and the colonic, partially sensitive to ouabain. Upregulation of Sch-28080-sensitive H(+)-K(+)-ATPase, or "gastric" H(+)-K(+)-ATPase, has been demonstrated in hypokalemic rat inner medullary collecting duct cells (IMCDs). Nevertheless, only colonic H(+)-K(+)-ATPase mRNA and protein abundance increase in this condition. This study was designed to determine whether Sch-28080 inhibits transporters other than the gastric H(+)-K(+)-ATPase. In the presence of bumetanide, Sch-28080 (200 microM) and ouabain (2 mM) inhibited (86)Rb(+) uptake (>90%). That (86)Rb(+) uptake was almost completely abolished by Sch-28080 indicates an effect of this agent on the Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase. ATPase assays in membranes, or lysed cells, demonstrated sensitivity to ouabain but not Sch-28080. Thus the inhibitory effect of Sch-28080 was dependent on cell integrity. (86)Rb(+)-uptake studies without bumetanide demonstrated that ouabain inhibited activity by only 50%. Addition of Sch-28080 (200 microM) blocked all residual activity. Intracellular ATP declined after Sch-28080 (200 microM) but recovered after removal of this agent. In conclusion, high concentrations of Sch-28080 inhibit K(+)-ATPase activity in mouse IMCD-3 (mIMCD-3) cells as a result of ATP depletion.
Cellular origin and hormonal regulation of K(+)-ATPase activities sensitive to Sch-28080 in rat collecting duct.[Pubmed:11097623]
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000 Dec;279(6):F1053-9.
Rat collecting ducts exhibit type I or type III K(+)-ATPase activities when animals are fed a normal (NK) or a K(+)-depleted diet (LK). This study aimed at determining functionally the cell origin of these two K(+)-ATPases. For this purpose, we searched for an effect on K(+)-ATPases of hormones that trigger cAMP production in a cell-specific fashion. The effects of 1-deamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin (dD-AVP), calcitonin, and isoproterenol in principal cells, alpha-intercalated cells, and beta-intercalated cells of cortical collecting duct (CCD), respectively, and of dD-AVP and glucagon in principal and alpha-intercalated cells of outer medullary collecting duct (OMCD), respectively, were examined. In CCDs, K(+)-ATPase was stimulated by calcitonin and isoproterenol in NK rats (type I K(+)-ATPase) and by dD-AVP in LK rats (type III K(+)-ATPase). In OMCDs, dD-AVP and glucagon stimulated type III but not type I K(+)-ATPase. These hormone effects were mimicked by the cAMP-permeant analog dibutyryl-cAMP. In conclusion, in NK rats, cAMP stimulates type I K(+)-ATPase activity in alpha- and beta-intercalated CCD cells, whereas in LK rats it stimulates type III K(+)-ATPase in principal cells of both CCD and OMCD and in OMCD intercalated cells.
A hybrid between Na+,K+-ATPase and H+,K+-ATPase is sensitive to palytoxin, ouabain, and SCH 28080.[Pubmed:11054424]
J Biol Chem. 2001 Jan 26;276(4):2608-15.
Na(+),K(+)-ATPase is inhibited by cardiac glycosides such as ouabain, and palytoxin, which do not inhibit gastric H(+),K(+)-ATPase. Gastric H(+),K(+)-ATPase is inhibited by SCH28080, which has no effect on Na(+),K(+)-ATPase. The goal of the current study was to identify amino acid sequences of the gastric proton-potassium pump that are involved in recognition of the pump-specific inhibitor SCH 28080. A chimeric polypeptide consisting of the rat sodium pump alpha3 subunit with the peptide Gln(905)-Val(930) of the gastric proton pump alpha subunit substituted in place of the original Asn(886)-Ala(911) sequence was expressed together with the gastric beta subunit in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast cells that express this subunit combination are sensitive to palytoxin, which interacts specifically with the sodium pump, and lose intracellular K(+) ions. The palytoxin-induced K(+) efflux is inhibited by the sodium pump-specific inhibitor ouabain and also by the gastric proton pump-specific inhibitor SCH 28080. The IC(50) for SCH 28080 inhibition of palytoxin-induced K(+) efflux is 14.3 +/- 2.4 microm, which is similar to the K(i) for SCH 28080 inhibition of ATP hydrolysis by the gastric H(+),K(+)-ATPase. In contrast, palytoxin-induced K(+) efflux from cells expressing either the native alpha3 and beta1 subunits of the sodium pump or the alpha3 subunit of the sodium pump together with the beta subunit of the gastric proton pump is inhibited by ouabain but not by SCH 28080. The acquisition of SCH 28080 sensitivity by the chimera indicates that the Gln(905)-Val(930) peptide of the gastric proton pump is likely to be involved in the interactions of the gastric proton-potassium pump with SCH 28080.
Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle tone by the H+, K+-ATPase inhibitor SCH 28080.[Pubmed:10933137]
J Pharm Pharmacol. 2000 Jul;52(7):857-62.
Vascular smooth muscle is thought to possess an H+-K+ ATPase that contributes to the regulation of intracellular K+ concentration and pH. We have examined the effect of the H+, K+-ATPase inhibitor SCH 28080 on vascular smooth muscle tone in guinea-pig and human isolated arteries, and on 86Rb+ uptake in cultured guinea-pig aortic smooth muscle cells. SCH 28080 (0.1-300 microM) produced relaxation of isolated guinea-pig aorta, guinea-pig pulmonary artery and human pulmonary artery. Relaxation occurred in tissues pre-contracted with phenylephrine, histamine or the thromboxane mimetic U44069. Relaxation. was reversible, and was not affected by tetrodotoxin, indomethacin, nordihydroguiaretic acid (NDGA), 1-aminobenzotriazole (1-ABT), N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), removal of the endothelium or removal of extracellular K+. SCH 28080 had no effect on 86Rb+ uptake in cultured guinea-pig aortic smooth muscle cells. In conclusion, SCH 28080 relaxes vascular smooth muscle at concentrations known to inhibit the H+-K+ ATPase. The persistence of relaxation in a K+-free medium and the failure of SCH 28080 to inhibit 86Rb+ uptake suggest that relaxation may be unrelated to H+, K+-ATPase inhibition, and indicate that this agent may not be considered as a selective H+, K+-ATPase inhibitor in vascular preparations.
SCH28080, a K+-competitive inhibitor of the gastric H,K-ATPase, binds near the M5-6 luminal loop, preventing K+ access to the ion binding domain.[Pubmed:12379118]
Biochemistry. 2002 Oct 22;41(42):12755-62.
Inhibition of the gastric H,K-ATPase by the imidazo[1,2-alpha]pyridine, SCH28080, is strictly competitive with respect to K+ or its surrogate, NH4+. The inhibitory kinetics [V(max), K(m,app)(NH4+), K(i)(SCH28080), and competitive, mixed, or noncompetitive] of mutants can define the inhibitor binding domain and the route to the ion binding region within M4-6. While mutations Y799F, Y802F, I803L, S806N, V807I (M5), L811V (M5-6), Y928H (M8), and Q905N (M7-8) had no effect on inhibitor kinetics, mutations P798C, Y802L, P810A, P810G, C813A or -S, I814V or -F, F818C, T823V (M5, M5-6, and M6), E914Q, F917Y, G918E, T929L, and F932L (M7-8 and M8) reduced the affinity for SCH28080 up to 10-fold without affecting the nature of the kinetics. In contrast, the L809F substitution in the loop between M5 and M6 resulted in an approximately 100-fold decrease in inhibitor affinity, and substitutions L809V, I816L, Y925F, and M937V (M5-6, M6, and M8) reduced the inhibitor affinity by 10-fold, all resulting in noncompetitive kinetics. The mutants L811F, Y922I, and I940A also reduced the inhibitor affinity up to 10-fold but resulted in mixed inhibition. The mutations I819L, Q923V, and Y925A also gave mixed inhibition but without a change in inhibitor affinity. These data, and the 9-fold loss of SCH28080 affinity in the C813T mutant, suggest that the binding domain for SCH28080 contains the surface between L809 in the M5-6 loop and C813 at the luminal end of M6, approximately two helical turns down from the ion binding region, where it blocks the normal ion access pathway. On the basis of a model of the Ca-ATPase in the E2 conformation (PDB entry 1kju), the mutants that change the nature of the kinetics are arranged on one side of M8 and on the adjacent side of the M5-6 loop and M6 itself. This suggests that mutations in this region modify the enzyme structure so that K+ can access the ion binding domain even with SCH28080 bound.
Studies on the mechanism of action of the gastric microsomal (H+ + K+)-ATPase inhibitors SCH 32651 and SCH 28080.[Pubmed:3026407]
Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 1;36(1):97-104.
The novel antisecretory agents SCH 32651 and SCH 28080 were evaluated for their antisecretory activities in vitro as well as for their abilities to inhibit the (H+ + K+)-ATPase enzyme activity in preparations of microsomal membranes from rabbit fundic mucosa. SCH 32651 and SCH 28080 inhibited both the histamine- and dibutyryl cAMP-stimulated uptake of [14C]-aminopyrine into isolated parietal cells with IC50 values of about 1.5 and 0.02 microM respectively. SCH 32651 and SCH 28080 competitively inhibited the K+-stimulated hydrolysis of ATP catalyzed by the (H+ + K+)-ATPase with Ki values of 16.3 and 0.12 microM respectively. The inhibition of the enzyme by both compounds was not affected by the addition of the sulfhydryl reducing agents dithiothreitol or beta-mercaptoethanol, was readily reversible by dilution or washing, and was dependent upon the concentration of KCl used to stimulate the enzyme. These data suggest that SCH 32651 and SCH 28080 are reversible, competitive inhibitors of the K+-stimulated hydrolysis of ATP.
Gastric antisecretory and cytoprotective activities of SCH 28080.[Pubmed:6864535]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jul;226(1):114-20.
SCH 28080 (2-methyl-8-(phenylmethoxy)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-acetonitrile) is a novel antiulcer agent which has both antisecretory and cytoprotective activities. The antisecretory ED50 values in the pylorus-ligated rat were 3.7 mg/kg p.o. and 2.8 mg/kg i.p., being 7 and 10 times more potent than cimetidine, respectively. In dogs, SCH 28080 was effective in inhibiting acid secretion stimulated by histamine (ED50 of 0.09 mg/kg i.v. and 4.4 mg/kg p.o.), dimaprit, pentagastrin, insulin and feeding. The cytoprotective activity of SCH 28080 was demonstrated by inhibition of ethanol-induced gastric lesions in a dose-dependent manner in rats (ED50:3.0 mg/kg p.o.). SCH 28080 was active in similar dose ranges (1-10 mg/kg) by both p.o. and i.v. routes of administration. This gastric cytoprotective activity was not affected by indomethacin pretreatment. Furthermore, the gastric potential difference was effectively sustained by SCH 28080 (3, 10 and 30 mg/kg p.o.) after intragastric ethanol. SCH 28080 (1-30 mg/kg p.o.) also inhibited gastric ulcers provoked by aspirin, aspirin + acid, indomethacin and stress (cold-restraint) in rats. The data support the concept that it is possible to have combined antisecretory and cytoprotectant actions in a single molecule which is not a prostaglandin.


