Ethyl 4-methoxycinnamateCAS# 24393-56-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

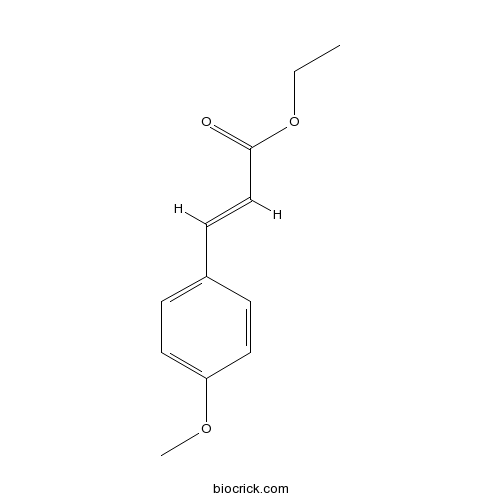
Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 24393-56-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281783 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C12H14O3 | M.Wt | 206.24 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol; insoluble in water | ||
| Chemical Name | ethyl (E)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate | ||
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)C=CC1=CC=C(C=C1)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DHNGCHLFKUPGPX-RMKNXTFCSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H14O3/c1-3-15-12(13)9-6-10-4-7-11(14-2)8-5-10/h4-9H,3H2,1-2H3/b9-6+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate(Ethyl 4-methoxycinnamate) has antifungal activity, it can inhibit the growth of Trichophyton rubrum, Aspergillus niger, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Epidermophyton floccosum at a concentration less than 10 mug/ml. Ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate has anti-inflammatory, it can dose-dependently inhibit carrageenan-induced edema with an MIC of 100 mg/kg, and non-selectively inhibit the activities of cyclooxygenases 1 and 2, with IC50 values of 1.12 uM and 0.83 uM respectively; it has chemopreventive activity against fibrosarcoma through inhibition of COX-2, and can block bFGF-induced vessel formation on Matrigel plug assay in vivo. Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate could be developed as a skin whitening agent to treat hyperpigmentary disorders. |
| Targets | COX-1 | COX-2 | Antifection |
| In vitro | Cytotoxicity Activity of Biotransformed Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate by Aspergillus niger.[Reference: WebLink]Oriental Journal of Chemistry, 2016, 32(5): 2731-4.
Hypopigmentary effects of ethyl P-methoxycinnamate isolated from Kaempferia galanga.[Pubmed: 23610003 ]Phytother Res. 2014 Feb;28(2):274-9. We isolated crystals from the chloroform fraction of an ethanol extract of Kaempferia galanga and identified it as ethyl p-methoxycinnamate(Ethyl 4-methoxycinnamate)through nuclear magnetic resonance analysis.
Isolation of Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate, the major antifungal principle of Curcumba zedoaria.[Pubmed: 785141]Lloydia. 1976 Jul-Aug;39(4):218-22.An antifungal principle of the dried rhizomes of Curcuma zedoaria was extracted with hot ethanol. |
| In vivo | Structure modification of ethyl p-methoxycinnamate and their bioassay as chemopreventive agent against mice's fibrosarcoma[Reference: WebLink]Int. J. Pharm. Pharm.Sci., 2012, 4:528-32.
|
| Animal Research | Antiangiogenic effects and mechanisms of trans-ethyl p-methoxycinnamate from Kaempferia galanga L.[Pubmed: 23106130]Bioactivity-guided isolation of ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate, an anti-inflammatory constituent, from Kaempferia galanga L. extracts.[Pubmed: 22825623]Molecules. 2012 Jul 23;17(7):8720-34.This study evaluated the anti-inflammatory effect of Kaempferia galanga (KG) using an activity-guided approach. KG rhizomes were serially extracted with petroleum ether, chloroform, methanol and water.
J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Nov 14;60(45):11309-17.Kaempferia galanga L. (Zingiberaceae) is an aromatic herb and a popular spice used as a condiment in Asian cuisine.
|

Ethyl 4-methoxycinnamate Dilution Calculator

Ethyl 4-methoxycinnamate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.8487 mL | 24.2436 mL | 48.4872 mL | 96.9744 mL | 121.218 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9697 mL | 4.8487 mL | 9.6974 mL | 19.3949 mL | 24.2436 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4849 mL | 2.4244 mL | 4.8487 mL | 9.6974 mL | 12.1218 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.097 mL | 0.4849 mL | 0.9697 mL | 1.9395 mL | 2.4244 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0485 mL | 0.2424 mL | 0.4849 mL | 0.9697 mL | 1.2122 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Kynurenic acid sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7754
CAS No.:2439-02-3
- 5-Iodotubercidin
Catalog No.:BCC1312
CAS No.:24386-93-4
- Glycoside L-F2
Catalog No.:BCN2158
CAS No.:243857-99-0
- pep4c
Catalog No.:BCC5783
CAS No.:243843-43-8
- pep2m
Catalog No.:BCC5782
CAS No.:243843-42-7
- L-(-)-Fucose
Catalog No.:BCN8326
CAS No.:2438-80-4
- Bufexamac
Catalog No.:BCC4427
CAS No.:2438-72-4
- (-)-alpha-Pinene
Catalog No.:BCC8295
CAS No.:2437-95-8
- 3,5-Cycloergosta-6,8(14),22-triene
Catalog No.:BCN5100
CAS No.:24352-51-0
- S-(5'-Adenosyl)-L-methionine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN2229
CAS No.:24346-00-7
- Apamin
Catalog No.:BCC7141
CAS No.:24345-16-2
- 6-Amino-1-methyluracil
Catalog No.:BCC8757
CAS No.:2434-53-9
- Cnicin
Catalog No.:BCN8546
CAS No.:24394-09-0
- TCS 401
Catalog No.:BCC2469
CAS No.:243967-42-2
- TAK-242 S enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC1978
CAS No.:243984-10-3
- TAK-242
Catalog No.:BCC1977
CAS No.:243984-11-4
- beta-D-glucose
Catalog No.:BCN8171
CAS No.:492-61-5
- (+)-Epipinoresinol
Catalog No.:BCN3255
CAS No.:24404-50-0
- Beta-Rotunol
Catalog No.:BCN6628
CAS No.:24405-57-0
- L-798,106
Catalog No.:BCC7654
CAS No.:244101-02-8
- Taxumairol R
Catalog No.:BCN6939
CAS No.:244167-04-2
- L-748,337
Catalog No.:BCC7475
CAS No.:244192-94-7
- Pulchinenoside E2
Catalog No.:BCN8186
CAS No.:244202-36-6
- Celaphanol A
Catalog No.:BCN5101
CAS No.:244204-40-8
Antiangiogenic effects and mechanisms of trans-ethyl p-methoxycinnamate from Kaempferia galanga L.[Pubmed:23106130]
J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Nov 14;60(45):11309-17.
Kaempferia galanga L. (Zingiberaceae) is an aromatic herb and a popular spice used as a condiment in Asian cuisine. The ethanol extract of the dried plant and its successive four subfractions were investigated on zebrafish model by quantitative endogenous alkaline phosphatase assay. Both n-hexane and ethyl acetate fractions had antiangiogenic activity, and two major active components (trans-ethyl p-methoxycinnamate and kaempferol) showed potent antiangiogenic effects on wild-type zebrafish. Because of its much stronger effect and no antiangiogenic activity reported, trans-ethyl p-methoxycinnamate was further investigated for its action mechanism. It dose dependently inhibited vessel formation on both wild- and Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1-type zebrafish embryos. The semiquantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assay suggested that trans-ethyl p-methoxycinnamate affects multiple molecular targets related to angiogenesis. In vitro, it specifically inhibited the migration and tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. In vivo, it could block bFGF-induced vessel formation on Matrigel plug assay.
Hypopigmentary effects of ethyl P-methoxycinnamate isolated from Kaempferia galanga.[Pubmed:23610003]
Phytother Res. 2014 Feb;28(2):274-9.
We isolated crystals from the chloroform fraction of an ethanol extract of Kaempferia galanga and identified it as ethyl p-methoxycinnamate through nuclear magnetic resonance analysis. In the present study, we found that ethyl p-methoxycinnamate significantly decreased melanin synthesis in B16F10 murine melanoma cells stimulated with alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH). In a cell-free system, however, ethyl p-methoxycinnamate did not directly inhibit tyrosinase, the rate-limiting enzyme of melanogenesis. Instead, it inhibited tyrosinase activity in B16F10 cells in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, Western blot analysis showed that ethyl p-methoxycinnamate decreased microphthalmia-associated transcription factor and tyrosinase levels in alpha-MSH-stimulated B16F10 cells. These results indicate that the pigment-inhibitory effect of ethyl p-methoxycinnamate results from downregulation of tyrosinase. Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate isolated from K. galanga could be developed as a skin whitening agent to treat hyperpigmentary disorders.
Isolation of Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate, the major antifungal principle of Curcumba zedoaria.[Pubmed:785141]
Lloydia. 1976 Jul-Aug;39(4):218-22.
An antifungal principle of the dried rhizomes of Curcuma zedoaria was extracted with hot ethanol. By successive chromatography on neutral alumina and silica gel, three antibiotic compounds A, B, and C, all active against Trichophyton rubrum, Aspergillus niger and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, were obtained in chemically pure form. By uv, ir, pmr and ms analysis, the structure of the most abundant one of these compounds (C, 69.8%; H, 6,8%; and 0.23.4%) was assigned as ethyl p-methoxycinnamate (EPMC). The proposed structure was confirmed by synthesis and comparison of the chemical and biological properties of the natural and synthetic products. EPMC inhibits the growth of Trichophyton rubrum, Aspergillus niger, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Epidermophyton floccosum at a concentration less than 10 mug/ml; A. fumigatus, Penicillium purpurogenum, Trignoposis variabilis, Microsporum gypseum, Sclerotium rolifsii, Geotricular candiade, Fusarium oxysporum and Helminthosporium oryzale at a concentration less than 25 mug/ml; and Candida krusei and T. mentagrophytes At a concentration less than 50 mug/ml. The spores of T. rubrum Lose viability or ability to germinate when wxposed to its ethanolic solution (30 mug/ml) for 2 hours.
Bioactivity-guided isolation of ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate, an anti-inflammatory constituent, from Kaempferia galanga L. extracts.[Pubmed:22825623]
Molecules. 2012 Jul 23;17(7):8720-34.
This study evaluated the anti-inflammatory effect of Kaempferia galanga (KG) using an activity-guided approach. KG rhizomes were serially extracted with petroleum ether, chloroform, methanol and water. These extracts (2 g/kg each) were tested for their ability to inhibit carrageenan-induced rat paw edema. The chloroform extract was found to exert the highest inhibition (42.9%) compared to control (p < 0.001), hence it was further fractionated by washing serially with hexane, hexane-chloroform (1:1) and chloroform. The chloroform fraction (1 g/kg) showed the highest inhibitory effect (51.9%, (p < 0.001), on carrageenan-induced edema. This chloroform fraction was further fractionated with hexane-chloroform (1:3) and chloroform, and of the two fractions, the hexane-chloroform sub-fraction was the most effective in inhibiting edema (53.7%, p < 0.001). GC-MS analysis of the active sub-fraction identified ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate (EPMC) as the major component, which was re-crystallized. EPMC dose-dependently inhibited carrageenan-induced edema with an MIC of 100 mg/kg. Moreover, in an in vitro study, EPMC non-selectively inhibited the activities of cyclooxygenases 1 and 2, with IC(5)(0) values of 1.12 microM and 0.83 microM respectively. These results validate the anti-inflammatory activity of KG which may be exerted by the inhibition of cyclooxygenases 1 and 2. EPMC isolated from this plant may be the active anti-inflammatory agent.


