Coronarin DCAS# 119188-37-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

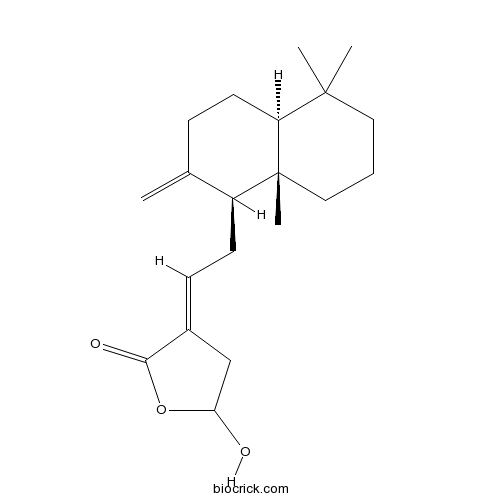
Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 119188-37-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 71595339 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H30O3 | M.Wt | 318.5 |
| Type of Compound | Diterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (3E)-3-[2-[(1S,4aS,8aS)-5,5,8a-trimethyl-2-methylidene-3,4,4a,6,7,8-hexahydro-1H-naphthalen-1-yl]ethylidene]-5-hydroxyoxolan-2-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CCCC2(C1CCC(=C)C2CC=C3CC(OC3=O)O)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DYYYQLXAGIXUGM-JQFPLDQISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H30O3/c1-13-6-9-16-19(2,3)10-5-11-20(16,4)15(13)8-7-14-12-17(21)23-18(14)22/h7,15-17,21H,1,5-6,8-12H2,2-4H3/b14-7+/t15-,16-,17?,20+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Coronarin D inhibits NF-kappaB activation pathway, which leads to inhibition of inflammation, invasion, and osteoclastogenesis, as well as potentiation of apoptosis. 2. Coronarin D is active against tested Gram-positive bacteria, inactive for tested Gram-negative bacteria, and weakly active against tested fungi; using coronarin D-antibiotic drug combination can combat the infectious diseases . 3. Coronarin D shows promising antifungal activity against C. albicans in vitro, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and the minimum fungicidal concentration (MFC) were 2 and 4 mg/mL, respectively. |
| Targets | NF-kB | Antifection | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | COX | c-Myc | TNF-α |

Coronarin D Dilution Calculator

Coronarin D Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1397 mL | 15.6986 mL | 31.3972 mL | 62.7943 mL | 78.4929 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6279 mL | 3.1397 mL | 6.2794 mL | 12.5589 mL | 15.6986 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.314 mL | 1.5699 mL | 3.1397 mL | 6.2794 mL | 7.8493 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0628 mL | 0.314 mL | 0.6279 mL | 1.2559 mL | 1.5699 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0314 mL | 0.157 mL | 0.314 mL | 0.6279 mL | 0.7849 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Coronarin A
Catalog No.:BCN6075
CAS No.:119188-33-9
- Glychionide A
Catalog No.:BCN3250
CAS No.:119152-50-0
- 3-Oxosapriparaquinone
Catalog No.:BCN3153
CAS No.:119139-56-9
- B-Raf inhibitor 1 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4183
CAS No.:1191385-19-9
- Ganomycin I
Catalog No.:BCN3504
CAS No.:1191255-15-8
- IOWH-032
Catalog No.:BCC3922
CAS No.:1191252-49-9
- 1-Acetoxy-5-deacetylbaccatin I
Catalog No.:BCN6357
CAS No.:119120-27-3
- Linolenic acid ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN8333
CAS No.:1191-41-9
- Phellolactone
Catalog No.:BCN3467
CAS No.:1190897-23-4
- Fluorobexarotene
Catalog No.:BCC6110
CAS No.:1190848-23-7
- Fmoc-Asp-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3085
CAS No.:119062-05-4
- Euchrenone B1
Catalog No.:BCN3575
CAS No.:119061-09-5
- Coronarin B
Catalog No.:BCN6077
CAS No.:119188-38-4
- 10-Hydroxyscandine
Catalog No.:BCN6078
CAS No.:119188-47-5
- CZC-25146
Catalog No.:BCC5371
CAS No.:1191911-26-8
- CZC 54252 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6218
CAS No.:1191911-27-9
- 4-(1H-1,2,4-Triazol-1-ylmethyl)aniline
Catalog No.:BCC8645
CAS No.:119192-10-8
- PHT-427
Catalog No.:BCC2554
CAS No.:1191951-57-1
- LX7101 HCL
Catalog No.:BCC6414
CAS No.:1192189-69-7
- Gomisin S
Catalog No.:BCN3622
CAS No.:119239-49-5
- Avibactam
Catalog No.:BCC1384
CAS No.:1192500-31-4
- Scutellarin methylester
Catalog No.:BCN2828
CAS No.:119262-68-9
- PE 154
Catalog No.:BCC7858
CAS No.:1192750-33-6
- Rocuronium Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC1068
CAS No.:119302-91-9
Antifungal activity of coronarin D against Candida albicans.[Pubmed:22727093]
Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2012 Jul;114(1):61-6.
OBJECTIVE: The objective of this study was to investigate the antifungal activity of Coronarin D on Candida albicans and its activity was compared with clotrimazole and nystatin. METHODS: Coronarin D was extracted by liquid chromatography and used in antifungal testing. The inhibitory effect of Coronarin D on C. albicans was determined by cultures and an applied broth dilution test. The rate of fungicidal activity was evaluated by time-kill curves. Morphologic alterations of fungal cells were investigated using scanning electron microscopy. RESULTS: Coronarin D was effective against C. albicans; the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and the minimum fungicidal concentration (MFC) were 2 and 4 mg/mL, respectively. The C. albicans killing activity of Coronarin D was higher than clotrimazole and nystatin at 2 x MFC and 4 x MFC, respectively. Morphologic alterations of fungal cells consistent with cell membrane damage were observed in the Coronarin D-treated cells. CONCLUSIONS: Coronarin D showed promising antifungal activity against C. albicans in vitro.
Coronarin D, a labdane diterpene, inhibits both constitutive and inducible nuclear factor-kappa B pathway activation, leading to potentiation of apoptosis, inhibition of invasion, and suppression of osteoclastogenesis.[Pubmed:18852134]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Oct;7(10):3306-17.
Compounds isolated from members of the Zingiberaceae family are traditionally used as a medicine against inflammatory diseases, but little is known about the mechanism. Here, we report the isolation and structural identification of Coronarin D [E-labda-8(17),12-diene-15-ol], a labdane-type diterpene, from Hedychium coronarium and delineate its mechanism of action. Because the transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) is a key mediator of inflammation, apoptosis, invasion, and osteoclastogenesis, we investigated the effect of Coronarin D on NF-kappaB activation pathway, NF-kappaB-regulated gene products, and NF-kappaB-regulated cellular responses. The Coronarin D inhibited NF-kappaB activation induced by different inflammatory stimuli and carcinogens. This labdane also suppressed constitutive NF-kappaB activity in different cell lines and inhibited IkappaBalpha kinase activation, thus leading to the suppression of IkappaBalpha phosphorylation, degradation, p65 nuclear translocation, and reporter gene transcription. Coronarin D also inhibited the NF-kappaB-regulated gene products involved in cell survival (inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1, Bcl-2, survivin, and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor-2), proliferation (c-myc, cyclin D1, and cyclooxygenase-2), invasion (matrix metalloproteinase-9), and angiogenesis (vascular endothelial growth factor). Suppression of these gene products by the diterpene enhanced apoptosis induced by TNF and chemotherapeutic agents, suppressed TNF-induced cellular invasion, and abrogated receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand-induced osteoclastogenesis. Coronarin D was found to be more potent than its analogue Coronarin D acid. Overall, our results show that Coronarin D inhibited NF-kappaB activation pathway, which leads to inhibition of inflammation, invasion, and osteoclastogenesis, as well as potentiation of apoptosis.
Antimicrobial activity of coronarin D and its synergistic potential with antibiotics.[Pubmed:24949458]
Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:581985.
Coronarin D is a labdane-type diterpene from the rhizomes of Hedychium coronarium. In the view of our ongoing effort to explore its novel biological activity, antimicrobial activity study of Coronarin D was performed. The results showed that Coronarin D was active against tested Gram-positive bacteria, inactive for tested Gram-negative bacteria, and weakly active against tested fungi. The antibacterial effect of the combination of Coronarin D with nine classical antibiotics against four Gram-positive bacteria was also evaluated. The fractional inhibitory concentration indices (FICI) of Coronarin D-antibiotics combinations, calculated from the checkerboard assay, were used as synergism indicator. Out of 36 combinations, 47% showed total synergism, 33% had partial synergistic interaction, 17% showed no effect, and 3% showed antagonism. By combination with Coronarin D at concentration of 0.25 minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC), the activities of antibiotics were boosted to 4- to 128-fold. These finding suggested an attractive approach to combat the infectious diseases by using Coronarin D-antibiotic drug combination.
Chemical constituents of the rhizomes of Hedychium coronarium and their inhibitory effect on the pro-inflammatory cytokines production LPS-stimulated in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells.[Pubmed:22071304]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Dec 15;21(24):7460-5.
The rhizomes of Hedychium coronarium have been used for the treatment of inflammation, skin diseases, headache, and sharp pain due to rheumatism in traditional medicine. From this plant, three new labdane-type diterpenes 1-3, named coronarins G-I as well as seven known 4-10, Coronarin D, Coronarin D methyl ether, hedyforrestin C, (E)-nerolidol, beta-sitosterol, daucosterol, and stigmasterol were isolated. Their chemical structures were elucidated by mass, 1D- and 2D-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. They were evaluated for inhibitory effects on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Among of them, compounds 1, 2, and 6 were significant inhibitors of LPS-stimulated TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-12 p40 productions with IC(50) ranging from 0.19+/-0.11 to 10.38+/-2.34 muM. The remains of compounds showed inactivity or due to cytotoxicity. These results warrant further studies concerning the potential anti-inflammatory benefits of labdane-type diterpenes from H. coronarium.


