BINASelective positive allosteric modulator of mGlu2 CAS# 866823-73-6 |
- CHIR-99021 (CT99021)
Catalog No.:BCC1275
CAS No.:252917-06-9
- SB 415286
Catalog No.:BCC3651
CAS No.:264218-23-7
- SB 216763
Catalog No.:BCC3650
CAS No.:280744-09-4
- AR-A014418
Catalog No.:BCC1366
CAS No.:487021-52-3
- LY2090314
Catalog No.:BCC1717
CAS No.:603288-22-8
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 866823-73-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9868580 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C30H30O4 | M.Wt | 454.56 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Biphenyl-indanone A | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
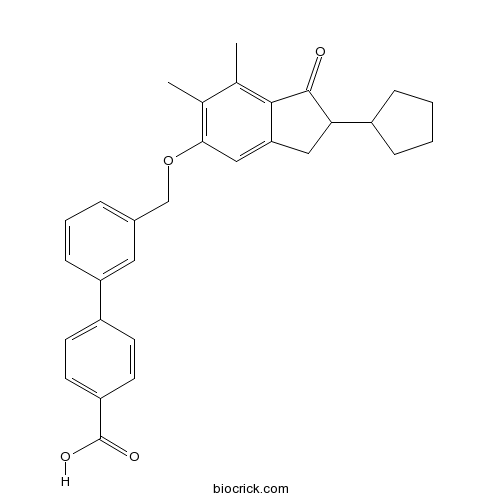
| Chemical Name | 4-[3-[(2-cyclopentyl-6,7-dimethyl-1-oxo-2,3-dihydroinden-5-yl)oxymethyl]phenyl]benzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C=C2CC(C(=O)C2=C1C)C3CCCC3)OCC4=CC=CC(=C4)C5=CC=C(C=C5)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KMKBEESNZAPKMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H30O4/c1-18-19(2)28-25(15-26(29(28)31)22-7-3-4-8-22)16-27(18)34-17-20-6-5-9-24(14-20)21-10-12-23(13-11-21)30(32)33/h5-6,9-14,16,22,26H,3-4,7-8,15,17H2,1-2H3,(H,32,33) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective positive allosteric modulator of mGlu2 (EC50 = 33.2 nM in CHO cells expressing human mGlu2). Displays no effect on glutamate-induced activation of other mGlu receptor subtypes. Exhibits antipsychotic and anxiolytic properties in mice. |

BINA Dilution Calculator

BINA Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1999 mL | 10.9996 mL | 21.9993 mL | 43.9986 mL | 54.9982 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.44 mL | 2.1999 mL | 4.3999 mL | 8.7997 mL | 10.9996 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.22 mL | 1.1 mL | 2.1999 mL | 4.3999 mL | 5.4998 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.044 mL | 0.22 mL | 0.44 mL | 0.88 mL | 1.1 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.022 mL | 0.11 mL | 0.22 mL | 0.44 mL | 0.55 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- (1S)-4,5-Dimethoxy-1-[(methylamino)methyl]benzocyclobutane hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8383
CAS No.:866783-13-3
- Yuexiandajisu E
Catalog No.:BCN3775
CAS No.:866556-16-3
- Yuexiandajisu D
Catalog No.:BCN3774
CAS No.:866556-15-2
- [Ala2,8,9,11,19,22,24,25,27,28]-VIP
Catalog No.:BCC5973
CAS No.:866552-34-3
- 7-Hydroxy-3-prenylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN4415
CAS No.:86654-26-4
- Dorsomorphin
Catalog No.:BCC5131
CAS No.:866405-64-3
- DPPI 1c hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2363
CAS No.:866396-34-1
- 10-Aminocamptothecin
Catalog No.:BCC8111
CAS No.:86639-63-6
- 7-Ethyl-10-Hydroxycamptothecin
Catalog No.:BCN2479
CAS No.:86639-52-3
- Xanthiside
Catalog No.:BCN2545
CAS No.:866366-86-1
- 3,4,5-Tricaffeoylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2384
CAS No.:86632-03-3
- PRX-08066 Maleic acid
Catalog No.:BCC1165
CAS No.:866206-55-5
- ARL 17477 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7647
CAS No.:866914-87-6
- (R)-(+)-2-Amino-3-methyl-1,1-diphenyl-1-butanol
Catalog No.:BCC8394
CAS No.:86695-06-9
- (S)-Methylisothiourea sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC6791
CAS No.:867-44-7
- ROCK inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1905
CAS No.:867017-68-3
- Magnoshinin
Catalog No.:BCC8205
CAS No.:86702-02-5
- Tropanyl 3-hydroxy-4-methoxycinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN1325
CAS No.:86702-58-1
- Colivelin
Catalog No.:BCC7821
CAS No.:867021-83-8
- Linsitinib
Catalog No.:BCC3697
CAS No.:867160-71-2
- TRC 051384
Catalog No.:BCC7968
CAS No.:867164-40-7
- TG 100572 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1995
CAS No.:867331-64-4
- TG 100801
Catalog No.:BCC1996
CAS No.:867331-82-6
- TG 100572
Catalog No.:BCC1994
CAS No.:867334-05-2
The mGluR2 positive allosteric modulator BINA decreases cocaine self-administration and cue-induced cocaine-seeking and counteracts cocaine-induced enhancement of brain reward function in rats.[Pubmed:20555310]
Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010 Sep;35(10):2021-36.
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 2/3 (mGluR2/3) agonists were shown previously to nonselectively decrease both cocaine- and food-maintained responding in rats. mGluR2 positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) may represent improved therapeutic compounds because of their modulatory properties and higher selectivity for mGluR2. We analyzed the effects of the selective, brain penetrant, and systemically active mGluR2 PAM potassium 3'-([(2-cyclopentyl-6-7-dimethyl-1-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl)oxy]methyl)biphe nyl l-4-carboxylate (BINA) and the mGluR2/3 agonist LY379268 on intravenous cocaine self-administration and cocaine-seeking behavior in rats that had short (1 h, ShA) or long (6 h, LgA) access to cocaine. The effects of BINA on food responding and food-seeking behavior were also analyzed. Finally, we examined the effects of BINA on brain reward function and cocaine-induced reward enhancement using the intracranial self-stimulation procedure. BINA decreased cocaine self-administration in both ShA and LgA rats, with no effect on food self-administration. Alternatively, LY379268 nonselectively decreased both cocaine and food self-administration. BINA decreased cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking with no effect on food seeking. The cocaine-induced enhancement of brain reward function was blocked by BINA, although the highest doses of BINA decreased brain reward function when administered alone, suggesting additive, rather than interactive, effects of BINA and cocaine. In conclusion, BINA attenuated the reinforcing and counteracted the reward-enhancing effects of cocaine and decreased cue-induced cocaine-seeking behavior, without affecting behaviors motivated by food reinforcement. The higher selectivity of BINA compared with an mGluR2/3 agonist for drug- vs food-motivated behaviors suggests a therapeutic role for mGluR2 PAMs for the treatment of cocaine addiction and possibly other drugs of abuse.
An oligomeric complex of BinA/BinB is not formed in-situ in mosquito-larvicidal Lysinibacillus sphaericus ISPC-8.[Pubmed:25196469]
J Invertebr Pathol. 2014 Oct;122:44-7.
BINAry toxin of Lysinibacillus sphaericus is composed of two polypeptides; receptor binding BinB and toxic BINA. Both the polypeptides are required for maximal toxicity. It has been suggested that BINAry toxin exerts toxicity as a heterotetramer constituted by two copies of each of the component polypeptides. It has also been observed that oligomers consisting of two copies of BINA and BinB are pre-formed in L. sphaericus spore-crystals. However, recomBINAnt proteins from Escherichia coli expression system elute individually as monomers. We purified the likely oligomeric complex from the spore-crystals of highly toxic L. sphaericus ISPC-8 strain and probed it with proteomic tools. The analysis showed that the high molecular mass complex in the toxic spore-crystals is composed of only surface layer protein (SlpC). The purified SlpC from the local isolate exists as a dimer and also showed poor mosquito-larvicidal activity.
BiNA: a visual analytics tool for biological network data.[Pubmed:24551056]
PLoS One. 2014 Feb 13;9(2):e87397.
Interactive visual analysis of biological high-throughput data in the context of the underlying networks is an essential task in modern biomedicine with applications ranging from metabolic engineering to personalized medicine. The complexity and heterogeneity of data sets require flexible software architectures for data analysis. Concise and easily readable graphical representation of data and interactive navigation of large data sets are essential in this context. We present BINA--the Biological Network Analyzer--a flexible open-source software for analyzing and visualizing biological networks. Highly configurable visualization styles for regulatory and metabolic network data offer sophisticated drawings and intuitive navigation and exploration techniques using hierarchical graph concepts. The generic projection and analysis framework provides powerful functionalities for visual analyses of high-throughput omics data in the context of networks, in particular for the differential analysis and the analysis of time series data. A direct interface to an underlying data warehouse provides fast access to a wide range of semantically integrated biological network databases. A plugin system allows simple customization and integration of new analysis algorithms or visual representations. BINA is available under the 3-clause BSD license at http://BINA.unipax.info/.
The cyclic-di-GMP phosphodiesterase BinA negatively regulates cellulose-containing biofilms in Vibrio fischeri.[Pubmed:20061475]
J Bacteriol. 2010 Mar;192(5):1269-78.
Bacteria produce different types of biofilms under distinct environmental conditions. Vibrio fischeri has the capacity to produce at least two distinct types of biofilms, one that relies on the symbiosis polysaccharide Syp and another that depends upon cellulose. A key regulator of biofilm formation in bacteria is the intracellular signaling molecule cyclic diguanylate (c-di-GMP). In this study, we focused on a predicted c-di-GMP phosphodiesterase encoded by the gene BINA, located directly downstream of syp, a cluster of 18 genes critical for biofilm formation and the initiation of symbiotic colonization of the squid Euprymna scolopes. Disruption or deletion of BINA increased biofilm formation in culture and led to increased binding of Congo red and calcofluor, which are indicators of cellulose production. Using random transposon mutagenesis, we determined that the phenotypes of the DeltaBINA mutant strain could be disrupted by insertions in genes in the bacterial cellulose biosynthesis cluster (bcs), suggesting that cellulose production is negatively regulated by BINA. Replacement of critical amino acids within the conserved EAL residues of the EAL domain disrupted BINA activity, and deletion of BINA increased c-di-GMP levels in the cell. Together, these data support the hypotheses that BINA functions as a phosphodiesterase and that c-di-GMP activates cellulose biosynthesis. Finally, overexpression of the syp regulator sypG induced BINA expression. Thus, this work reveals a mechanism by which V. fischeri inhibits cellulose-dependent biofilm formation and suggests that the production of two different polysaccharides may be coordinated through the action of the cellulose inhibitor BINA.
A selective positive allosteric modulator of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 2 blocks a hallucinogenic drug model of psychosis.[Pubmed:17526600]
Mol Pharmacol. 2007 Aug;72(2):477-84.
Recent clinical studies reveal that selective agonists of group II metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors have robust efficacy in treating positive and negative symptoms in patients with schizophrenia. Group II mGlu receptor agonists also modulate the in vivo activity of psychotomimetic drugs and reduce the ability of psychotomimetic hallucinogens to increase glutamatergic transmission. Because increased excitation of the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) has been implicated in pathophysiology of schizophrenia, the ability of group II mGlu receptor agonists to reduce hallucinogenic drug action in this region is believed to be directly related to their antipsychotic efficacy. A novel class of ligands, termed positive allosteric modulators, has recently been identified, displaying exceptional mGlu2 receptor selectivity. These compounds do not activate mGlu2 receptors directly but potentiate the ability of glutamate and other agonists to activate this receptor. We now report that the mGlu2 receptor-selective positive allosteric modulator biphenyl-indanone A (BINA) modulates excitatory neurotransmission in the mPFC and attenuates the in vivo actions of the hallucinogenic 5-HT(2A/2C) receptor agonist (-)2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromoamphetamine [(-)DOB]. BINA attenuates serotonin-induced increases in spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents in the mPFC, mimicking the effect of the mGlu2/3 receptor agonist (2S,2'R,3'R)-2-(2',3'-dicarboxycyclopropyl)glycine (DCG-IV). In addition, BINA reduced (-)DOB-induced head twitch behavior and Fos expression in mPFC, effects reversed by pretreatment with the mGlu2/3 receptor antagonist 2S-2-amino-2-(1S,2S-2-carboxycyclopropan-1-yl) -3 - (xanth-9-yl-)propionic acid (LY341495). These data confirm the relevance of excitatory signaling in the mPFC to the behavioral actions of hallucinogens and further support the targeting of mGlu2 receptors as a novel strategy for treating glutamatergic dysfunction in schizophrenia.
Biphenyl-indanone A, a positive allosteric modulator of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 2, has antipsychotic- and anxiolytic-like effects in mice.[Pubmed:16608916]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Jul;318(1):173-85.
Previous studies indicate that agonists of the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs), mGluR2 and mGluR3, may provide a novel approach for the treatment of anxiety disorders and schizophrenia. However, the relative contributions of the mGluR2 and mGluR3 subtypes to the effects of the group II mGluR agonists remain unclear. In the present study, we describe an alternate synthesis and further pharmacological characterization of a recently reported positive allosteric modulator of mGluR2 termed biphenyl-indanone A (BINA). In recomBINAnt systems, BINA produced a robust and selective potentiation of the response of mGluR2 to glutamate with no effect on the glutamate response of other mGluR subtypes. In hippocampal brain slices, BINA (1 microM) significantly potentiated the mGluR2/3 agonist-induced inhibition of excitatory synaptic transmission at the medial perforant path-dentate gyrus synapse. BINA was also efficacious in several models predictive of antipsychotic- and anxiolytic-like activity in mice. The behavioral effects of BINA were blocked by the mGluR2/3 antagonist (2S)-2-amino-2-[(1S,2S)-2-carboxycycloprop-1-yl]-3-(xanth-9-yl) propanoic acid (LY341495), suggesting that the in vivo effects of BINA are mediated by increased activation of mGluR2. Collectively, these results indicate that BINA is a selective mGluR2 positive allosteric modulator and provide further support for the growing evidence that selective allosteric potentiators of mGluR2 mimic many of the in vivo actions of mGluR2/3 agonists that may predict therapeutic utility of these compounds.
Biphenyl-indanones: allosteric potentiators of the metabotropic glutamate subtype 2 receptor.[Pubmed:16046122]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Oct 1;15(19):4354-8.
We have identified and synthesized a series of biphenyl-carboxylic acid indanones as allosteric potentiators of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 2. Structure-activity relationship studies directed toward improving the potency and the brain to plasma ratio of the initial lead led to the discovery of 5 and 23 (EC50=111 and 5 nM, respectively).


