SB 415286GSK-3 inhibitor,potent and selective CAS# 264218-23-7 |
- SB 216763
Catalog No.:BCC3650
CAS No.:280744-09-4
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure
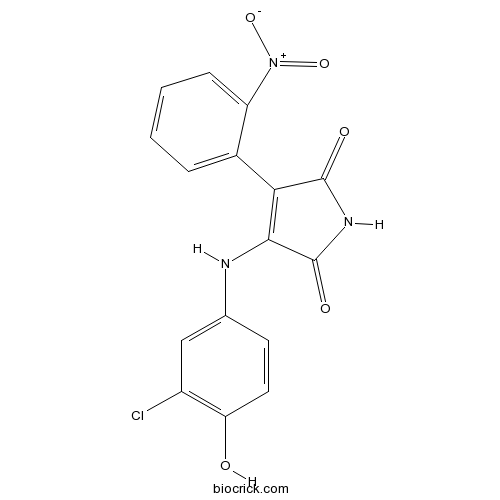
3D structure
| Cas No. | 264218-23-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 4210951 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H10ClN3O5 | M.Wt | 359.73 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 25 mM in ethanol and to 50 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 3-(3-chloro-4-hydroxyanilino)-4-(2-nitrophenyl)pyrrole-2,5-dione | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C(=C1)C2=C(C(=O)NC2=O)NC3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)Cl)[N+](=O)[O-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PQCXVIPXISBFPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H10ClN3O5/c17-10-7-8(5-6-12(10)21)18-14-13(15(22)19-16(14)23)9-3-1-2-4-11(9)20(24)25/h1-7,21H,(H2,18,19,22,23) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent and selective glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) inhibitor (Ki = 31 nM for GSK-3α); competes with ATP. Has minimal activity against 24 other protein kinases (IC50 > 10 μ M). Stimulates glycogen synthesis, gene transcription and is neuroprotective. |

SB 415286 Dilution Calculator

SB 415286 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7799 mL | 13.8993 mL | 27.7986 mL | 55.5973 mL | 69.4966 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.556 mL | 2.7799 mL | 5.5597 mL | 11.1195 mL | 13.8993 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.278 mL | 1.3899 mL | 2.7799 mL | 5.5597 mL | 6.9497 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0556 mL | 0.278 mL | 0.556 mL | 1.1119 mL | 1.3899 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0278 mL | 0.139 mL | 0.278 mL | 0.556 mL | 0.695 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
SB-415286 is a potent and selective cell permeable inhibitor of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) with Ki of 31 nM. It shows similar potency against GSK-3 and GSK3β [1].
SB-415286 inhibited GSK-3 activity and promoted glycogen synthesis in human liver cells and induced expression of reporter gene regulated by catenin-LEF/TCF in HEK293 cells [1]. In primary neurons, it can prevent cell death induced by repressed PI3k pathway activity [2]. Further studies showed that reduced GSK3β activity induced by SB-415286 could inhibit down-regulation of cyclin D1, cell cycle arrest and chemosensitivity, which were all mediated by rapamycin [3]. Pharmacologic inhibition of GSK-3β dramatically impaired p53-dependent transactivation of p21 and Puma but facilitated p53-dependent conformational activation of Bax, resulting in the conversion of p53-mediated damage response from cell cycle arrest to apoptosis [4]. SB-415286 reduced ischemia-reperfusion injury by mechanisms which were associated with mitochondria. SB-415286 reduced adenine nucleotide transport and phosphorylation of VDAC, then increased Bcl-2 binding to mitochondria and blocked opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore in cardiomyocytes [5]. SB-415286 had protective effect of hippocampal neurons on radiation-induced apoptosis as well. GSK-3β inhibition induced by SB-415286 could result in the upregulation of MDM2, which, in turn, regulated p53 degradation and p53-dependent cellular responses [6].
Recent research in a mouse model further confirmed that SB-415286 is a neuroprotectant against radiation-induced central nervous system necrosis. Mice treated with SB415286 prior to irradiation (i.e. a single 45-Gy fraction targeted to the left hemisphere), showed significant protection from radiation-induced necrosis, which was determined by in vivo MRI, in contrast with DMSO-treated mice [7].
References:
Selective small molecule inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 modulate glycogen metabolism and gene transcription. Chem Biol. 2000 Oct;7(10):793-803.
Selective small-molecule inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity protect primary neurones from death. J Neurochem. 2001 Apr;77(1):94-102.
Role of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in rapamycin-mediated cell cycle regulation and chemosensitivity. Cancer Res. 2005 Mar 1;65(5):1961-72.
Pharmacologic modulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta promotes p53-dependent apoptosis through a direct Bax-mediated mitochondrial pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005 Oct 1;65(19):9012-20.
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibition slows mitochondrial adenine nucleotide transport and regulates voltage-dependent anion channel phosphorylation. Circ Res. 2008 Oct 24;103(9):983-91. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.178970. Epub 2008 Sep 18.
Glycogen synthase kinase 3β inhibitors protect hippocampal neurons from radiation-induced apoptosis by regulating MDM2-p53 pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2012 Mar;19(3):387-96. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.94. Epub 2011 Jul 8.
A GSK-3β inhibitor protects against radiation necrosis in mouse brain. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014 Jul 15;89(4):714-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.04.018.
- Z-Orn-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2757
CAS No.:2640-58-6
- DPPA (Kg)
Catalog No.:BCC2690
CAS No.:26386-88-9
- S 25585
Catalog No.:BCC7687
CAS No.:263849-50-9
- AG 045572
Catalog No.:BCC7464
CAS No.:263847-55-8
- 3-Acetoxy-27-hydroxy-20(29)-lupen-28-oic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN1466
CAS No.:263844-80-0
- 3,27-Dihydroxy-20(29)-lupen-28-oic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN1467
CAS No.:263844-79-7
- Buergerinin G
Catalog No.:BCN4659
CAS No.:263764-83-6
- EMDT oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7888
CAS No.:263744-72-5
- PPT
Catalog No.:BCC7062
CAS No.:263717-53-9
- ESI-09
Catalog No.:BCC5504
CAS No.:263707-16-0
- Stachysterone D
Catalog No.:BCC8362
CAS No.:26361-67-1
- H-Lys-OMe .2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2981
CAS No.:26348-70-9
- Methyl 5-{2-[(tert-butylamino)carbothioyl]carbohydrazonoyl}-1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC7906
CAS No.:264233-05-8
- 6',7'-Dihydroxybergamottin
Catalog No.:BCN5142
CAS No.:264234-05-1
- Oxypeucedanin hydrate
Catalog No.:BCN2698
CAS No.:2643-85-8
- Methyl 2,2-dithienylglycolate
Catalog No.:BCC9034
CAS No.:26447-85-8
- Bz-Arg-OEt.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2686
CAS No.:2645-08-1
- PR-619
Catalog No.:BCC3627
CAS No.:2645-32-1
- SSR 146977 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7635
CAS No.:264618-38-4
- MRS 1706
Catalog No.:BCC7120
CAS No.:264622-53-9
- MRS 1754
Catalog No.:BCC7473
CAS No.:264622-58-4
- 26-Deoxyactein
Catalog No.:BCN8076
CAS No.:264624-38-6
- Humulone
Catalog No.:BCN2682
CAS No.:26472-41-3
- Catharanthine Tartrate
Catalog No.:BCN2462
CAS No.:2648-21-5
Use of lithium and SB-415286 to explore the role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in the regulation of glucose transport and glycogen synthase.[Pubmed:12950267]
Eur J Biochem. 2003 Sep;270(18):3829-38.
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) is inactivated by insulin and lithium and, like insulin, Li also activates glycogen synthase (GS) via inhibition of GSK3. Li also mimics insulin's ability to stimulate glucose transport (GT), an observation that has led to the suggestion that GSK3 may coordinate hormonal increases in GT and glycogen synthesis. Here we have used Li and SB-415286, a selective GSK3 inhibitor, to establish the importance of GSK3 in the hormonal activation of GT in terms of its effect on GS in L6 myotubes and 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Insulin, Li and SB-415286 all induced a significant inhibition of GSK3, which was associated with a marked dephosphorylation and activation of GS. In L6 myotubes, SB-415286 induced a much greater activation of GS (6.8-fold) compared to that elicited by insulin (4.2-fold) or Li (4-fold). In adipocytes, insulin, Li and SB-415286 all caused a comparable activation of GS despite a substantial differentiation-linked reduction in GSK3 expression ( approximately 85%) indicating that GSK3 remains an important determinant of GS activation in fat cells. Whilst Li and SB-415286 both inhibit GSK3 in muscle and fat cells, only Li stimulated GT. This increase in GT was not sensitive to inhibitors of PI3-kinase, MAP kinase or mTOR, but was suppressed by the p38 MAP kinase inhibitor, SB-203580. Consistent with this, phosphorylation of p38 MAP kinase induced by Li correlated with its stimulatory effect on GT. Our findings support a crucial role for GSK3 in the regulation of GS, but based on the differential effects of Li and SB-415286, it is unlikely that acute inhibition of GSK3 contributes towards the rapid stimulation of GT by insulin in muscle and fat cells.
A molecular study of pathways involved in the inhibition of cell proliferation in neuroblastoma B65 cells by the GSK-3 inhibitors lithium and SB-415286.[Pubmed:18624766]
J Cell Mol Med. 2009 Sep;13(9B):3906-17.
Pharmacological GSK-3 inhibitors are potential drugs for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, cancer and diabetes. We examined the antiproliferative effects of two GSK-3 inhibitors, lithium and SB-415286, on B65 neuroblastoma cell line. Treatment of B65 cells with either drug administered separately caused a decrease in cell proliferation that was associated with G(2)/M cell cycle arrest. Cell-cycle proteins such as cyclins D, E, A, cdk4 and cdk2 were up-regulated. Since lithium and SB-415286-induced G(2)/M arrest we studied changes in the expression of proteins involved in this phase, specifically cyclin B, cdc2 and the phosphorylated form of this protein (tyr15-cdc2). Both drugs increased the expression of tyr15-cdc2, thus inhibiting mitosis. On the other hand, SB-415286 increased the expression of SIRT2, involved in the regulation of proliferation. Moreover, cell-cycle arrest mediated by SB-415286 was accompanied by apoptosis that was not prevented by 100 microM of zVAD-fmk (benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp-fluoromethylketone), a pan-caspase inhibitor. Likewise, GSK-3 inhibitors did not affect the mitochondrial release of apoptosis inducing factor (AIF). We conclude that inhibitors of GSK-3 induced cell-cycle arrest, mediated by the phosphorylation of cdc2 and, in the case of SB-415286, SIRT2 expression, which induced apoptosis in a caspase-independent manner.
GSK-3 beta inhibition and prevention of mitochondrial apoptosis inducing factor release are not involved in the antioxidant properties of SB-415286.[Pubmed:18502415]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Jul 7;588(2-3):239-43.
The antioxidant effects of lithium and SB-415286, two glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3 beta) inhibitors, were studied in cerebellar granule neurons by measuring changes in 2, 7-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (H2DCFDA) fluorescence. GSK-3 beta inhibitors inhibit apoptosis mediated by serum and potassium withdrawal (S/K withdrawal) and GSK-3 beta activation, as measured by beta-catenin degradation. Furthermore, as both drugs prevent mitochondrial apoptosis inducing factor (AIF) release, these data indicate that GSK-3 beta inhibitors prevent caspase-independent apoptosis in cerebellar granule neurons induced by S/K withdrawal. While the most specific GSK-3 beta inhibitor, SB-415286, demonstrated antioxidant effects, Li+ 10 mM did not. These results indicate that lithium 10 mM and SB-415286 20 microM exert anti-apoptotic effects in cases of S/K withdrawal mediated by GSK-3 beta inhibition. However, these antioxidant properties are independent of GSK-3 beta inhibition and prevention of mitochondrial AIF release.
Neuroprotective effects of SB-415286 on hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in B65 rat neuroblastoma cells and neurons.[Pubmed:18342477]
Int J Dev Neurosci. 2008 May-Jun;26(3-4):269-76.
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is involved in the pathogenesis of several neurodegenerative diseases. In addition, as oxidative stress has been implicated in all neurodegenerative disorders, the inhibition of both pathways offers a potential strategy for preventing or delaying neurodegeneration. We examined the cytoprotective effects of lithium and SB-415286, two inhibitors of GSK-3, using a rat B65 cell line and also in cerebellar granule cells (CGN). H(2)O(2) decreased the inactive form of GSK-3 (phospho-GSK-3 at Ser9), as measured by immunoblot experiments involving an antibody against the inactive form of the enzyme. Moreover, lithium inhibited this effect. While SB-415286 exerted a protective effect, lithium did not attenuate the toxic effects of H(2)O(2) (1mM). We then examined those mechanisms implicated in the protective effects of SB-415286. When we analyzed reactive oxygen species (ROS) production using the fluorescent probe 2,7-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate in B65 cells, as well as in CGN, we found that SB-415286 strongly reduced DCF fluorescence. Lithium, however, did not exhibit any antioxidant properties. We conclude that the GSK-3 inhibitor SB-415286 has antioxidant properties, which may explain the cytoprotective effects against H(2)O(2) damage. Furthermore, inhibition of GSK-3 activity was not involved in this protective effect.
Regulation and function of glycogen synthase kinase-3 isoforms in neuronal survival.[Pubmed:17148450]
J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 9;282(6):3904-17.
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a serine/threonine kinase consisting of two isoforms, alpha and beta. The activities of GSK-3 are regulated negatively by serine phosphorylation but positively by tyrosine phosphorylation. GSK-3 inactivation has been proposed as a mechanism to promote neuronal survival. We used GSK-3 isoform-specific small interfering RNAs, dominant-negative mutants, or pharmacological inhibitors to search for functions of the two GSK-3 isoforms in regulating neuronal survival in cultured cortical neurons in response to glutamate insult or during neuronal maturation/aging. Surprisingly, RNA interference-induced depletion of either isoform was sufficient to block glutamate-induced excitotoxicity, and the resulting neuroprotection was associated with enhanced N-terminal serine phosphorylation in both GSK-3 isoforms. However, GSK-3beta depletion was more effective than GSK-3alpha depletion in suppressing spontaneous neuronal death in extended culture. This phenomenon is likely due to selective and robust inhibition of GSK-3beta activation resulting from GSK-3beta Ser9 dephosphorylation during the course of spontaneous neuronal death. GSK-3alpha silencing resulted in reduced tyrosine phosphorylation of GSK-3beta, suggesting that tyrosine phosphorylation is also a critical autoregulatory event. Interestingly, GSK-3 inhibitors caused a rapid and long-lasting increase in GSK-3alpha Ser21 phosphorylation levels, followed by a delayed increase in GSK-3beta Ser9 phosphorylation and a decrease in GSK-3alpha Tyr279 and GSK-3beta Tyr216 phosphorylation, thus implying additional levels of GSK-3 autoregulation. Taken together, our results underscore important similarities and dissimilarities of GSK-3alpha and GSK-3beta in the roles of cell survival as well as their distinct modes of regulation. The development of GSK-3 isoform-specific inhibitors seems to be warranted for treating GSK-3-mediated pathology.
Selective small-molecule inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity protect primary neurones from death.[Pubmed:11279265]
J Neurochem. 2001 Apr;77(1):94-102.
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase)/protein kinase B (PKB; also known as Akt) signalling pathway is recognized as playing a central role in the survival of diverse cell types. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a ubiquitously expressed serine/threonine protein kinase that is one of several known substrates of PKB. PKB phosphorylates GSK-3 in response to insulin and growth factors, which inhibits GSK-3 activity and leads to the modulation of multiple GSK-3 regulated cellular processes. We show that the novel potent and selective small-molecule inhibitors of GSK-3; SB-415286 and SB-216763, protect both central and peripheral nervous system neurones in culture from death induced by reduced PI 3-kinase pathway activity. The inhibition of neuronal death mediated by these compounds correlated with inhibition of GSK-3 activity and modulation of GSK-3 substrates tau and beta-catenin. Thus, in addition to the previously assigned roles of GSK-3, our data provide clear pharmacological and biochemical evidence that selective inhibition of the endogenous pool of GSK-3 activity in primary neurones is sufficient to prevent death, implicating GSK-3 as a physiologically relevant principal regulatory target of the PI 3-kinase/PKB neuronal survival pathway.
Selective small molecule inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 modulate glycogen metabolism and gene transcription.[Pubmed:11033082]
Chem Biol. 2000 Oct;7(10):793-803.
BACKGROUND: Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a serine/threonine protein kinase, the activity of which is inhibited by a variety of extracellular stimuli including insulin, growth factors, cell specification factors and cell adhesion. Consequently, inhibition of GSK-3 activity has been proposed to play a role in the regulation of numerous signalling pathways that elicit pleiotropic cellular responses. This report describes the identification and characterisation of potent and selective small molecule inhibitors of GSK-3. RESULTS: SB-216763 and SB-415286 are structurally distinct maleimides that inhibit GSK-3alpha in vitro, with K(i)s of 9 nM and 31 nM respectively, in an ATP competitive manner. These compounds inhibited GSK-3beta with similar potency. However, neither compound significantly inhibited any member of a panel of 24 other protein kinases. Furthermore, treatment of cells with either compound stimulated responses characteristic of extracellular stimuli that are known to inhibit GSK-3 activity. Thus, SB-216763 and SB-415286 stimulated glycogen synthesis in human liver cells and induced expression of a beta-catenin-LEF/TCF regulated reporter gene in HEK293 cells. In both cases, compound treatment was demonstrated to inhibit cellular GSK-3 activity as assessed by activation of glycogen synthase, which is a direct target of this kinase. CONCLUSIONS: SB-216763 and SB-415286 are novel, potent and selective cell permeable inhibitors of GSK-3. Therefore, these compounds represent valuable pharmacological tools with which the role of GSK-3 in cellular signalling can be further elucidated. Furthermore, development of similar compounds may be of use therapeutically in disease states associated with elevated GSK-3 activity such as non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and neurodegenerative disease.


