Aristolochic acid ACAS# 313-67-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

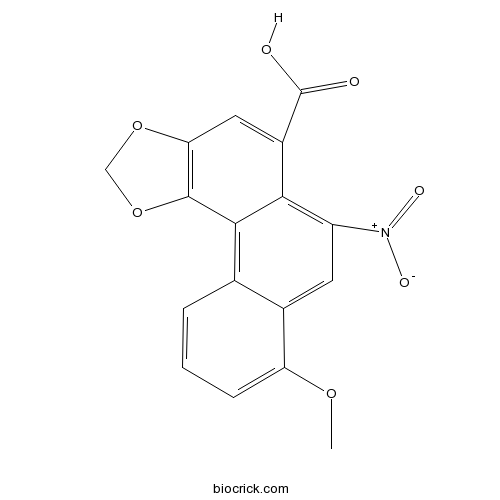
Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 313-67-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2236 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C17H11O7N | M.Wt | 341.27 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Aristolochic acid; Aristolochic acid A | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 25 mg/mL (73.26 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC=CC2=C3C(=C(C=C21)[N+](=O)[O-])C(=CC4=C3OCO4)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BBFQZRXNYIEMAW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Aristolochic acid A is a potent nephrotoxin, which strongly induced toxic damage during ovarian maturation by inhibiting Akt phosphorylation-mediated suppression of apoptosis. |
| Targets | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | PARP | Akt |
| In vitro | Aristolochic Acid A induces ovarian toxicity by inhibition of akt phosphorylation.[Pubmed: 25406029]Chem Res Toxicol. 2014 Dec 15;27(12):2128-35.Aristolochic acids are natural products found in Chinese herbs of the Aristolochiaceae family. Aristolochic acid I (Aristolochic acid A,AAI) is a potent carcinogen and was found to be toxic in animal and clinical studies. Apoptosis is a rapid, selective process of physiological cell deletion that regulates the balance between cell proliferation and cell death and is induced by various kinds of damage. However, the toxicity of AAI during ovarian maturation in the mouse is unclear and is the subject of the present investigation.
|
| In vivo | The determination of aristolochic acid A in different processed Aristolochia manshuriensis and the test of influence about renal function in rats.[Pubmed: 21213532]Zhong Yao Cai. 2010 Aug;33(8):1228-33.To study and approach the processing methods and mechanism which can markedly reduce the content of aristolochic acid in Aristolochia manshuriensis and lighten the nephrotoxicity of aristolochic acid.
|

Aristolochic acid A Dilution Calculator

Aristolochic acid A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9302 mL | 14.6512 mL | 29.3023 mL | 58.6046 mL | 73.2558 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.586 mL | 2.9302 mL | 5.8605 mL | 11.7209 mL | 14.6512 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.293 mL | 1.4651 mL | 2.9302 mL | 5.8605 mL | 7.3256 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0586 mL | 0.293 mL | 0.586 mL | 1.1721 mL | 1.4651 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0293 mL | 0.1465 mL | 0.293 mL | 0.586 mL | 0.7326 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Estradiol Cypionate
Catalog No.:BCC4477
CAS No.:313-06-4
- Arjunic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5229
CAS No.:31298-06-3
- LDN-27219
Catalog No.:BCC6236
CAS No.:312946-37-5
- TCS JNK 5a
Catalog No.:BCC5148
CAS No.:312917-14-9
- Raucaffricine
Catalog No.:BCN4653
CAS No.:31282-07-2
- Hygromycin B
Catalog No.:BCC1204
CAS No.:31282-04-9
- Indacaterol
Catalog No.:BCC1650
CAS No.:312753-06-3
- gamma-Mangostin
Catalog No.:BCN5228
CAS No.:31271-07-5
- THIQ
Catalog No.:BCC7539
CAS No.:312637-48-2
- SKI II
Catalog No.:BCC5029
CAS No.:312636-16-1
- Tetrahydrocannabivarin
Catalog No.:BCN6935
CAS No.:31262-37-0
- IQ 3
Catalog No.:BCC8093
CAS No.:312538-03-7
- ICA 121431
Catalog No.:BCC6358
CAS No.:313254-51-2
- Regadenoson
Catalog No.:BCC6438
CAS No.:313348-27-5
- Reversan
Catalog No.:BCC7764
CAS No.:313397-13-6
- VU 590 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7803
CAS No.:313505-85-0
- T0070907
Catalog No.:BCC2261
CAS No.:313516-66-4
- INH1
Catalog No.:BCC6040
CAS No.:313553-47-8
- Bombesin
Catalog No.:BCC5708
CAS No.:31362-50-2
- PD 118057
Catalog No.:BCC7499
CAS No.:313674-97-4
- 13-Oxo-9,11-octadecadienoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8437
CAS No.:31385-09-8
- [Des-octanoyl]-Ghrelin (human)
Catalog No.:BCC7304
CAS No.:313951-59-6
- FLI-06
Catalog No.:BCC5110
CAS No.:313967-18-9
- o-3M3FBS
Catalog No.:BCC7210
CAS No.:313981-55-4
Aristolochic Acid I induces ovarian toxicity by inhibition of akt phosphorylation.[Pubmed:25406029]
Chem Res Toxicol. 2014 Dec 15;27(12):2128-35.
Aristolochic acids are natural products found in Chinese herbs of the Aristolochiaceae family. Aristolochic acid I (AAI) is a potent carcinogen and was found to be toxic in animal and clinical studies. Apoptosis is a rapid, selective process of physiological cell deletion that regulates the balance between cell proliferation and cell death and is induced by various kinds of damage. However, the toxicity of AAI during ovarian maturation in the mouse is unclear and is the subject of the present investigation. We used Chinese hamster ovary-K1 (CHO-K1) cells and an AAI injection mouse model: MTT assay was used to assess AA toxicity to cells; ovary size and weight were measured to determine the toxicity of AA to mouse ovary; western blot was used to assess apoptosis; TUNEL assay was used to evaluate apoptotic cell death; and immunohistochemistry was used to examine the local expression of apoptotic proteins in ovary tissue. We found that AAI significantly inhibits the viability of CHO-K1 cells and strongly induces apoptotic cell death in CHO-K1 cells and in mouse ovary. In addition, we observed that AAI markedly increases the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins, including Bax, caspase-3, caspase-9, and poly(ADP) ribose polymerase (PARP). In contrast, anti-apoptotic proteins, such as Bcl-2 and survivin, were decreased by AAI treatment. Furthermore, we observed that ovary size and weight were significantly reduced and that the number of ovulated oocytes was markedly suppressed in AAI-treated mice. These results suggest that AAI strongly induces toxic damage during ovarian maturation by inhibiting Akt phosphorylation-mediated suppression of apoptosis.
[The determination of aristolochic acid A in different processed Aristolochia manshuriensis and the test of influence about renal function in rats].[Pubmed:21213532]
Zhong Yao Cai. 2010 Aug;33(8):1228-33.
OBJECTIVE: To study and approach the processing methods and mechanism which can markedly reduce the content of aristolochic acid in Aristolochia manshuriensis and lighten the nephrotoxicity of aristolochic acid. METHODS: A traditional "attenuation" processing method was used and 30 types of samples which contain one crude and 29 types of processed sample were obtained. The contents of Aristolochic acid A in every sample were determined by HPLC. According to the Rat's acute renal injury test, the influence of animal's renal function was investigated for representative samples. RESULTS: The content of aristolochic acid in six types of samples depressed markedly (30% or more depressed) which processing with boiling in the limewater, steaming with limewater, boiling in the juice of liquorice, boiling in the decoction of black soybean, boiling in the soda water and stir-baked with talcum powder, the content of aristolochic acid in other processed samples also depressed with a large discrepancy. The toxicology test results showed that the above-mentioned 6 samples all can relieve renal injury of rats. There could be some associativity between the degree of renal injury relieving and the content of Aristolochic acid A in the samples. CONCLUSION: The content of aristolochic acid can be reduced and the nephrotoxicity for animals can be lightened with some eligible processing methods for the traditional Chinese medicines containing aristolochic acid with the representative of Aristolochia manshuriensis.


