(S)-4-CarboxyphenylglycineGroup I mGlu antagonist/weak group II agonist CAS# 134052-73-6 |
- I-BET-762
Catalog No.:BCC4474
CAS No.:1260907-17-2
- Bromodomain Inhibitor, (+)-JQ1
Catalog No.:BCC1132
CAS No.:1268524-70-4
- I-BET151 (GSK1210151A)
Catalog No.:BCC4476
CAS No.:1300031-49-5
- GSK1324726A
Catalog No.:BCC4038
CAS No.:1300031-52-0
- PFI-1 (PF-6405761)
Catalog No.:BCC2225
CAS No.:1403764-72-6
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 134052-73-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5311459 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C9H9NO4 | M.Wt | 195.17 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (<em>S</em>)-4CPG | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in 1eq. NaOH with gentle warming | ||
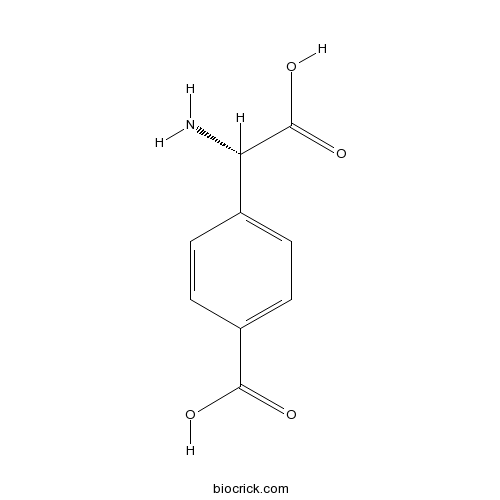
| Chemical Name | 4-[(S)-amino(carboxy)methyl]benzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C(C(=O)O)N)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VTMJKPGFERYGJF-ZETCQYMHSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H9NO4/c10-7(9(13)14)5-1-3-6(4-2-5)8(11)12/h1-4,7H,10H2,(H,11,12)(H,13,14)/t7-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Competitive group I metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist, with selectivity for mGlu1a/1a over mGlu5a/5b. (RS)-4-Carboxyphenylglycine and (R)-4-Carboxyphenylglycine also available. |

(S)-4-Carboxyphenylglycine Dilution Calculator

(S)-4-Carboxyphenylglycine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.1237 mL | 25.6187 mL | 51.2374 mL | 102.4748 mL | 128.0935 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0247 mL | 5.1237 mL | 10.2475 mL | 20.495 mL | 25.6187 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5124 mL | 2.5619 mL | 5.1237 mL | 10.2475 mL | 12.8093 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1025 mL | 0.5124 mL | 1.0247 mL | 2.0495 mL | 2.5619 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0512 mL | 0.2562 mL | 0.5124 mL | 1.0247 mL | 1.2809 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- (R)-4-Carboxyphenylglycine
Catalog No.:BCC6602
CAS No.:134052-68-9
- (RS)-4-Carboxy-3-hydroxyphenylglycine
Catalog No.:BCC6598
CAS No.:134052-66-7
- Selaginellin F
Catalog No.:BCN6420
CAS No.:1340493-24-4
- H-Ala-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3194
CAS No.:13404-22-3
- Methyl beta-D-fructofuranoside
Catalog No.:BCN6183
CAS No.:13403-14-0
- Phaseollin
Catalog No.:BCN4816
CAS No.:13401-40-6
- d-Laserpitin
Catalog No.:BCN3616
CAS No.:134002-17-8
- 4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN6186
CAS No.:134-96-3
- Lobeline Sulphate
Catalog No.:BCC8203
CAS No.:134-64-5
- (-)-Lobeline hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6927
CAS No.:134-63-4
- Azaguanine-8
Catalog No.:BCC4629
CAS No.:134-58-7
- Pelargonidin chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3111
CAS No.:134-04-3
- Ponasterone A
Catalog No.:BCN6184
CAS No.:13408-56-5
- TP-0903
Catalog No.:BCC6462
CAS No.:1341200-45-0
- INCB8761(PF-4136309)
Catalog No.:BCC1649
CAS No.:1341224-83-6
- Fmoc-Tyr(PO3Bzl2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3566
CAS No.:134150-51-9
- Methylcobalamin
Catalog No.:BCC5188
CAS No.:13422-55-4
- RKI-1447
Catalog No.:BCC1903
CAS No.:1342278-01-6
- Daphnelantoxin B
Catalog No.:BCN3228
CAS No.:134273-12-4
- 3,5-Dibromo-4-[3-(dimethylamino)propoxy]cinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1582
CAS No.:134276-56-5
- BIMU 8
Catalog No.:BCC7928
CAS No.:134296-40-5
- Tolcapone
Catalog No.:BCC2334
CAS No.:134308-13-7
- alpha,beta-Methyleneadenosine 5'-triphosphate trisodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7603
CAS No.:1343364-54-4
- 2-ThioUTP tetrasodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7625
CAS No.:1343364-70-4
(R,S)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG) fails to block long-term potentiation under urethane anaesthesia in vivo.[Pubmed:9423922]
Neuropharmacology. 1997 Oct;36(10):1339-54.
The effects of the metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist (R,S)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG) on the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) in the dentate gyrus were examined under urethane anaesthesia in vivo. In experiment 1, bilateral intraventricular infusion of either 20 mM or 200 mM (R,S)-MCPG (5 microl each side) failed to block LTP in the perforant path-granule cell projection, relative to vehicle-infused controls; 30 mM D-AP5 (5 microl each side) infused in the same way as MCPG completely blocked LTP. Experiment 2, in which the contralateral perforant path-dentate gyrus pathway was used as a non-tetanized control, revealed that slight baseline changes induced by MCPG infusion were transient; again no block of LTP was obtained. The efficacy of mGluR blockade was confirmed in experiment 3, in which MCPG antagonized an increase in spontaneous activity induced by (1S,3R)-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid (ACPD). In experiment 4, significant depotentiation was induced by low frequency stimulation (5 Hz for 1 min) given 2 min after high frequency tetanization, but MCPG remained ineffective in blocking LTP after a second tetanus. In experiment 5, increasing the period of low frequency stimulation from 1 to 10 min produced greater depotentiation, but still did not unmask an MCPG-sensitive component of LTP. These experiments fail to support a role for mGluRs in the induction of LTP in the dentate gyrus under urethane anaesthesia in vivo, nor do they support the idea that a metabotropic switch controlling sensitivity to MCPG is reset by depotentiation.
A glutamate receptor antagonist, S-4-carboxyphenylglycine (S-4-CPG), inhibits vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage in haptoglobin 2-2 mice [corrected].[Pubmed:23842553]
Neurosurgery. 2013 Oct;73(4):719-28; discussion 729.
BACKGROUND: Vasospasm contributes to delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). Glutamate concentrations increase after SAH and correlate with vasospasm in experimental SAH. The haptoglobin (Hp) 2-2 genotype is associated with higher risk of vasospasm after SAH. We tested the efficacy of (S)-4-Carboxyphenylglycine (S-4-CPG), a metabotropic glutamate receptor inhibitor, for the treatment of vasospasm after SAH in Hp 2-2 and Hp 1-1 mice. OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the effect on vasospasm and neurobehavioral scores after SAH of systemic S-4-CPG, as well as its toxicity, and phosphorylation of vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) in Hp 2-2 mice. METHODS: Western blot was used to assess changes in VASP phosphorylation in response to glutamate with and without S-4-CPG. A pharmacokinetics study was done to evaluate S-4-CPG penetration through the blood-brain barrier in vivo. Toxicity was assessed by administering increasing S-4-CPG doses. Efficacy of S-4-CPG assessed the effect of S-4-CPG on lumen patency of the basilar artery and animal behavior after SAH in Hp 1-1 and Hp 2-2 mice. Immunohistochemistry was used to evaluate the presence of neutrophils surrounding the basilar artery after SAH. RESULTS: Exposure of human brain microvascular endothelial cells to glutamate decreased phosphorylation of VASP, but glutamate treatment in the presence of S-4-CPG maintains phosphorylation of VASP. S-4-CPG crosses the blood-brain barrier and was not toxic to mice. S-4-CPG treatment significantly prevents vasospasm after SAH. S-4-CPG administered after SAH resulted in a trend toward improvement of animal behavior. CONCLUSION: S-4-CPG prevents vasospasm after experimental SAH in Hp2-2 mice. S-4-CPG was not toxic and is a potential therapeutic agent for vasospasm after SAH.
(R,S)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG) blocks spatial learning in rats and long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus in vivo.[Pubmed:8177513]
Neurosci Lett. 1994 Feb 14;167(1-2):141-4.
Recently, it was demonstrated by the use of the competitive and selective antagonist (R,S)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG) that metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) activation is required to induce long-term potentiation (LTP) in the hippocampus. Accordingly, we investigated whether MCPG also inhibits spatial learning. Rats were trained on a spatial alternation task in a Y-maze with footshock reinforcement, and MCPG (0.0208 mg) was injected intracerebroventricularly prior to training and/or retention test. Animals injected pre-training are clearly impaired in retention, whereas preretention application was without effect. A state dependency could be excluded. Additionally, MCPG at the same concentration completely blocks a potentiation at perforant path/dentate gyrus synapses in vivo. These results strongly implicate a role of mGluRs in spatial learning and LTP.
Competitive antagonism at metabotropic glutamate receptors by (S)-4-carboxyphenylglycine and (RS)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine.[Pubmed:8381746]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 15;244(2):195-7.
Two phenylglycine derivates, (S)-4-Carboxyphenylglycine and (RS)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine, competitively antagonised (1S,3R)-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylate (ACPD)-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat cerebral cortical slices. The same phenylglycine derivatives selectively antagonized ACPD-induced depolarization in neonatal rat spinal motoneurones and rate thalamic neurones relative to depolarization or excitation induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) or alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA). Both phenylglycine derivatives also selectively depressed synaptic excitation in thalamic neurones evoked by noxious thermal stimuli, without affecting the synaptic stimulation of the same cells by non-noxious stimuli.
Antagonist activity of alpha-substituted 4-carboxyphenylglycine analogues at group I metabotropic glutamate receptors expressed in CHO cells.[Pubmed:10051137]
Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Jan;126(1):205-10.
1. We have investigated the antagonist properties of 6 alpha-substituted phenylglycine analogues based on the structure of 4-carboxyphenylglycine (4-CPG) for group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGlu1alpha and mGlu5a) permanently expressed in CHO cells. 2. (S)-4-CPG and (S)-MCPG were the most selective mGlu1alpha receptor antagonists. Longer chain alpha-carbon substitutions resulted in a progressive loss of antagonist affinity at mGlu1alpha receptors but not at mGlu5a receptors. Thus mGlu1alpha receptor antagonists require small aliphatic groups at the alpha-position. Alpha-cyclopropyl-4-CPG showed a tendency towards mGlu5a selectivity, suggesting that bulky groups at this position may favour mGlu5a receptor antagonism. 3. We demonstrate that the mGlu5a receptor displays agonist-dependent antagonism. L-glutamate-induced Ca2+ release in mGlu5a receptor expressing cells was more susceptible to antagonism by cyclic alpha-carbon derivatives than (S)-3,5-dihydroxyphenylglycine (DHPG)-induced Ca2+ release in the same cell line. 4. The data presented suggests that mGlu1alpha and mGlu5a receptors have different steric and/or conformational requirements for the binding of antagonists and different amino acids which could interact with agonists. 5. These phenylglycine analogues could provide leads for the development of subtype selective antagonists.
Phenylglycine derivatives discriminate between mGluR1- and mGluR5-mediated responses.[Pubmed:8532171]
Neuropharmacology. 1995 Aug;34(8):895-903.
The effects of the phenylglycine derivatives, alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG), 4-carboxyphenylglycine (4CPG), 4-carboxy-3-hydroxyphenylglycine (4C3HPG), 3-hydroxyphenylglycine (3HPG) and 3,5-dihydrohyphenylglycine (DHPG) were tested on LLC-PK1 cells transiently expressing the rat mGluR1a or mGluR5a receptors. As previously reported by others, (S)-3HPG and (RS)-DHPG were found to be partial agonists at mGluR1a, whereas(+)-MCPG,(S)-4CPG and (S)-4C3HPG competitively antagonized the effect of Glu. Surprisingly, the 4-carboxy derivatives of phenylglycine antagonized the effect of 1S,3R-ACPD on mGluR1a with lower KB values. On mGluR5a, (S)-3HPG and (RS)-DHPG are also partial agonists. However, in contrast to their effects on mGluR1a,(S)-4CPG did not inhibit the effect of Glu or 1S,3R-ACPD, and (S)-4C3HPG acted as an agonist at high concentration. Whereas no significant antagonism of the Glu effect on mGluR5a was observed with 1 mM (+)-MCPG, this compound was found to potently and competitively antagonize the effect of 1S,3R-ACPD. Finally, the effect of 4CPG was also examined on cultured cortical and cerebellar neurons that express mGluR5 and mGluR1 mRNA, respectively. 4CPG inhibited 1S,3R-ACPD-stimulated IP production in cerebellar neurons only. These results(1) demonstrate that phenylglycine derivatives can be used to discriminate between effects mediated by mGluR1 and mGluR5 and (2) suggest that the apparent potency of phenylglycine antagonists depends on the agonist used to activate these receptors.
Phenylglycine derivatives as new pharmacological tools for investigating the role of metabotropic glutamate receptors in the central nervous system.[Pubmed:7680790]
Neuroscience. 1993 Feb;52(3):481-8.
The possible roles of G-protein coupled metabotropic glutamate receptors in central nervous function are currently the focus of intensive investigation. The complexity of effects produced by agonists at these receptors probably reflects the activity of a range of sub-types. The metabotropic glutamate receptors first described are linked to phospholipase C, mediating phosphoinositide hydrolysis and release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores. A substance generally considered to be a selective agonist for these receptors is (1S,3R)-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid (ACPD). This substance not only stimulates phosphoinositide hydrolysis, but also inhibits cyclic AMP formation. A family of metabotropic glutamate receptors, incorporating both phospholipase C- and adenylcyclase-linked sub-types has been cloned. Various effects of metabotropic glutamate receptor agonists on membrane ion fluxes and synaptic events have been reported, including neuronal depolarization and/or excitation, hyperpolarization, inhibition of Ca(2+)-dependent and voltage-gated K+ currents, potentiation of N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced responses, depression of synaptic excitation and either induction or augmentation of long-term potentiation. To clarify the role of metabotropic glutamate receptors in central nervous activity and to aid the characterization of the various receptor types that may be involved, a range of highly selective agonists and antagonists is required. To date, currently available antagonists such as L-2-amino-3-phosphonopropionate and L-aspartic acid-beta-hydroxamate appear to be unselective and insufficiently potent. We report here the actions of three phenylglycine derivatives, the particular agonist and/or antagonist properties of which may help to elucidate the roles of metabotropic glutamate receptors in central nervous activity.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)


