Vitamin A AcetateUnsaturated nutritional hydrocarbons CAS# 127-47-9 |
- Daptomycin
Catalog No.:BCC1057
CAS No.:103060-53-3
- Nelarabine
Catalog No.:BCC1072
CAS No.:121032-29-9
- Gemcitabine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1076
CAS No.:122111-03-9
- Clofarabine
Catalog No.:BCC1078
CAS No.:123318-82-1
- Ifosfamide
Catalog No.:BCC1164
CAS No.:3778-73-2
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 127-47-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 638034 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H32O2 | M.Wt | 328.49 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (152.21 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
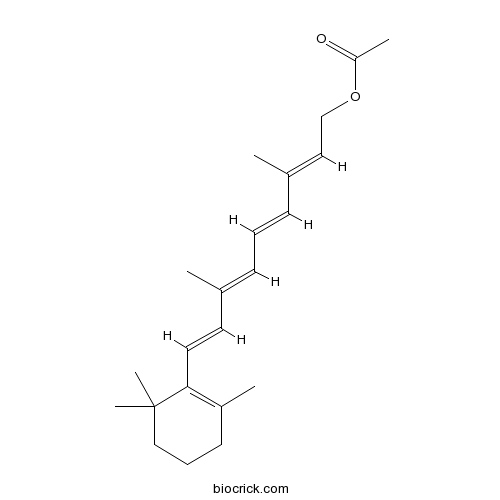
| Chemical Name | [(2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenyl] acetate | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(CCC1)(C)C)C=CC(=CC=CC(=CCOC(=O)C)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QGNJRVVDBSJHIZ-QHLGVNSISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H32O2/c1-17(9-7-10-18(2)14-16-24-20(4)23)12-13-21-19(3)11-8-15-22(21,5)6/h7,9-10,12-14H,8,11,15-16H2,1-6H3/b10-7+,13-12+,17-9+,18-14+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Vitamin A Acetate Dilution Calculator

Vitamin A Acetate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0442 mL | 15.2212 mL | 30.4423 mL | 60.8847 mL | 76.1058 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6088 mL | 3.0442 mL | 6.0885 mL | 12.1769 mL | 15.2212 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3044 mL | 1.5221 mL | 3.0442 mL | 6.0885 mL | 7.6106 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0609 mL | 0.3044 mL | 0.6088 mL | 1.2177 mL | 1.5221 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0304 mL | 0.1522 mL | 0.3044 mL | 0.6088 mL | 0.7611 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Vitamin A acetate (also known as retinyl acetate) is a fatty acid ester form of vitamin A with antineoplastic and chemopreventive effect. Retinyl acetate activated retinoid receptor to induce cell differentiation and decrease cell proliferation. It also exhibited immunomodulatory properties and blocks carcinogen-induced neoplastic transformation.
Retinoid receptors mediate retinoids activities and involved in normal growth and development maintenance, immune response and reproduction.
In rat renal glomerular epithelial cells, retinyl acetate modulated growth, morphology, function and cell organization. [1]
By supplementing normal diet with retinyl acetate in newborn CBA mice of lymphoid cells from (CBA X C57BL/10ScSn) F1 hybrids increased the proportion of the T-cell moiety population that generated IL-2. [2] In Sprague-Dawley rats, chemoprotective properties of retinyl acetate and combination of RA with Mel were demonstrated in mammary carcinogenesis activated by DMBA. [3]
References:
[1] Yamada M, Moritoh C, Kawaguchi M, Okigaki T. Growth, morphology, function, and morphogenetic properties of rat renal glomerular epithelial cells in vitro: effects of retinyl acetate. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;49(2):252-8.
[2] Malkovský M, Medawar PB, Thatcher DR, Toy J, Hunt R, Rayfield LS, Doré C. Acquired immunological tolerance of foreign cells is impaired by recombinant interleukin 2 or vitamin A acetate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):536-8.
[3] Hlersová E, Ahlers I, Kubatka P, Bojková B, Môciková K, Gajdosová S, Onderková HM. Melatonin and retinyl acetate as chemopreventives in DMBA-induced mammary carcinogenesis in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Folia Biol (Praha). 2000;46(2):69-72.
- Lutein
Catalog No.:BCN6151
CAS No.:127-40-2
- Lasiocarpine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN2002
CAS No.:127-30-0
- Pimaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN6149
CAS No.:127-27-5
- Taraxerol
Catalog No.:BCN6148
CAS No.:127-22-0
- Sodium acetate
Catalog No.:BCC7587
CAS No.:127-09-3
- Hydroxyurea
Catalog No.:BCC4912
CAS No.:127-07-1
- Locustatachykinin I
Catalog No.:BCC5926
CAS No.:126985-97-5
- 1-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)heptane-3,5-diyl diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN6572
CAS No.:1269839-26-0
- 5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)heptan-3-yl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN6586
CAS No.:1269839-24-8
- CDK inhibitor II
Catalog No.:BCC1464
CAS No.:1269815-17-9
- Tetrahydro tanshinone I
Catalog No.:BCN2602
CAS No.:126979-84-8
- Methylenedihydrotanshinquinone
Catalog No.:BCN3221
CAS No.:126979-81-5
- 2,2-Bis(4-hydroxy-3-isopropylphenyl)propane
Catalog No.:BCC8494
CAS No.:127-54-8
- Sulfacetamide Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4383
CAS No.:127-56-0
- Sulfamerazine sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5205
CAS No.:127-58-2
- Sulfisoxazole
Catalog No.:BCC4860
CAS No.:127-69-5
- Sulfamerazine
Catalog No.:BCC4854
CAS No.:127-79-7
- Beta-Pinene
Catalog No.:BCC8302
CAS No.:127-91-3
- 4,9-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN3107
CAS No.:1270001-72-3
- CGP 42112
Catalog No.:BCC5921
CAS No.:127060-75-7
- Sulfo-NHS-LC-Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3578
CAS No.:127062-22-0
- Glyceryl hexacosanoate
Catalog No.:BCC8991
CAS No.:127098-14-0
- BMS-911543
Catalog No.:BCC2204
CAS No.:1271022-90-2
- MI-3
Catalog No.:BCC1747
CAS No.:1271738-59-0
Nanoencapsulation of coenzyme Q10 and vitamin E acetate protects against UVB radiation-induced skin injury in mice.[Pubmed:27870992]
Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017 Feb 1;150:32-40.
This study aimed to investigate the feasibility of producing semisolid formulations based on nanocapsule suspensions containing the association of the coenzyme Q10 and vitamin E acetate by adding gellan gum (2%) to the suspensions. Furthermore, we studied their application as an alternative for the treatment of inflammation induced by ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation. For this, an animal model of injury induced by UVB-radiation was employed. All semisolids presented pH close to 5.5, drug content above 95% and mean diameter on the nanometric range, after redispersion in water. Besides, the semisolids presented non-Newtonian flow with pseudoplastic behavior and suitable spreadability factor values. The results also showed that the semisolid containing coenzyme Q10-loaded nanocapsules with higher vitamin E acetate concentration reduced in 73+/-8% the UVB radiation-induced ear edema. Moreover, all formulations tested were able to reduce inflammation parameters evaluated through MPO activity and histological procedure on injured tissue and the semisolids containing the nanoencapsulated coenzyme Q10 reduced oxidative parameters assessment through the non-protein thiols levels and lipid peroxidation. This way, the semisolids based on nanocapsules may be considered a promising approach for the treatment and prevention of skin inflammation diseases.
Associated use of silicone-vitamin E gauzes and alpha-tocopherol acetate oil in healing of skin graft donor sites.[Pubmed:28111908]
Int Wound J. 2017 Oct;14(5):813-817.
Split-thickness skin graft is one of the most used procedures in plastic surgery. This procedure involves numerous painful dressings at the donor site. alpha-Tocopherol acetate has anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory properties and it can reduce the local bacterial growth, thereby promoting wound healing. We designed a prospective study to evaluate the effects of two different kinds of dressings at skin graft donor sites. A total of 30 patients were subjected to daily dressings with alpha-tocopherol acetate oil and traditional moist gauzes (group 1). Another 30 patients were subjected to dressings every 4 days with alpha-tocopherol acetate oil and silicone-vitamin E gauzes (group 2). Healing time, infection rate, patient's pain perception and costs were evaluated in both the groups. No statistically significant difference was found in terms of healing time. The infection rate was slightly different in the two groups. Significant reduction of pain perception was detected in group 2. In the same group, significant reduction in the total cost of the treatment was also observed. alpha-Tocopherol acetate oil and silicone-vitamin E gauzes may represent a safe, simple, painless and inexpensive method for improving skin graft donor site healing.
Vitamin E plasma kinetics in swine show low bioavailability and short half-life of -alpha-tocopheryl acetate.[Pubmed:27898857]
J Anim Sci. 2016 Oct;94(10):4188-4195.
Vitamin E is important for animal production because of its effects on health and product quality, but the amount and form required remains controversial. Our objective was to quantify the absolute bioavailability of oral -alpha-tocopheryl acetate (alpha-TAc) in swine (22 +/- 1 kg and 8 wk old, fitted with jugular catheters) adapted to a diet supplemented with 75 mg/kg -alpha-TAc; 75 mg/kg was chosen because this level represents the nonweighted average inclusion level in piglet diets across Western key swine-producing countries. For this, a 350-g test meal (6% fat) was supplied at time 0 containing 75 mg deuterated (D9) -alpha-TAc to 9 animals, and 8 animals received an intravenous () dose containing deuterated (D6) RRR-alpha-tocopherol (alpha-T) at one-eighth the oral dose and a test meal without supplemental vitamin E. Plasma samples (12 to 13 per animal) were obtained at incremental intervals over 75 h for analysis of deuterated alpha-T using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Surprisingly, the i.v. dose rapidly disappeared from plasma and then reappeared. The half-life for this first peak was only 1.7 +/- 0.3 min. The second peak had an appearance rate (Ka) of 0.10 +/- 0.06 d and a half-life of 5.9 +/- 1.2 h. Oral dosing resulted, after a lag of 56 min, in a Ka of 0.91 +/- 0.21 d and a half-life of 2.6 +/- 0.8 h. The bioavailability for oral alpha-TAc was 12.5%, whereas the area under the curve was only 5.4%. This low bioavailability, small area under the curve, and short half-life are likely because of various factors, that is, the use of only 6% fat in the diet, the use of the acetate ester and , and the high dose relative to requirements. In conclusion, i.v. dosed vitamin E shows both a rapid and a very slow pool, whereas orally dosed vitamin E shows a single slow pool. The oral material has a very short half-live (44% of i.v. or 2.6 h), low bioavailability (12.5%), and a very small area under the curve (5.4%), bringing into question the efficacy of typical doses of vitamin E in swine diets for alleviating oxidative stress.


