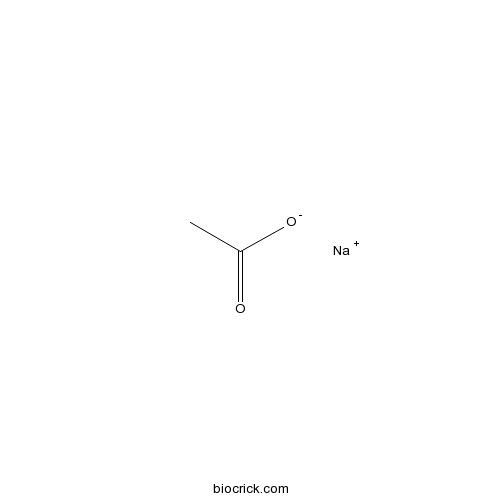
Sodium acetateCAS# 127-09-3 |
- Tiratricol
Catalog No.:BCC4738
CAS No.:51-24-1
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 127-09-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 517045 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C2H3NaO2 | M.Wt | 82.03 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 1000 mM in water | ||
| Chemical Name | sodium;acetate | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)[O-].[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VMHLLURERBWHNL-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C2H4O2.Na/c1-2(3)4;/h1H3,(H,3,4);/q;+1/p-1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Commonly used laboratory reagent |

Sodium acetate Dilution Calculator

Sodium acetate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 12.1907 mL | 60.9533 mL | 121.9066 mL | 243.8132 mL | 304.7665 mL |
| 5 mM | 2.4381 mL | 12.1907 mL | 24.3813 mL | 48.7626 mL | 60.9533 mL |
| 10 mM | 1.2191 mL | 6.0953 mL | 12.1907 mL | 24.3813 mL | 30.4767 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.2438 mL | 1.2191 mL | 2.4381 mL | 4.8763 mL | 6.0953 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.1219 mL | 0.6095 mL | 1.2191 mL | 2.4381 mL | 3.0477 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Hydroxyurea
Catalog No.:BCC4912
CAS No.:127-07-1
- Locustatachykinin I
Catalog No.:BCC5926
CAS No.:126985-97-5
- 1-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)heptane-3,5-diyl diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN6572
CAS No.:1269839-26-0
- 5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)heptan-3-yl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN6586
CAS No.:1269839-24-8
- CDK inhibitor II
Catalog No.:BCC1464
CAS No.:1269815-17-9
- Tetrahydro tanshinone I
Catalog No.:BCN2602
CAS No.:126979-84-8
- Methylenedihydrotanshinquinone
Catalog No.:BCN3221
CAS No.:126979-81-5
- Sar-[D-Phe8]-des-Arg9-Bradykinin
Catalog No.:BCC5996
CAS No.:126959-88-4
- LGX818
Catalog No.:BCC4184
CAS No.:1269440-17-6
- MK 1903
Catalog No.:BCC6242
CAS No.:1268882-43-4
- 3-Methoxy-5-heneicosylphenol
Catalog No.:BCN6147
CAS No.:126882-76-6
- Ssioriside
Catalog No.:BCN6146
CAS No.:126882-53-9
- Taraxerol
Catalog No.:BCN6148
CAS No.:127-22-0
- Pimaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN6149
CAS No.:127-27-5
- Lasiocarpine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN2002
CAS No.:127-30-0
- Lutein
Catalog No.:BCN6151
CAS No.:127-40-2
- Vitamin A Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4748
CAS No.:127-47-9
- 2,2-Bis(4-hydroxy-3-isopropylphenyl)propane
Catalog No.:BCC8494
CAS No.:127-54-8
- Sulfacetamide Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4383
CAS No.:127-56-0
- Sulfamerazine sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5205
CAS No.:127-58-2
- Sulfisoxazole
Catalog No.:BCC4860
CAS No.:127-69-5
- Sulfamerazine
Catalog No.:BCC4854
CAS No.:127-79-7
- Beta-Pinene
Catalog No.:BCC8302
CAS No.:127-91-3
- 4,9-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN3107
CAS No.:1270001-72-3
Sodium acetate inhibits Staphylococcus aureus internalization into bovine mammary epithelial cells by inhibiting NF-kappaB activation.[Pubmed:28351710]
Microb Pathog. 2017 Jun;107:116-121.
Bovine mastitis is one of the most costly and prevalent disease affecting dairy cows worldwide. It was reported that Staphylococcus aureus could internalize into bovine mammary epithelial cells (bMEC) and induce mastitis. Some short chain fatty acids (SCFA) have shown to suppress S. aureus invasion into bMEC and regulate antimicrobial peptides expression. But it has not been evaluated that Sodium acetate has the similar effect. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of Sodium acetate on the invasion of bovine mammary epithelial cells (bMEC) by S. aureus. Gentamicin protection assay showed that the invasion of S. aureus into bMEC was inhibited by Sodium acetate in a dose-dependent manner. Sodium acetate (0.25-5 mM) did not affect S. aureus growth and bMEC viability. The TAP gene level was decreased, while the BNBD5 mRNA level was enhanced in Sodium acetate treated bMEC. In Sodium acetate treated and S. aureus challenged bMEC, the TAP gene expression was increased and BNBD5 gene expression was not modified at low concentrations, but decreased at high concentrations. The Nitric oxide (NO) production of bMEC after S. aureus stimulation was decreased by Sodium acetate treatment. Furthermore, Sodium acetate treatment suppressed S. aureus-induced NF-kappaB activation in bMEC in a dose manner. In conclusion, our results suggested that Sodium acetate exerts an inhibitory property on S. aureus internalization and modulates antimicrobial peptides gene expression.
Apoptotic effect of sodium acetate on a human gastric adenocarcinoma epithelial cell line.[Pubmed:27808354]
Genet Mol Res. 2016 Oct 5;15(4). pii: gmr8375.
The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of Sodium acetate on the viability of the human gastric adenocarcinoma (AGS) epithelial cell line. AGS cells were exposed to a range of concentrations of Sodium acetate for different periods of time, and the Sodium acetate-induced cytotoxic effects, including cell viability, DNA fragmentation, apoptotic gene expression, and caspase activity, were assessed. The changes in these phenotypes were quantified by performing a lactate dehydrogenase cell viability assay, annexin V staining, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL), and several caspase activity assays. In vitro studies demonstrated that the cytotoxicity of Sodium acetate on the AGS cell line were dose- and time-dependent manners. No differences were found between the negative control and Sodium acetate-treated cells stained with annexin V and subjected to the TUNEL assay. However, caspase-3 activity was increased in AGS cells exposed to Sodium acetate. Overall, it was concluded that Sodium acetate exerted an apoptotic effect in AGS cells via a caspase-dependent apoptotic pathway.
Multi-spectroscopic and molecular modeling studies of bovine serum albumin interaction with sodium acetate food additive.[Pubmed:28317723]
Food Chem. 2017 Aug 1;228:265-269.
Sodium acetate (SA) has been used as a highly effective protectant in food industry and the possible effect of this additive on the binding to albumin should be taken into consideration. Therefore, for the first time, the mechanism of SA interaction with bovine serum albumin (BSA) has been investigated by multi-spectroscopic and molecular modeling methods under physiological conditions. Stern-Volmer fluorescence quenching analysis showed an increase in the fluorescence intensity of BSA upon increasing the amounts of SA. The high affinity of SA to BSA was demonstrated by a binding constant value (1.09x10(3) at 310 degrees K). The thermodynamic parameters indicated that hydrophobic binding plays a main role in the binding of SA to Albumin. Furthermore, the results of UV-vis spectra confirmed the interaction of this additive to BSA. In addition, molecular modeling study demonstrated that A binding sites of BSA play the main role in the interaction with acetate.
iTRAQ analysis of low-phytate mung bean sprouts treated with sodium citrate, sodium acetate and sodium tartrate.[Pubmed:27719911]
Food Chem. 2017 Mar 1;218:285-293.
The effects of sodium citrate (SC), Sodium acetate (SA) and sodium tartrate (ST) spraying on mung bean germination were investigated. Exogenous SC, ST and SA treatments significantly reduced the phytic acid content and increased the antioxidant enzyme activities. In this study, an iTRAQ-based proteomic approach was employed to explore the proteomes of mung bean sprouts, and 81, 101 and 90 differentially expressed proteins were identified in 4-day-old SC-, SA- and ST-treated mung bean sprouts, with 38 proteins present in all samples. Functional classification analysis showed that most of the differentially expressed proteins in mung bean sprouts subjected to the three treatments were involved in carbohydrate and energy metabolism. The inhibitory effect of the SA treatment was probably due to impairments in protein biosynthesis, whereas enhanced energy metabolism, accelerated reserve hydrolysis and protein processing were very important strategies for growth stimulation in response to ST and SC treatments.


