Valproic acidHDAC1 inhibitor CAS# 99-66-1 |
- Resminostat hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1888
CAS No.:1187075-34-8
- M344
Catalog No.:BCC2162
CAS No.:251456-60-7
- Pyroxamide
Catalog No.:BCC2424
CAS No.:382180-17-8
- LAQ824 (NVP-LAQ824,Dacinostat)
Catalog No.:BCC2160
CAS No.:404951-53-7
- AR-42 (OSU-HDAC42)
Catalog No.:BCC2161
CAS No.:935881-37-1
- KD 5170
Catalog No.:BCC2420
CAS No.:940943-37-3
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 99-66-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3121 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C8H16O2 | M.Wt | 144.21 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | VPA; 2-Propylpentanoic Acid | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (693.43 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : 1 mg/mL (6.93 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
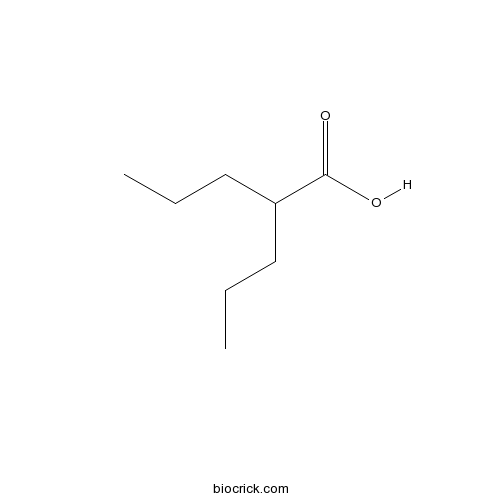
| Chemical Name | 2-propylpentanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCCC(CCC)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NIJJYAXOARWZEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H16O2/c1-3-5-7(6-4-2)8(9)10/h7H,3-6H2,1-2H3,(H,9,10) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Valproic acid is an HDAC inhibitor, with IC50 in the range of 0.5 and 2 mM, also inhibits HDAC1 (IC50, 400 μM), and induces proteasomal degradation of HDAC2; Valproic acid sodium salt is used in the treatment of epilepsy, bipolar disorder and prevention of migraine headaches.In Vitro:Valproic acid inhibits the growth dose- and time-dependently with an IC50 of appr 10 and 4 mM at 24 and 72 h, respectively. Valproic acid significantly attenuates the activities of total, cytosol and nuclear HDACs. Valproic acid increases the form of acetylated histone 3 in HeLa cells. Valproic acid (1-3 mM) induces a G1 phase arrest, while 10 mM Valproic acid significantly induces a G2/M phase arrest of cell cycle in HeLa cells. In addition, Valproic acid increases the percentage of sub-G1 cells in HeLa cells in a dose-dependent manner at 24 h[1]. Valproic acid inhibits the mRNA and protein expression of VEGF, VEGFR2 and bFGF. Valproic acid inhibits the protein expression of HDAC1, increases histone H3 acetylation, and enhances the accumulation of hyperacetylated histone H3 on VEGF promoters[2]. Valproic acid treatment results in increased levels of phosphorylated AMPK/ACC in primary mouse hepatocytes. Phosphorylation of ACC following Valproic acid treatment is AMPK-dependent. Valproic acid inhibits the deacetylase activity of both mouse liver nuclear extracts and human recombinant HDAC1 while of the metabolites of Valproic acid, only 2-ene-Valproic acid and 4-ene-Valproic acid diminish deacetylase activity[4].In Vivo:Valproic acid (500 mg/kg, i.p.) inhibits the tumor growth and angiogenesisin the mice transplanted with Kasumi-1 cells. The IR rate in the Valproic acid group is 57.25% at the end of the experiment[2]. Valproic acid (350 mg/kg, i.p.) demonstrates more social investigation and play fighting than control animals[3]. References: | |||||

Valproic acid Dilution Calculator

Valproic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.9343 mL | 34.6717 mL | 69.3433 mL | 138.6866 mL | 173.3583 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.3869 mL | 6.9343 mL | 13.8687 mL | 27.7373 mL | 34.6717 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6934 mL | 3.4672 mL | 6.9343 mL | 13.8687 mL | 17.3358 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1387 mL | 0.6934 mL | 1.3869 mL | 2.7737 mL | 3.4672 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0693 mL | 0.3467 mL | 0.6934 mL | 1.3869 mL | 1.7336 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Valproic acid is an inhibitor of HDAC1 with IC50 value of 0.4mM [1].
Valproic acid (VPA) is a branched short-chain fatty acid. It is previously synthesized and used as an inert solvent of organic compounds. VPA is then found to have ability in preventing pentylenetetrazol-induced convulsions in rodents. It is used as an antiepileptic drug via inhibiting the activity of GABA. VPA is found to inhibit the degradation of GABA and increase GABA synthesis as well as inhibit GABA Transaminobutyratre. It also blocks Na+ channels, Ca2+ channels and voltage-gated K+ channels. Besides that, VPA is reported as an inhibitor of HDAC, making it to be a potential therapeutic for cancers. VPA inhibits HDAC1 in vitro with IC50 value of 0.4mM. For nuclear extracts from HeLa cells, VPA inhibits HDACs with IC50 values from 0.5mM to 2mM [1, 2].
References:
[1] Phiel C J, Zhang F, Huang E Y, et al. Histone deacetylase is a direct target of valproic acid, a potent anticonvulsant, mood stabilizer, and teratogen. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001, 276(39): 36734-36741.
[2] Chateauvieux S, Morceau F, Dicato M, et al. Molecular and therapeutic potential and toxicity of valproic acid. BioMed Research International, 2010, 2010.
- 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4537
CAS No.:99-50-3
- 2-Methyl-5-Isopropenyl-2-Cyclohexenone
Catalog No.:BCC8279
CAS No.:99-49-0
- Chelidonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6547
CAS No.:99-32-1
- Methyl gallate
Catalog No.:BCN3823
CAS No.:99-24-1
- Trehalose
Catalog No.:BCC9182
CAS No.:99-20-7
- Prunasin
Catalog No.:BCN4535
CAS No.:99-18-3
- Ac-DL-Leu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2977
CAS No.:99-15-0
- 3,5-DHBA
Catalog No.:BCC7951
CAS No.:99-10-5
- Fmoc-Arg(Mtr)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3074
CAS No.:98930-01-9
- Fmoc-His(Fmoc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3500
CAS No.:98929-98-7
- Limonol
Catalog No.:BCN4533
CAS No.:989-61-7
- (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate
Catalog No.:BCN6326
CAS No.:989-51-5
- Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCN4540
CAS No.:99-76-3
- 4-Isopropyltoluene
Catalog No.:BCC8282
CAS No.:99-87-6
- 4'-Hydroxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN4544
CAS No.:99-93-4
- 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4546
CAS No.:99-96-7
- Fentanyl citrate
Catalog No.:BCC6000
CAS No.:990-73-8
- Imiquimod
Catalog No.:BCC2492
CAS No.:99011-02-6
- Imiquimod hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4196
CAS No.:99011-78-6
- [Ala107]-MBP (104-118)
Catalog No.:BCC5835
CAS No.:99026-77-4
- [Ala113]-MBP (104-118)
Catalog No.:BCC5836
CAS No.:99026-78-5
- Limonexic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4534
CAS No.:99026-99-0
- Kushenol I
Catalog No.:BCN2983
CAS No.:99119-69-4
- Kushenol E
Catalog No.:BCN3348
CAS No.:99119-72-9
Evaluate the effects of long-term valproic acid treatment on metabolic profiles in newly diagnosed or untreated female epileptic patients: A prospective study.[Pubmed:28365440]
Seizure. 2017 May;48:15-21.
PURPOSE: Excessive weight gain associated with sodium valproate (VPA) may predispose patients with epilepsy to other health problems such as insulin resistance. We prospectively evaluated the long-term impact of VPA monotherapy compared with lamotrigine (LTG) monotherapy on anthropometric and metabolic parameters in women with epilepsy. Our primary objective is to understand the underlying mechanism responsible for VPA-induced obesity. METHODS: Sixty-six female patients with newly diagnosed or untreated epilepsy were included in the study. Thirty-four patients with VPA and thirty-two patients with LTG were treated for a period of one year in our center. Anthropometric and clinical data were collected at 5 time points: before, at 6th week, 3rd month, 6th month, 9th month and 12th month (last visit). Biochemical and hormonal data were collected 2 time points: before and last visit. RESULTS: Subjects in the VPA group had significantly higher body weight than LTG-treated subjects (64.88+/-3.25 vs. 58.28+/-2.43, P<0.001). HOMA-IR level was significantly increased (2.76 vs. 1.35, P<0.05), and adiponectin levels were significantly lower in the VPA group (3.46 vs. 6.22, P<0.05). Triglycerides levels were significantly increased (118 vs. 96, P<0.05), and HDL-C levels were significantly lower in the VPA group. Both the VPA-treated group and the LTG-treated group showed no significant difference in term of total cholesterol, LDL-C, fasting blood glucose and serum leptin levels. CONCLUSIONS: Based on the findings of this study, we proposed that VPA induced hypoadiponectinemia which correlates significantly with insulin resistance. These two factors may be responsible for weight gain, possible by stimulating appetite. Valproic acid appears to be use cautionally in obese females with epilepsy.
The histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid inhibits NKG2D expression in natural killer cells through suppression of STAT3 and HDAC3.[Pubmed:28338101]
Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 24;7:45266.
NKG2D is a major activating receptor of NK cells and plays a critical role in tumor immunosurveillance. NKG2D expression in NK cells is inhibited by the histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor Valproic acid (VPA) and enhanced by the narrow-spectrum HDAC inhibitor entinostat. We previously demonstrated that entinostat enhanced NKG2D transcription by increasing acetylation of Histones H3 and H4. However, the mechanism by which VPA reduces NKG2D expression in NK cells is not known. We have also shown that NKG2D transcription is regulated by STAT3 phosphorylation. In this study, we investigated regulation of NKG2D expression in NK cells by VPA and entinostat by assessing protein expression, phosphorylation, and interaction of HDACs and STAT3. We find that VPA selectively inhibits STAT3 tyrosine705 phosphorylation, but entinostat does not. STAT3 complexes with HDAC3, and HDAC3 inhibition represses STAT3 phosphorylation and therefore NKG2D expression. NK cells from STAT3 wild-type mice downregulate NKG2D in response to VPA, but not NK cells from STAT3 knockout mice. These results show that VPA is a potent inhibitor of STAT3 phosphorylation and demonstrate that histone acetylation and STAT3 tyrosine705 phosphorylation cooperate in regulating NKG2D expression in NK cells.
Valproic acid malabsorption in 30 year-old female patient - Case study.[Pubmed:28341336]
Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2017 May - Jun;51(3):259-262.
AIM: Valproic acid (VPA) is used in epilepsy treatment and as a stabilizer in bipolar affective disorder for over 40 years. Although, the pharmacokinetic properties of Valproic acid are well known, it is often forgotten that the formulation of the drug significantly influences its gastrointestinal absorption. CASE: We are describing the case of 30 year-old female patient, diagnosed at the age of 13 with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Complete ineffectiveness of the treatment was caused by malabsorption of sodium valproate and Valproic acid in the patient. The change of the drug formulation resulted in a several times higher bioavailability of the drug and a partial improvement of the patient's clinical condition. COMMENTARY: Low concentration of Valproic acid after administration the slow-released tablets are usually observed. However, a low bioavailability beside the bad compliance should be considered when the minimal level is extremely low during therapy. It is known that form of the drug, beside presence of food and its components, as well as gastrointestinal tract condition or interactions with other drugs can influence the drug level. Modification of the formulation of the drug may lead to improvement of absorption and increase its effectiveness.
Bilateral subacute lacrimal gland enlargement mimicking dacryoadenitis in a 7-year-old boy: a rare adverse effect of valproic acid (sodium valproate).[Pubmed:28359767]
J AAPOS. 2017 Jun;21(3):257-258.
A healthy 7-year-old boy presented with bilateral symmetrical lacrimal gland enlargement; a week later salivary gland enlargement was also noted. Clinical investigations suggested no diagnosis, and surgical biopsy was considered. Valproic acid (sodium valproate), which he was taking for absence seizures, has been reported to cause salivary gland swelling in adults. Suspecting that a similar mechanism could be causal, the drug was discontinued. Complete resolution of the lacrimal and salivary gland enlargement rapidly ensued. This is the first report of lacrimal gland enlargement caused by Valproic acid.


