(+)-RutamarinCAS# 13164-05-1 |
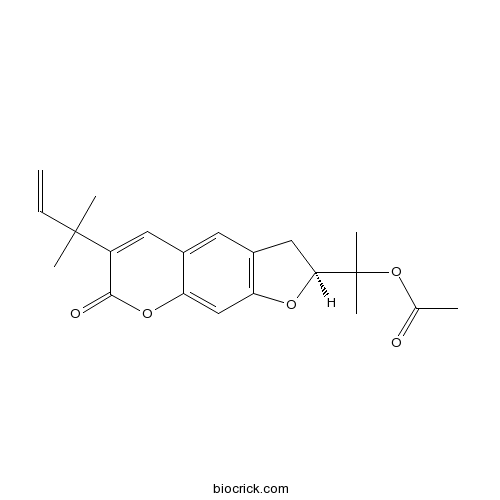
- Rutamarin
Catalog No.:BCN7509
CAS No.:14882-94-1
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 13164-05-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 442148 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H24O5 | M.Wt | 356.4 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-[(2S)-6-(2-methylbut-3-en-2-yl)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydrofuro[3,2-g]chromen-2-yl]propan-2-yl acetate | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)OC(C)(C)C1CC2=C(O1)C=C3C(=C2)C=C(C(=O)O3)C(C)(C)C=C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AWMHMGFGCLBSAY-SFHVURJKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H24O5/c1-7-20(3,4)15-9-13-8-14-10-18(21(5,6)26-12(2)22)24-16(14)11-17(13)25-19(15)23/h7-9,11,18H,1,10H2,2-6H3/t18-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

(+)-Rutamarin Dilution Calculator

(+)-Rutamarin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8058 mL | 14.0292 mL | 28.0584 mL | 56.1167 mL | 70.1459 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5612 mL | 2.8058 mL | 5.6117 mL | 11.2233 mL | 14.0292 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2806 mL | 1.4029 mL | 2.8058 mL | 5.6117 mL | 7.0146 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0561 mL | 0.2806 mL | 0.5612 mL | 1.1223 mL | 1.4029 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0281 mL | 0.1403 mL | 0.2806 mL | 0.5612 mL | 0.7015 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 7α-Galloyloxysweroside
Catalog No.:BCN9203
CAS No.:2222365-76-4
- Viburnumoside
Catalog No.:BCN9202
CAS No.:2222365-74-2
- 12-Hydroxyalbrassitriol
Catalog No.:BCN9201
CAS No.:2193060-23-8
- (Z)-ethyl cinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN9200
CAS No.:4192-77-2
- 5-Hydroxymethyl-2-furoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9199
CAS No.:6338-41-6
- 7β-Galloyloxysweroside
Catalog No.:BCN9198
CAS No.:2222365-75-3
- Dehydroherbarin
Catalog No.:BCN9197
CAS No.:36379-74-5
- Herbarin
Catalog No.:BCN9196
CAS No.:36379-67-6
- Euglobal Ia1
Catalog No.:BCN9195
CAS No.:77844-93-0
- Filicane-3β,4α,25-triol
Catalog No.:BCN9194
CAS No.:2361548-00-5
- Aflavazole
Catalog No.:BCN9193
CAS No.:2043963-70-6
- Primeverose
Catalog No.:BCN9192
CAS No.:26531-85-1
- 3,3-Dimethylacrylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9205
CAS No.:541-47-9
- O-Demethylstachartin C
Catalog No.:BCN9206
CAS No.:1219361-60-0
- Qingyangshengenin 3-O-α-L-cymaropyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-oleandropyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-cymaropyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-cymaropyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN9207
CAS No.:1808159-02-5
- Chimaphilin
Catalog No.:BCN9208
CAS No.:482-70-2
- Ethyl chlorogenate
Catalog No.:BCN9209
CAS No.:425408-42-0
- Jacaranone
Catalog No.:BCN9210
CAS No.:60263-07-2
- 6-O-(p-Hydroxybenzoyl)glucose
Catalog No.:BCN9211
CAS No.:202337-44-8
- 3"-O-Desmethylspinorhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN9212
CAS No.:2220243-41-2
- Loroglossin
Catalog No.:BCN9213
CAS No.:58139-22-3
- 3α-Cinnamoyloxy-9β,17-dihydroxy-ent-kaur-15-en-19-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9214
CAS No.:2186648-60-0
- 3'-O-Methyltaxifolin
Catalog No.:BCN9215
CAS No.:55812-91-4
- Acutumine
Catalog No.:BCN9216
CAS No.:17088-50-5
Rutamarin: Efficient Liquid-Liquid Chromatographic Isolation from Ruta graveolens L. and Evaluation of Its In Vitro and In Silico MAO-B Inhibitory Activity.[Pubmed:32527030]
Molecules. 2020 Jun 9;25(11). pii: molecules25112678.
Naturally occurring coumarins are a group of compounds with many documented central nervous system (CNS) activities. However, dihydrofuranocoumarins have been infrequently investigated for their bioactivities at CNS level. Within the frame of this study, an efficient liquid-liquid chromatography method was developed to rapidly isolate rutamarin from Ruta graveolens L. (Rutaceae) dichloromethane extract (DCM). The crude DCM (9.78 mg/mL) and rutamarin (6.17 M) were found to be effective inhibitors of human monoamine oxidase B (hMAO-B) with inhibition percentages of 89.98% and 95.26%, respectively. The inhibitory activity against human monoamine oxidase A (hMAO-A) for the DCM extract was almost the same (88.22%). However, for rutamarin, it significantly dropped to 25.15%. To examine the molecular interaction of rutamarin with hMAO- B, an in silico evaluation was implemented. A docking study was performed for the two enantiomers (R)-rutamarin and (S)-rutamarin. The (S)-rutamarin was found to bind stronger to the hMAO-B binging cavity.
Metabolite Profiling by Hyphenated Liquid Chromatographic Mass Spectrometric Technique (HPLC-DAD-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS) and Neurobiological Potential of Haplophyllum sahinii and H. vulcanicum Extracts.[Pubmed:31365785]
Chem Biodivers. 2019 Sep;16(9):e1900333.
In the current study, the ethanol extracts of flower, stem, and root parts of two endemic Turkish species, e. g., Haplophyllum sahinii O. Tugay & D. Ulukus and H. vulcanicum Boiss. & Heldr., were screened against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) associated with Alzheimer's disease as well as tyrosinase (TYR) linked to Parkinson's disease using ELISA microplate assay at 200 mug/mL. Among the extracts, the highest inhibition was caused by the stem extract of H. sahinii against BChE (IC50 =64.93+/-1.38 mug/mL). Consistently, all of the extracts were found to exert a selective inhibition towards BChE to some extent. It was only the root extract of H. vulcanicum that could inhibit AChE at low level (IC50 =203.18+/-5.33 mug/mL). None of the extracts displayed an inhibition over 50 % against TYR. Metabolite profiling of the extracts was achieved by a highly hyphenated liquid chromatographic mass spectrometric technique (HPLC-DAD-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS), which revealed the presence of furoquinoline (beta-fagarine, gamma-fagarine) and amide (tubasenicine, tubacetine) alkaloids; furano- (rutamarin), pyrano- (xanthyletine), and geranyloxy coumarins; phenylpropanoid (secoisolariciresinol), arylnaphthalene (mono-O-acetyldiphyllin apioside), and dibenzylbutyrolactone (kusunokinin, haplomyrfolin) lignans. Several important differences were observed between the extracts analyzed. beta-Fagarine was the major alkaloid in H. vulcanicum, whereas gamma-fagarine was present only in the roots of both Haplophyllum species; moreover, secoisolariciresinol and secoisolariciresinol dimethyl ether were the main lignans in the stems and flowers. This is the first study identifying ChE and TYR inhibitory effect and metabolic profiles of H. vulcanicum and H. sahinii.
Rutamarin, an Active Constituent from Ruta angustifolia Pers., Induced Apoptotic Cell Death in the HT29 Colon Adenocarcinoma Cell Line.[Pubmed:28808378]
Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Jul;13(Suppl 2):S179-S188.
BACKGROUND: Ruta angustifolia Pers. is a perennial herb that is cultivated worldwide, including Southeast Asia, for the treatment of various diseases as traditional medicine. OBJECTIVE: The purpose of the study was to identify an active principle of R. angustifolia and to investigate its effect on the HT29 cell death. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The methanol and fractionated extracts (hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, and water) of R. angustifolia Pers. were initially investigated for their cytotoxic activity against two human carcinoma cell lines (MCF7 and HT29) and a normal human colon fibroblast cell line (CCD-18Co) using sulforhodamine B cytotoxicity assay. Eight compounds including rutamarin were isolated from the active chloroform extract and evaluated for their cytotoxic activity against HT29 human colon carcinoma cell line and CCD-18Co noncancer cells. Further studies on the induction of apoptosis such as morphological examinations, biochemical analyses, cell cycle analysis, and caspase activation assay were conducted in rutamarin-treated HT29 cells. RESULTS: Rutamarin exhibited remarkable cytotoxic activity against HT29 cells (IC50 value of 5.6 muM) but was not toxic to CCD-18Co cells. The morphological and biochemical hallmarks of apoptosis including activation of caspases 3, 8, and 9 were observed in rutamarin-treated HT29 cells. These may be associated with cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 and G2/M checkpoints, which was also observed in HT29 cells. CONCLUSIONS: The present study describes rutamarin-induced apoptosis in the HT29 cell line for the first time and suggests that rutamarin has the potential to be developed as an anticancer agent. SUMMARY: Rutamarin was cytotoxic to HT29 colon cancer cells but exerted no damage to normal colon cellsRutamarin induced morphological and biochemical hallmarks of apoptosis in HT29 cellsRutamarin induced cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 and G2/M checkpoints in a dose-dependent manner in HT29 cellsRutamarin activated caspases 3, 8, and 9 in a dose-dependent manner in HT29 cells. Abbreviations used: ACN: Acetonitrile, ANOVA: One-way analysis of variance, BrdU: Bromodeoxyuridine, 13C-NMR: Carbon-13 Nuclear magnetic resonance, CAD: Caspase-activated endonuclease, CCD-18Co: Human colon normal, DLD1: Human Duke's type C colorectal adenocarcinoma, DMRT: Duncan's multiple range test, DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide, DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid, DR4/5: Death receptor 4/5 protein, EMEM: Eagle's minimum essential media, FBS: Fetal bovine serum, FITC Annexin V: Annexin V conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate, FITC-DEVD-FMK: Fluorescein isothiocyanate conjugate of caspase inhibitor Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-fluoromethyl ketone, FITC-IETD-FMK: Fluorescein isothiocyanate conjugate of caspase inhibitor Ile-Glu-Thr-Asp-fluoromethyl ketone, FITC-LEHD-FMK: Fluorescein isothiocyanate conjugate of caspase inhibitor Leu-Glu-His-Asp-fluoromethyl ketone, G0: Quiescent phase of cell cycle, G1: Gap 1 phase of cell cycle, G2: Gap 2 phase of cell cycle, GC-MS: Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, HeLa: Human cervical adenocarcinoma, HPLC: High performance liquid chromatography, HT29: Human colon adenocarcinoma, Huh7.5: Human hepatocellular carcinoma, IC50: Half maximal inhibitory concentration, KSHV: Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, M phase: Mitotic phase of cell cycle, MCF7: Human breast adenocarcinoma, NMR: Nuclear magnetic resonance, PBS: Phosphate-buffered saline, PI: Propidium iodide, RNase: Ribonuclease, rt: Retention time, S phase: Synthesis phase of cell cycle, SD: Standard deviation, SRB: Sulforhodamine B, TCA: Trichloroacetic acid, TLC: Thin layer chromatography, TNF-R1: Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 protein, TUNEL: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) dUTP nick-end labeling, UV: Ultraviolet.
Semisynthesis of (-)-Rutamarin Derivatives and Their Inhibitory Activity on Epstein-Barr Virus Lytic Replication.[Pubmed:28093914]
J Nat Prod. 2017 Jan 27;80(1):53-60.
(+)-Rutamarin inhibits EBV lytic DNA replication with an IC50 of 7.0 muM. (-)-Chalepin, a (-)-rutamarin derivative, was isolated from the whole plant of Ruta graveolens and used as a precursor of (-)-rutamarin. Altogether, 28 (-)-rutamarin derivatives were synthesized starting from (-)-chalepin. Of these, 16 compounds (2a-e, 3b-e, 3g, 4f, 4k, 4m-p) were found to be more potent against EBV lytic DNA replication than (-)-chalepin. Compounds 4m, 4n, and 4p exhibited IC50 values of 1.5, 0.32, and 0.83 muM and showed selectivity index values (SI) of 801, 211, and >120, respectively. Thus, compounds 4m, 4n, and 4p are considered promising leads for further laboratory investigation.
Chalepin: isolated from Ruta angustifolia L. Pers induces mitochondrial mediated apoptosis in lung carcinoma cells.[Pubmed:27729078]
BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Oct 12;16(1):389.
BACKGROUND: Cancer has been one of the leading causes of mortality in this era. Ruta angustifolia L. Pers has been traditionally used as an abortifacient, antihelmintic, emmenagogue and ophthalmic. In Malaysia and Singapore, the local Chinese community used it for the treatment of cancer. METHODS: In this study, the methanol and fractionated extracts (hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate and water) of R. angustifolia were tested for its cytotoxicity using the sulforhodamide (SRB) cytotoxicity assay against HCT-116, A549, Ca Ski and MRC5 cell lines. Chemical isolation was carried out by using the high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and the isolated compounds were tested for its cytotoxicity against A549 cell line. Cellular and nuclear morphological changes were observed in the cells using phase contrast microscopy and Hoechst/PI fluorescent staining. The externalisation of phosphatidylserine was observed through FITC-labelling Annexin V/PI assay whilst DNA fragmentation was observed through the TUNEL assay. Other indication of apoptosis occuring through the mitochondrial pathway were the attenuation of mitochondrial membrane potential and increase in ROS production. Activation of caspase 9 and 3 were monitored. Western blot analysis was done to show the expression levels of apoptotic proteins. RESULTS: The chloroform extract (without chlorophyll) exhibited the highest cytotoxic activity with IC50 of 10.1 +/- 0.15 mug/ml against A549 cell line. Further chemical investigation was thus directed to this fraction which led to the isolation of 12 compounds identified as graveoline, psoralen, kokusaginine, methoxysalen, bergapten, arborinine, moskachan B, chalepin, moskachan D, chalepensin, rutamarin and neophytadiene. Among these compounds, chalepin exhibited excellent cytotoxicity against A549 cell line with an IC50 value of 8.69 +/- 2.43 mug/ml (27.64 muM). In western blot analysis, expression of p53, truncated Bid, Bax and Bak while the anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2, survivin, XIAP, Bcl-XL,cFLIP decreased in a time-dependent manner when A549 cells were treated with 36 mug/ml of chalepin. In addition, the level of PARP was found to decrease. CONCLUSION: Hence these findings indicated that chalepin-induced cell death might involve the intrinsic mitochodrial pathway resulting in the upregulation of pro-apoptotic proteins and downregulation of anti-apoptotic proteins. Thus, chalepin could be an excellent candidate for the development of an anticancer agent.
Phytochemicals from Ruta graveolens Activate TAS2R Bitter Taste Receptors and TRP Channels Involved in Gustation and Nociception.[Pubmed:26501253]
Molecules. 2015 Oct 16;20(10):18907-22.
Ruta graveolens (rue) is a spontaneous plant in the Mediterranean area with a strong aroma and a very intense bitter taste, used in gastronomy and in folk medicine. From the leaves, stems and fruits of rue, we isolated rutin, rutamarin, three furanocoumarins, two quinolinic alkaloids, a dicoumarin and two long chain ketones. Bitter taste and chemesthetic properties have been evaluated by in vitro assays with twenty receptors of the TAS2R family and four TRP ion channels involved in gustation and nociception. Among the alkaloids, skimmianine was active as a specific agonist of T2R14, whereas kokusaginin did not activate any of the tested receptors. The furanocoumarins activates TAS2R10, 14, and 49 with different degrees of selectivity, as well as the TRPA1 somatosensory ion channel. Rutamarin is an agonist of TRPM5 and TRPV1 and a strong antagonist of TRPM8 ion channels.
Antiviral activity of topoisomerase II catalytic inhibitors against Epstein-Barr virus.[Pubmed:24821256]
Antiviral Res. 2014 Jul;107:95-101.
Herpesviruses require several cellular proteins for their lytic DNA replication including topoisomerase II (Topo II). Thus, Topo II could be an effective drug target against herpesviral infection. In this study, we examined several Topo II catalytic inhibitors for their potentials in blocking EBV replication and becoming efficacious antiviral agents. Topo II catalytic inhibitors in general exhibited marked inhibition of EBV lytic replication and minimal cytotoxicity. In particular, (+)-Rutamarin, with the best selectivity index (SI>63) among the inhibitors tested in this study, is effective in inhibiting EBV DNA replication and virion production but shows little adverse effect on cell proliferation, suggesting its potential to become an efficacious and safe drug for the treatment of human diseases associated with EBV infection.
Antiviral activity of (+)-rutamarin against Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus by inhibition of the catalytic activity of human topoisomerase II.[Pubmed:24295975]
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(1):563-73.
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is an etiological agent of several AIDS-associated malignancies, including Kaposi's sarcoma (KS), primary effusion lymphoma (PEL), and multicentric Castleman's disease (MCD). Its lytic replication cycle has been proven to be critical for the pathogenesis of KSHV-associated diseases. In KS lesions, lytic viral replication, production of virion particles, and reinfection of endothelial cells are essential to sustain the population of infected cells that otherwise would be quickly lost as spindle cells divide. Thus, antivirals that block KSHV replication could be a strategy in the treatment of KSHV-associated diseases. However, there is no effective anti-KSHV drug currently available. Our previous work showed that human topoisomerase II (Topo II) is indispensable for KSHV lytic replication and is suggested to be an effective target for antiviral drugs. Here, we report the discovery and characterization of a novel catalytic inhibitor of human Topo IIalpha, namely, (+)-Rutamarin. The binding mode of (+)-Rutamarin to the ATPase domain of human Topo IIalpha was established by docking and validated by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. More importantly, (+)-Rutamarin efficiently inhibits KSHV lytic DNA replication in BCBL-1 cells with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 1.12 muM and blocks virion production with a half-maximal antiviral effective concentration (EC50) of 1.62 muM. It possesses low cytotoxicity, as indicated by the selectivity index (SI) of 84.14. This study demonstrated great potential for (+)-Rutamarin to become an effective drug for treatment of human diseases associated with KSHV infection.
(+)-Rutamarin as a dual inducer of both GLUT4 translocation and expression efficiently ameliorates glucose homeostasis in insulin-resistant mice.[Pubmed:22384078]
PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31811.
Glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) is a principal glucose transporter in response to insulin, and impaired translocation or decreased expression of GLUT4 is believed to be one of the major pathological features of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Therefore, induction of GLUT4 translocation or/and expression is a promising strategy for anti-T2DM drug discovery. Here we report that the natural product (+)-Rutamarin (Rut) functions as an efficient dual inducer on both insulin-induced GLUT4 translocation and expression. Rut-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes exhibit efficiently enhanced insulin-induced glucose uptake, while diet-induced obese (DIO) mice based assays further confirm the Rut-induced improvement of glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in vivo. Subsequent investigation of Rut acting targets indicates that as a specific protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibitor Rut induces basal GLUT4 translocation to some extent and largely enhances insulin-induced GLUT4 translocation through PI3 kinase-AKT/PKB pathway, while as an agonist of retinoid X receptor alpha (RXRalpha), Rut potently increases GLUT4 expression. Furthermore, by using molecular modeling and crystallographic approaches, the possible binding modes of Rut to these two targets have been also determined at atomic levels. All our results have thus highlighted the potential of Rut as both a valuable lead compound for anti-T2DM drug discovery and a promising chemical probe for GLUT4 associated pathways exploration.
Application of chitin and chitosan as elicitors of coumarins and fluoroquinolone alkaloids in Ruta graveolens L. (common rue).[Pubmed:18211259]
Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2008 Oct;51(Pt 2):91-6.
Common rue (Ruta graveolens L.) accumulates various types of secondary metabolites, such as coumarins furanocoumarins, acridone and quinolone alkaloids and flavonoids. Elicitation is a tool extensively used for enhancing secondary-metabolite yields. Chitin and chitosan are examples of elicitors inducing phytoalexin accumulation in plant tissue. The present paper describes the application of chitin and chitosan as potential elicitors of secondary-metabolite accumulation in R. graveolens shoots cultivated in vitro. The simple coumarins, linear furanocoumarins, dihydrofuranocoumarins and fluoroquinolone alkaloids biosynthesized in the presence of chitin and chitosan were isolated, separated and identified. There was a significant increase in the growth rate of R. graveolens shoots in the presence of either chitin or chitosan. Moreover, the results of the elicitation of coumarins and alkaloids accumulated by R. graveolens shoots in the presence of chitin and chitosan show that both compounds induced a significant increase in the concentrations of nearly all the metabolites. Adding 0.01% chitin caused the increase in the quantity (microg/g dry weight) of coumarins (pinnarin up to 116.7, rutacultin up to 287.0, bergapten up to 904.3, isopimpinelin up to 490.0, psoralen up to 522.2, xanhotoxin up to 1531.5 and rutamarin up to 133.7). The higher concentration of chitosan (0.1%) induced production of simple coumarins (pinnarin up to 116.7 and rutacultin up to 287.0), furanocoumarins (bergapten up to 904.3, isopimpinelin up to 490.0, psoralen up to 522.2, xanhotoxin up to 1531.5) and dihydrofuranocoumarins (chalepin up to 18 and rutamarin up to 133.7). Such a dramatic increase in the production of nearly all metabolites suggests that these compounds may be participating in the natural resistance mechanisms of R. graveolens. The application of chitin- and chitosan-containing media may be considered a promising prospect in the biotechnological production of xanthotoxin, isopimpinelin, psoralen, chalepin or methoxylated dictamnine derivatives.
Identification of Ruta graveolens L. metabolites accumulated in the presence of abiotic elicitors.[Pubmed:18052337]
Biotechnol Prog. 2008 Jan-Feb;24(1):128-33.
The study aimed to elucidate the effects of benzothiadiazole (BTH) and saccharin on the biosynthesis of simple coumarins, linear furanocoumarins, dihydrofuranocoumarins, and furoquinolone alkaloids in shoots of R. graveolens cultivated in vitro. The biosynthesized metabolites were analyzed and identified by GC-MS and by comparison of Kovats indices. Eight coumarin metabolites were identified: bergapten, chalepin, isopimpinelin, pinnarin, psoralen, rutacultin, rutamarin, and xanthotoxin, and also four alkaloids: dictamnine, gamma-fagarine, skimmianine, and kokusaginine. Each of the tested BTH concentrations induced a significant production of furanocoumarins and furoquinolone alkaloids. The use of saccharin also increased the production of bergapten, isopimpinelin, pinnarin, psoralen, and xanthotoxin several times.
Effective biotic elicitation of Ruta graveolens L. shoot cultures by lysates from Pectobacterium atrosepticum and Bacillus sp.[Pubmed:17968510]
Biotechnol Lett. 2008 Mar;30(3):541-5.
Growth of Ruta graveolens shoots was induced when Bacillus sp. cell lysates were added to the culture medium. Elicitation of coumarin by this lysate was also very effective; the concentrations of isopimpinelin, xanthotoxin and bergapten increased to 610, 2120 and 1460 microg g(-1) dry wt, respectively. It also had a significant effect on the production of psoralen and rutamarin (680 and 380 microg g(-1) dry wt) and induced the biosynthesis of chalepin, which was not detected in the control sample, up to 47 microg g(-1) dry wt With lysates of the Pectobacterium atrosepticum, their effect on growth was not so significant and had no effect on the induction of coumarin accumulation. But elicitation with this lysate was much more effective for inducing the production of furoquinolone alkaloids; the concentrations of gamma-fagarine, skimmianine, dictamnine and kokusaginine rose to 99, 680, 172 and 480 microg g(-1) dry wt, respectively.
Bioactive coumarins from Boenninghausenia sessilicarpa.[Pubmed:17365191]
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2007 Jan-Feb;9(1):59-65.
Bioassay guided fractionation of Boenninghausenia sessilicarpa (Rutaceae) resulted in the isolation of a new dimeric coumarin glucoside 9'-methoxyl rutarensin (1) and a cytotoxic compound rutamarin (4), as well as an antivirus component leptodactylone (8), together with six known coumarins. Their structures were elucidated by 1D- and 2D NMR spectroscopy and ESI-MS analyses, respectively. Rutamarin (4) showed significant inhibitory activities against A-549, Bel-7402, HepG-2 and HCT-8 tumour cell lines with IC50s of 1.318, 2.082, 2.306 and 2.497 microg/ml. In addition, leptodactylone (8) showed potent protective activity on cells infected by SARS-CoV with ratio of 60% at 100 microg/ml.
[Studies on lactone constituents from Boennighausenia sessilicarpa Levl].[Pubmed:2816386]
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 1989;24(4):260-3.
Two compounds have been isolated from the ether extract of Boennighausenia sessilicarpa Levl. On the basis of physico-chemical constants, IR, NMR and MS, they were identified as shijiaocaolactone A (I) and rutamarin (II), the former being a new compound.


