Pravastatin sodiumHMG-CoA reductase inhibitor,highly selective and competitive CAS# 81131-70-6 |
- Clopidogrel
Catalog No.:BCC2497
CAS No.:120202-66-6
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

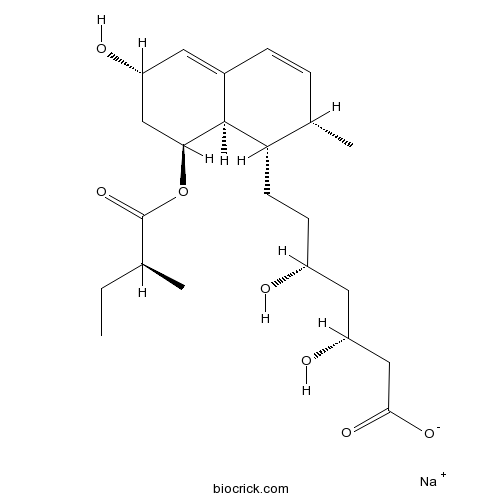
Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 81131-70-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16759173 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H35NaO7 | M.Wt | 446.51 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Eptastatin sodium | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (223.96 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : ≥ 50 mg/mL (111.98 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | sodium;(3R,5R)-7-[(1S,2S,6S,8S,8aR)-6-hydroxy-2-methyl-8-[(2S)-2-methylbutanoyl]oxy-1,2,6,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate | ||
| SMILES | CCC(C)C(=O)OC1CC(C=C2C1C(C(C=C2)C)CCC(CC(CC(=O)[O-])O)O)O.[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VWBQYTRBTXKKOG-IYNICTALSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H36O7.Na/c1-4-13(2)23(29)30-20-11-17(25)9-15-6-5-14(3)19(22(15)20)8-7-16(24)10-18(26)12-21(27)28;/h5-6,9,13-14,16-20,22,24-26H,4,7-8,10-12H2,1-3H3,(H,27,28);/q;+1/p-1/t13-,14-,16+,17+,18+,19-,20-,22-;/m0./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Water-soluble, competitive inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. Potently blocks cholesterol synthesis in vivo (Ki~ 1 nM) and displays cardioprotective properties. |

Pravastatin sodium Dilution Calculator

Pravastatin sodium Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2396 mL | 11.198 mL | 22.3959 mL | 44.7918 mL | 55.9898 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4479 mL | 2.2396 mL | 4.4792 mL | 8.9584 mL | 11.198 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.224 mL | 1.1198 mL | 2.2396 mL | 4.4792 mL | 5.599 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0448 mL | 0.224 mL | 0.4479 mL | 0.8958 mL | 1.1198 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0224 mL | 0.112 mL | 0.224 mL | 0.4479 mL | 0.5599 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Pravastatin sodium is a high selective inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme-A (HMG-CoA) reductase of 44.1nM [1].
Pravastatin is a competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase. It has shown to reduce the level of plasma LDL both in animals and humans through inhibiting cellular cholesterol synthesis. Pravastatin was reported to reduce cellular cholesterol synthesis in three types of macrophages including J-774 A.1 macrophage-like cell line, human monocyte derived macrophages (HMDM) and mouse peritoneal macrophages (MPM) with IC50 values of 0.08, 6.3 and 7.8μg/ml, respectively [2].
Besides the benefit in cardiovascular disease prevention, pravastatin also has efficacy of preventing tumor growth in some degree. However, it has shown that the normal hepatocytes are more sensitive to pravastatin than the tumor cells since pravastatin is selectively taken up by OATP1B1 which is exclusively expressed in normal hepatocytes [3].
References:
[1] Bolego C, Poli A, Cignarella A, Catapano AL, Paoletti R. Novel statins: pharmacological and clinical results. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2002 May;16(3):251-7.
[2] Keidar S, Aviram M, Maor I, Oiknine J, Brook JG. Pravastatin inhibits cellular cholesterol synthesis and increases low density lipoprotein receptor activity in macrophages: in vitro and in vivo studies. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;38(6):513-9.
[3] Menter DG, Ramsauer VP, Harirforoosh S, Chakraborty K, Yang P, Hsi L, Newman RA, Krishnan K. Differential effects of pravastatin and simvastatin on the growth of tumor cells from different organ sites. PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28813.
- Cilastatin sodium
Catalog No.:BCC7457
CAS No.:81129-83-1
- (Z)-Lachnophyllum lactone
Catalog No.:BCN4746
CAS No.:81122-95-4
- N-Nonyldeoxynojirimycin
Catalog No.:BCC7752
CAS No.:81117-35-3
- Racecadotril
Catalog No.:BCC4614
CAS No.:81110-73-8
- Clarithromycin
Catalog No.:BCC9219
CAS No.:81103-11-9
- Cisapride
Catalog No.:BCC4207
CAS No.:81098-60-4
- Pravastatin
Catalog No.:BCC4141
CAS No.:81093-37-0
- Kauniolide
Catalog No.:BCC5313
CAS No.:81066-45-7
- EUK 134
Catalog No.:BCC4317
CAS No.:81065-76-1
- Methyl 4-prenyloxycinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN7520
CAS No.:81053-49-8
- 4-Hydroxy-4-(methoxycarbonylmethyl)cyclohexanone
Catalog No.:BCN1346
CAS No.:81053-14-7
- Rhodamine B
Catalog No.:BCN7215
CAS No.:81-88-9
- RR-src
Catalog No.:BCC6956
CAS No.:81156-93-6
- Imiloxan hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6875
CAS No.:81167-22-8
- Apatinib
Catalog No.:BCC5099
CAS No.:811803-05-1
- Boc-D-Tyr(2-Br-Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3464
CAS No.:81189-61-9
- Panaxynol
Catalog No.:BCN3833
CAS No.:81203-57-8
- L-741,626
Catalog No.:BCC6886
CAS No.:81226-60-0
- 15-Deoxoeucosterol
Catalog No.:BCN4348
CAS No.:81241-53-4
- ent-9-Hydroxy-15-oxo-16-kauren-19-oic acid beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN1345
CAS No.:81263-96-9
- ent-6,11-Dihydroxy-15-oxo-16-kauren-19-oic acid beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN1344
CAS No.:81263-97-0
- ent-6,9-Dihydroxy-15-oxo-16-kauren-19-oic acid beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN1343
CAS No.:81263-98-1
- ent-6,9-Dihydroxy-15-oxo-16-kauren-19-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1342
CAS No.:81264-00-8
- D-AP7
Catalog No.:BCC6559
CAS No.:81338-23-0
Formulation and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Microcapsules Containing Pravastatin Sodium Using Rats.[Pubmed:27595040]
Scientifica (Cairo). 2016;2016:7623193.
Pravastatin sodium has a cholesterol lowering agent. It has shorter half-life and undergoes first-pass metabolism. Frequent dose is required in case of conventional dosage form. The purpose of the study is to formulate and evaluate microcapsules containing Pravastatin sodium by complex with cholestyramine resins coated with Eudragit RLPO and Eudragit RSPO polymers for achieving control release. Complexation of drug on resin was carried out by batch method. Microencapsulation was carried out by nonaqueous solvent evaporation method. Pharmacokinetic studies were done by using rats. The intermediate stability studies were carried out on the most satisfactory formulations. FTIR, X-ray diffraction, and DSC spectra of drug, drug-resinates, and polymers revealed no chemical interaction. The % DEE and % yield were observed for formulations of f1 to f7 that were varied from 97.1 +/- 0.8 to 98.9 +/- 0.5% and 95.0 +/- 3.25 to 98.8 +/- 7.1%, respectively. Most satisfactory formulation, f6, showed drug release up to 72.6%. No changes in % DEE and % CDR were observed after stability studies. Microcapsules of f6 formulation achieved best performance regarding in vitro drug release and from pharmacokinetic evaluation mean residence time was found to be 6.3 h, thus indicated, Pravastatin sodium microcapsules were released and absorbed slowly over a prolonged period of time.
A laboratory data-based evaluation of the efficacy and safety of generic pravastatin sodium for long-term use.[Pubmed:26819746]
J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2015 Dec 18;2:1.
BACKGROUND: Increasing the use of generic drugs may reduce the growing healthcare spending. Nevertheless, in Japan, the generic drug market share remains low compared to that of European countries and the United States, mainly because of the general distrust of generic drugs. To address this problem, we retrospectively evaluated the efficacy and safety of the long-term use of generic Pravastatin sodium in a study from January 2008 to December 2011. METHODS: Patients receiving generic Pravastatin sodium for >/=15 months were defined as long-term users and were included in the study, totaling 595 out of 1337 patients. Efficacy assessment was based on the total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) plasma levels. Safety assessment was based on the aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), creatine phosphokinase (CPK), gamma-glutamyl transferase (gamma-GTP), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), total-bilirubin (T-Bil), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum creatinine (Scr), and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) plasma levels. The patients' reasons for discontinuing generic Pravastatin sodium were obtained from the electronic medical records. RESULTS & DISCUSSION: No significant difference in the laboratory data was observed between short-term and long-term users, except for significantly lower ALT levels in the long-term users than in the short-term users. No liver dysfunction was observed. Although 37 patients discontinued the study possibly owing to drug-related adverse events, we considered these events unrelated to generic Pravastatin sodium. CONCLUSIONS: This study shows that the long-term use of generic Pravastatin sodium is effective and safe, and may help dispel the concerns about generic drugs.
Duodenum-triggered delivery of pravastatin sodium: II. Design, appraisal and pharmacokinetic assessments of enteric surface-decorated nanocubosomal dispersions.[Pubmed:27094305]
Drug Deliv. 2016 Nov;23(9):3266-3278.
CONTEXT: Pravastatin sodium (PVS) is a freely water-soluble HMG-CoA inhibitor that suffers from instability at gastric pH, extensive first pass metabolism, short elimination half-life (1-3 h) and low oral bioavailability (18%). OBJECTIVE: To overpower these drawbacks and to maximize drug absorption at its main site of absorption at the duodenum, enteric surface-coated PVS-loaded nanocubosomal dispersions were presented. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Glyceryl monooleate (GMO)-based dispersions were developed by the fragmentation or the liquid precursor methods using Pluronic(R) F127 or Cremophor(R) EL as surfactants. As a challenging enteric-coating approach, the promising dispersions were surface-coated via lyophilization with Eudragit(R) L100-55; a duodenum-targeting polymer. The drug content, particle size, zeta potential, morphology and release studies of PVS-loaded dispersions were evaluated before and after surface-coating. Compared to an aqueous PVS solution, the pharmacokinetics of the best achieved system (E-F8) was evaluated (UPLC-MS/MS) in rats. RESULTS: The enteric surface-coated nanocubosomal dispersions were more or less spherical in shape and showed high drug-loading, negative zeta potential values and fine-tuned biphasic drug-release patterns characterized by retarded (2 h) and sustained (10 h) phases in pH 1.2 and pH 6.8, respectively. E-F8 system showed significantly (p< 0.05) higher oral bioavailability, delayed Tmax and prolonged MRT0-infinity following oral administration in rats. CONCLUSIONS: The duodenum-triggering potential and the controlled-release characteristics of the best achieved system for smart PVS delivery were revealed.
Design of fixed dose combination and physicochemical characterization of enteric-coated bilayer tablet with circadian rhythmic variations containing telmisartan and pravastatin sodium.[Pubmed:28330645]
Int J Pharm. 2017 May 15;523(1):343-356.
The aim of this study was to investigate a fixed dose combination (FDC) of telmisartan (TEL) and Pravastatin sodium (PRA) in enteric-coated bilayer tablets, which was designed for once-daily bedtime dose in order to match circadian rhythmic variations of hypertension and cholesterol synthesis and optimize the patient friendly dosing treatment. Due to the poor aqueous solubility of TEL, ternary solid dispersions (SD) consisting of TEL, polyethylene glycol 6000 (PEG 6000) and magnesium oxide (MgO) were designed to enhance its dissolution rate in intestinal fluid. MgO was added as an effective alkalizer to maintain the high microenvironmental pH of the saturated solution in the immediate vicinity of TEL particles because TEL is known to be ionizable but poorly soluble in intestinal fluid. In contrast, PRA is known to be very unstable in low pH conditions. In the SD system, TEL was present in an amorphous structure and formed an intermolecular hydrogen bonding with MgO, giving complete drug release without precipitation in intestinal fluid. In addition, the amount of hydrophilic carrier (PEG 6000) was also a factor. In the design of tablet formulation, the diluents and superdisintegrants could play a key role in release profiles. Then, to fulfill the unmet needs of the two model drugs and match circadian rhythmic variations of hypertension and cholesterol synthesis, enteric-coated bilayer tablet consisting of TEL SD and PRA was finally prepared using Acryl-EZE((R)) as an enteric coating material. Prior to enteric coating, a seal coating layer (Opadry((R)), 2% weight gains) was firstly introduced to separate the core bilayer tablet from the acidic enteric coating polymers to avoid premature degradation. Dissolution profiles of finished tablets revealed that enteric-coated bilayer tablets with 6% weight gains remained intact in acidic media (pH 1.0) for 2h and then released drugs completely within 45min after switching to the intestinal media (pH 6.8). It was observed that enteric-coated bilayer tablets were stable during 3 month under the accelerated condition of 40 degrees C/75% RH. The delayed drug release and bedtime dosage regimen using enteric-coated bilayer tablet containing TEL and PRA, matching the circadian rhythms of hypertension and hyperlipidemia can provide therapeutic benefits for elderly patients in terms of maximizing the therapeutic effects.
Hydrophilicity/lipophilicity: relevance for the pharmacology and clinical effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors.[Pubmed:9509899]
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1998 Jan;19(1):26-37.
The recent development of specific competitive inhibitors of the hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase such as lovastatin, simvastatin, pravastatin and fluvastatin has provided an important new and effective approach to the treatment of hyperlipidaemia and atherosclerosis. These agents are designed to be hepatoselective because the primary site of cholesterol synthesis is the liver and peripheral inhibition of cholesterol synthesis would be more likely to cause adverse drug effects. In this review, Bettina Hamelin and Jacques Turgeon discuss how specific physico-chemical and pharmacological properties (first-pass effect or carrier-mediated uptake) confer hepatoselectivity to either lipophilic or hydrophilic HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors.


