MDL 72527Polyamine oxidase (PAO) inhibitor CAS# 93565-01-6 |
- Acetyl-Calpastatin (184-210) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC2350
CAS No.:123714-50-1
- CA 074
Catalog No.:BCC1141
CAS No.:134448-10-5
- PD 151746
Catalog No.:BCC5485
CAS No.:179461-52-0
- Odanacatib (MK-0822)
Catalog No.:BCC1197
CAS No.:603139-19-1
- E-64-c
Catalog No.:BCC3588
CAS No.:76684-89-4
- SID 26681509
Catalog No.:BCC2362
CAS No.:958772-66-2
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 93565-01-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3035046 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C12H22Cl2N2 | M.Wt | 265.23 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water and to 75 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | N,N'-bis(buta-2,3-dienyl)butane-1,4-diamine;dihydrochloride | ||
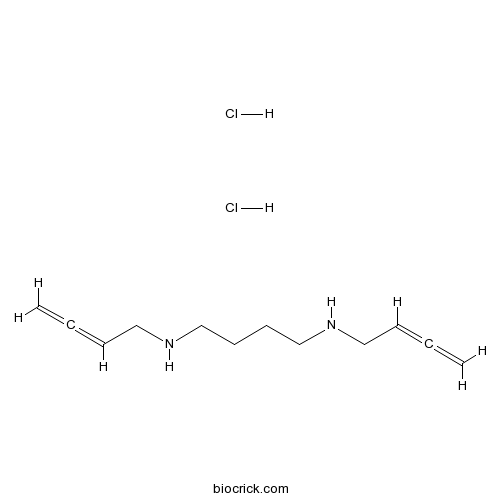
| SMILES | C=C=CCNCCCCNCC=C=C.Cl.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ITVRWVVFVHINOH-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H20N2.2ClH/c1-3-5-9-13-11-7-8-12-14-10-6-4-2;;/h5-6,13-14H,1-2,7-12H2;2*1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Polyamine oxidase (POA) inhibitor. Does not inhibit monoamine oxidase or D-Amino acid oxidase. Displays anticancer and neuroprotective activity in vivo. |

MDL 72527 Dilution Calculator

MDL 72527 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.7703 mL | 18.8516 mL | 37.7031 mL | 75.4063 mL | 94.2578 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7541 mL | 3.7703 mL | 7.5406 mL | 15.0813 mL | 18.8516 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.377 mL | 1.8852 mL | 3.7703 mL | 7.5406 mL | 9.4258 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0754 mL | 0.377 mL | 0.7541 mL | 1.5081 mL | 1.8852 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0377 mL | 0.1885 mL | 0.377 mL | 0.7541 mL | 0.9426 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Euphorbia factor L7a
Catalog No.:BCN3784
CAS No.:93550-94-8
- TH-237A
Catalog No.:BCC5378
CAS No.:935467-97-3
- (4->2)-Abeo-16-hydroxycleroda-2,13-dien-15,16-olide-3-al
Catalog No.:BCN7498
CAS No.:935293-70-2
- 2-Iodomelatonin
Catalog No.:BCC6772
CAS No.:93515-00-5
- Glimepiride
Catalog No.:BCC2109
CAS No.:93479-97-1
- Karavilagenin D
Catalog No.:BCN4480
CAS No.:934739-29-4
- Cobimetinib (racemate)
Catalog No.:BCC1492
CAS No.:934662-91-6
- Cobimetinib (R-enantiomer)
Catalog No.:BCC1493
CAS No.:934660-94-3
- Cobimetinib
Catalog No.:BCC1491
CAS No.:934660-93-2
- 8-Deacetylyunaconitine
Catalog No.:BCN7609
CAS No.:93460-55-0
- TAK-901
Catalog No.:BCC2180
CAS No.:934541-31-8
- Glucoliquiritin
Catalog No.:BCN6760
CAS No.:93446-18-5
- AZD1480
Catalog No.:BCC2191
CAS No.:935666-88-9
- BIX 01294
Catalog No.:BCC1131
CAS No.:935693-62-2
- AR-42 (OSU-HDAC42)
Catalog No.:BCC2161
CAS No.:935881-37-1
- Oprozomib (ONX-0912)
Catalog No.:BCC1146
CAS No.:935888-69-0
- 5-(6-Hydroxybenzofuran-2-yl)-2-(3-methylbut-1-enyl)benzene-1,3-diol
Catalog No.:BCN1304
CAS No.:936006-11-0
- Daphnenone
Catalog No.:BCN3229
CAS No.:936006-13-2
- cAMPS-Sp, triethylammonium salt
Catalog No.:BCC8081
CAS No.:93602-66-5
- TG101209
Catalog No.:BCC2198
CAS No.:936091-14-4
- TG101348 (SAR302503)
Catalog No.:BCC2190
CAS No.:936091-26-8
- ACET
Catalog No.:BCC7462
CAS No.:936095-50-0
- Ajuganipponin A
Catalog No.:BCN3660
CAS No.:936323-13-6
- PCI-32765 Racemate
Catalog No.:BCC5124
CAS No.:936563-87-0
Cytotoxicity of spermine oxidation products to multidrug resistant melanoma M14 ADR2 cells: sensitization by the MDL 72527 lysosomotropic compound.[Pubmed:19639169]
Int J Oncol. 2009 Sep;35(3):485-98.
It has been confirmed that multidrug resistant (MDR) human melanoma cells are more sensitive than their wild-type counterparts to H2O2 and aldehydes, the products of bovine serum amine oxidase (BSAO)-catalyzed oxidation of spermine. The metabolites formed by BSAO and spermine are more toxic than exogenous H2O2 and acrolein, even though their concentration is lower during the initial phase of incubation due to their more gradual release than the exogenous products. Both wild-type and MDR cells, after pre-treatment with MDL 72527, an inactivator of polyamine oxidase and a lysosomotropic compound, show to be sensitized to subsequent exposure to BSAO/spermine. Evidence of ultrastructural aberrations and acridine orange release from lysosomes is presented in this work that is in favor of the permeabilization of the lysosomal membrane as the major cause of sensitization by MDL 72527. Owing to its lysosomotropic effect, pre-treatment with MDL 72527 amplifies the ability of the metabolites formed from spermine by oxidative deamination to induce cell death. Since it is conceivable that combined treatment with a lysosomotropic compound and BSAO/spermine would be effective against tumor cells, it is of interest to search for such novel compounds, which might be promising for application in a therapeutic setting.
Toxicity of enzymatic oxidation products of spermine to human melanoma cells (M14): sensitization by heat and MDL 72527.[Pubmed:16962187]
Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Oct;1763(10):1040-50.
In situ formation of cytotoxic metabolites by an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is a recent approach in cancer chemotherapy. We demonstrate that multidrug resistant human melanoma cells (M14 ADR) are more sensitive than the corresponding wild type cells (M14 WT) to hydrogen peroxide and aldehydes, the products of bovine serum amine oxidase (BSAO)-catalyzed oxidation of spermine. Hydrogen peroxide was mainly responsible for the loss of cell viability. With about 20%, the aldehydes formed from spermine contribute also to cytotoxicity. Elevation of temperature from 37 degrees C to 42 degrees C decreased survival of both cell lines by about one log unit. Pre-treatment with N1,N4-bis(2,3-butadienyl)-1,4-butanediamine (MDL 72527), a lysosomotropic compound, sensitized cells to toxic spermine metabolites. MDL 72527 (at 300 microM) produced in M14 cells numerous cytoplasmic vacuoles which, however, disappeared by 24 h, even in the presence of the drug. Mitochondrial damage, as observed by transmission electron microscopy, correlated better with the cytotoxic effects of the treatment than vacuole formation. Since the release of lysosomal enzymes causes oxidative stress and apoptosis, we suggest that the lysosomotropic effect of MDL 72527 is the major reason for its sensitizing effect.
Effect of Lysosomotropic Polyamineoxidase Inhibitor MDL-72527 on Platelet Activation.[Pubmed:27160671]
Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(5):1695-702.
BACKGROUND/AIMS: The polyamine oxidase inhibitor MDL-72527 (N1,N4-bis(2,3-butadienyl)-1,4-butanediamine) were expected to increase the abundance of spermine, a powerful inhibitor of platelet activation. Nothing is known, however, on the sensitivity of platelet function and survival to MDL-72527 exposure. The present study thus explored whether MDL-72527 modifies function and survival of platelets without and with platelet activation by collagen related peptide (CRP). METHODS: Platelets isolated from wild-type mice were exposed for 30 minutes to MDL-72527 (100 microM) with or without subsequent activation with CRP (2-5 microg/ml). Flow cytometry was employed to estimate cytosolic Ca2+-activity ([Ca2+]i) from Fluo-3 fluorescence, platelet degranulation from P-selectin abundance, integrin activation from alphaIIbbeta3 integrin abundance, generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) from DCFDA fluorescence, phospholipid scrambling of the cell membrane from annexin-V-binding, platelet volume from forward scatter and aggregation utilizing staining with CD9-APC and CD9-PE. RESULTS: In the absence of CRP, exposure of platelets to MDL-72527 did not significantly modify [Ca2+]i, P-selectin abundance, alphaIIbbeta3 integrin abundance, ROS, annexin-V-binding, and forward scatter. The addition of 2-5 microg/ml CRP was followed by significant increase of [Ca2+]i, P-selectin abundance, alphaIIbbeta3 integrin activation, ROS abundance, annexin-V-binding, and aggregation as well as a significant decrease of forward scatter, all effects significantly blunted or virtually abolished in the presence of MDL-72527. CONCLUSIONS: MDL-72527 is a powerful inhibitor of platelet activation, apoptosis and aggregation.
MDL 72527 and spermine oxidation products induce a lysosomotropic effect and mitochondrial alterations in tumour cells.[Pubmed:17371275]
Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Apr;35(Pt 2):343-8.
Cytotoxic products of polyamines generated in situ by an enzyme-catalysed reaction may be useful as a new avenue in combating cancer. This study demonstrated that MDR (multidrug-resistant) cancer cells (colon adenocarcinoma and melanoma) are significantly more sensitive than the corresponding WT (wild-type) ones to H(2)O(2) and aldehydes, the products of BSAO (bovine serum amine oxidase)-catalysed oxidation of spermine. Moreover, cytotoxicity was considerably greater when the treatment was carried out at 42 degrees C than at 37 degrees C. TEM (transmission electron microscopy) observations showed major ultrastructural alterations of the mitochondria. These were more pronounced in MDR than in WT cells. After treatment with BSAO/spermine, a higher mitochondrial membrane depolarization and an increased mitochondrial activity in drug-resistant cells were observed.
A small molecule polyamine oxidase inhibitor blocks androgen-induced oxidative stress and delays prostate cancer progression in the transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate model.[Pubmed:19773450]
Cancer Res. 2009 Oct 1;69(19):7689-95.
High levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) present in human prostate epithelia are an important etiologic factor in prostate cancer (CaP) occurrence, recurrence, and progression. Androgen induces ROS production in the prostate by a yet unknown mechanism. Here, to the best of our knowledge, we report for the first time that androgen induces an overexpression of spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase, the rate-limiting enzyme in the polyamine oxidation pathway. As prostatic epithelia produce a large excess of polyamines, the androgen-induced polyamine oxidation that produces H2O2 could be a major reason for the high ROS levels in the prostate epithelia. A small molecule polyamine oxidase inhibitor N,N'-butanedienyl butanediamine (MDL 72,527 or CPC-200) effectively blocks androgen-induced ROS production in human CaP cells, as well as significantly delays CaP progression and death in animals developing spontaneous CaP. These data show that polyamine oxidation is not only a major pathway for ROS production in prostate, but inhibiting this pathway also successfully delays CaP progression.
Effects of MDL 72527, a specific inhibitor of polyamine oxidase, on brain edema, ischemic injury volume, and tissue polyamine levels in rats after temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion.[Pubmed:9930751]
J Neurochem. 1999 Feb;72(2):765-70.
The possible effects of the polyamine interconversion pathway on tissue polyamine levels, brain edema formation, and ischemic injury volume were studied by using a selective irreversible inhibitor, MDL 72527, of the interconversion pathway enzyme, polyamine oxidase. In an intraluminal suture occlusion model of middle cerebral artery in spontaneously hypertensive rats, 100 mg/kg MDL 72527 changed the brain edema formation from 85.7 +/- 0.3 to 84.5 +/- 0.9% in cortex (p < 0.05) and from 79.9 +/- 1.7 to 78.4 +/- 2.0% in subcortex (difference not significant). Ischemic injury volume was reduced by 22% in the cortex (p < 0.05) and 17% in the subcortex (p < 0.05) after inhibition of polyamine oxidase by MDL 72527. There was an increase in tissue putrescine levels together with a decrease in spermine and spermidine levels at the ischemic site compared with the nonischemic site after ischemia-reperfusion injury. The increase in putrescine levels at the ischemic cortical and subcortical region was reduced by a mean of 45% with MDL 72527 treatment. These results suggest that the polyamine interconversion pathway has an important role in the postischemic increase in putrescine levels and that blocking of this pathway can be neuroprotective against neuronal cell damage after temporary focal cerebral ischemia.


