H-Arg(NO2)-OHCAS# 2149-70-4 |
- Hydroxyfasudil
Catalog No.:BCC1635
CAS No.:105628-72-6
- chroman 1
Catalog No.:BCC1480
CAS No.:1273579-40-0
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- Hydroxyfasudil hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1636
CAS No.:155558-32-0
- H-1152 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1616
CAS No.:871543-07-6
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
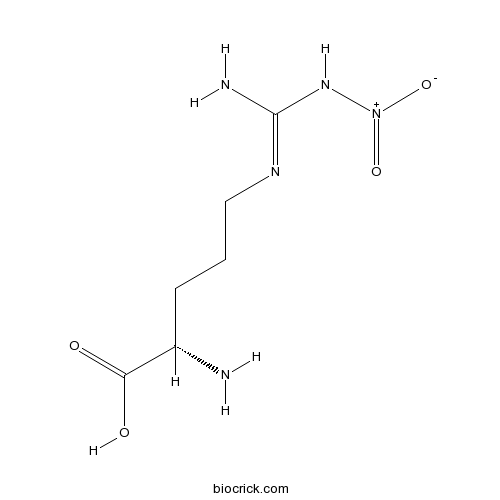
| Cas No. | 2149-70-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 440005 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C6H13N5O4 | M.Wt | 219.2 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 5 mM in water | ||
| SMILES | C(CC(C(=O)O)N)CN=C(N)N[N+](=O)[O-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MRAUNPAHJZDYCK-BYPYZUCNSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C6H13N5O4/c7-4(5(12)13)2-1-3-9-6(8)10-11(14)15/h4H,1-3,7H2,(H,12,13)(H3,8,9,10)/t4-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | NO synthase inhibitor. |

H-Arg(NO2)-OH Dilution Calculator

H-Arg(NO2)-OH Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.562 mL | 22.8102 mL | 45.6204 mL | 91.2409 mL | 114.0511 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9124 mL | 4.562 mL | 9.1241 mL | 18.2482 mL | 22.8102 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4562 mL | 2.281 mL | 4.562 mL | 9.1241 mL | 11.4051 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0912 mL | 0.4562 mL | 0.9124 mL | 1.8248 mL | 2.281 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0456 mL | 0.2281 mL | 0.4562 mL | 0.9124 mL | 1.1405 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
H-Arg(NO2)-OH
- 2-Deacetyltaxachitriene A
Catalog No.:BCN7415
CAS No.:214769-96-7
- AMT hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6823
CAS No.:21463-31-0
- (+)-Syringaresinol
Catalog No.:BCN7496
CAS No.:21453-69-0
- 1400W dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7057
CAS No.:214358-33-5
- 16alpha-Hydroxybauerenol
Catalog No.:BCN7724
CAS No.:214351-30-1
- Rosamultic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3516
CAS No.:214285-76-4
- Demethylsuberosin
Catalog No.:BCN6508
CAS No.:21422-04-8
- 5,7-dimethoxy-2,2-dimethylchromene
Catalog No.:BCN8030
CAS No.:21421-66-9
- N-Benzylphthalimide
Catalog No.:BCC9096
CAS No.:2142-01-0
- Picrotin
Catalog No.:BCC8233
CAS No.:21416-53-5
- 1-Decarboxy-3-oxo-ceanothic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4924
CAS No.:214150-74-0
- 26-Deoxycimicifugoside
Catalog No.:BCN2906
CAS No.:214146-75-5
- Agrimonolide
Catalog No.:BCN4925
CAS No.:21499-24-1
- Bruceine D
Catalog No.:BCN2894
CAS No.:21499-66-1
- 7,3',4'-Trihydroxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN4674
CAS No.:2150-11-0
- Protocatechuic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN3542
CAS No.:2150-43-8
- Methyl 2,6-dihydroxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCN3563
CAS No.:2150-45-0
- BMS 493
Catalog No.:BCC7697
CAS No.:215030-90-3
- Pemoline
Catalog No.:BCC5967
CAS No.:2152-34-3
- Betamethasone Valerate
Catalog No.:BCC3736
CAS No.:2152-44-5
- BMS 753
Catalog No.:BCC6031
CAS No.:215307-86-1
- Senampeline F
Catalog No.:BCN7804
CAS No.:71075-43-9
- Mianserin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1114
CAS No.:21535-47-7
- SU 5402
Catalog No.:BCC1970
CAS No.:215543-92-3
Enhancement of crystalloid cardioplegic protection by structural analogs of apelin-12.[Pubmed:25491175]
J Surg Res. 2015 Mar;194(1):18-24.
BACKGROUND: C-terminal fragments of adipokine apelin are able to attenuate myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury, but whether their effects are manifested during cardioplegic arrest remain obscure. This study was designed to evaluate the efficacy of natural apelin-12 (H-Arg-Pro-Arg-Leu-Ser-His-Lys-Gly-Pro-Met-Pro-Phe-OH, A12) and its novel structural analogs (H-(N(alpha)Me)Arg-Pro-Arg-Leu-Ser-His-Lys-Gly-Pro-Nle-Pro-Phe-OH, AI, and N(G)-Arg(N(G)NO2)-Pro-Arg-Leu-Ser-His-Lys-Gly-Pro-Nle-Pro-Phe-NH2, AII) as additives to crystalloid cardioplegia and explore benefits of early reperfusion with these peptides. METHODS: Isolated working rat hearts subjected to normothermic global ischemia and further reperfusion were used. St. Thomas' Hospital cardioplegic solution No.2 (STH2) containing 140 muM A12, AI, or AII was infused for 5 min at 25 degrees C before ischemia. In separate series, peptide administration was used for 5 min after ischemia. Metabolic state of the hearts was evaluated by myocardial content of high energy phosphates and lactate. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) leakage was assessed in myocardial effluent on early reperfusion. RESULTS: Addition of the peptides to STH2 enhanced functional and metabolic recovery of reperfused hearts compared with those of control (STH2 without additives). Cardioplegia with analog AII was the most effective and accompanied by a reduction of postischemic LDH leakage. Infusion of A12, AI, or AII after ischemia improved the majority indices of cardiac function and metabolic state of the heart by the end of reperfusion. However, the overall protective effect of the peptides was less than when they were added to STH2. CONCLUSIONS: Enhancement of apelin bioavailability may minimize myocardial I/R damage during cardiac surgery. Structural analogs of A12 are promising components of clinical cardioplegic solutions.
Synthesis, conformation, and biological activity of the carbohydrate-free vespulakinin 1.[Pubmed:3679673]
Int J Pept Protein Res. 1987 Aug;30(2):240-56.
Synthesis of the carbohydrate-free heptadecapeptide corresponding to the amino acid sequence of vespulakinin 1 was achieved by the continuous flow solid phase procedure on 4-hydroxymethyl-phenoxyacetyl-norleucyl derivatized Kieselguhr-supported polydimethylacrylamide resin, as well as by a combination of solid phase and solution syntheses. Preformed Fmoc-amino acid symmetrical anhydrides (Boc derivative for the N-terminal residue) were used for amine acylation in the continuous flow method. Serine and threonine were side chain protected as tert.-butyl ethers and the 4-methoxy-2, 3, 6,-trimethyl-benzenesulfonyl group was used for masking the guanidino function of arginine residues. After cleavage from the resin the final peptide was purified by ion exchange chromatography and characterized by amino acid analysis, high voltage electrophoresis, and RP-HPLC analysis. Alternatively, the protected N-terminal octapeptide, Fmoc-Thr(But)-Ala-Thr(But)-Thr(But)-Arg(Mtr)-Arg-(Mtr)-Arg(Mtr)-Gly-OH was prepared on 4-hydroxymethyl-3-methoxyphenoxyacetyl-norleucyl derivatized Kieselguhr-supported polydimethylacrylamide resin and the C-terminal nonapeptide H-Arg(NO2)-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg-(NO2)-OBzl was synthesized in solution through the fragment condensation method. The two fragments were coupled by the DCC-HOBt procedure and the resulting heptadecapeptide was deblocked and purified. The conformational features of the synthesized peptides are reported. Preliminary pharmacological experiments indicated that carbohydrate-free vespulakinin 1 is more potent than bradykinin in lowering rat blood pressure.
Synthesis and biological activity of [L-hydroxyproline]3-tuftsin analogue and its alpha- or beta-O-D-glucosylated derivatives.[Pubmed:8436445]
Int J Pept Protein Res. 1993 Jan;41(1):43-51.
Syntheses are described of the Hyp3-tuftsin analogue and of its derivatives alpha- or beta-O-glycosylated at the side chain function of the hydroxyproline residue. The carbohydrate-free tetrapeptide was prepared by reacting Z-Thr-Lys(Z)-OH with H-Hyp-Arg(NO2)-OBzl by the mixed anhydride procedure. In the synthesis of the alpha-glycosylated analogue the O-glycosyl amino acid was incorporated by reacting Boc-(Glc alpha+beta)Hyp-OH with H-Arg(NO2)-OBzl through the same procedure. The alpha-glucosylated dipeptide was isolated from the diastereomeric mixture, selectively deblocked, and acylated with Z-Thr-Lys(Z)-OH by the mixed anhydride procedure. In the preparation of the beta-glucosylated analogue the BOP procedure was used for reacting Boc-[Glc(Ac)4 beta]Hyp-OH with H-Arg(NO)2-OBzl was well as for the final coupling to tetrapeptide. Removal of protecting groups from crude tetrapeptides was achieved by catalytic hydrogenation. Deacetylation of the sugar moiety of the beta-glucosylated tetrapeptide was achieved by treatment with sodium methoxide in methanol. The synthetic compounds were isolated by ion exchange chromatography, and characterized by elemental analysis, amino acid analysis, optical rotation and proton NMR. Their capacity to evoke the release of interleukin 1 from mouse peritoneal macrophages and to modulate immunogenic activity of antigen-fed cells was evaluated, in comparison with tuftsin and rigin. All of the analogues were found to possess tuftsin-like activity.
Nitric oxide synthase: irreversible inhibition by L-NG-nitroarginine in brain in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:1710109]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 15;176(3):1136-41.
Inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) synthase activity by L-NG-Nitroarginine (NO2Arg) in brain preparations is not reversed by dialysis and is enhanced by prolonged preincubation of NO2Arg with the enzyme. By contrast, the weaker inhibition by NO2Arg of macrophage NO synthase is fully reversible. NO2Arg inhibits NO synthase activity in the brain after i.p. administration of 5 or 50 mg/kg. This in vivo inhibition also appears to be irreversible. The potent in vivo inhibition of central NO synthase by NO2Arg may facilitate studies of the physiologic function of NO as a neuronal messenger.


