FITCAS# 85951-63-9 |
- Cyclo (-RGDfK)
Catalog No.:BCC3590
CAS No.:161552-03-0
- BIO 1211
Catalog No.:BCC3945
CAS No.:187735-94-0
- Cilengitide
Catalog No.:BCC3942
CAS No.:188968-51-6
- TR-14035
Catalog No.:BCC4266
CAS No.:232271-19-1
- BIO 5192
Catalog No.:BCC8002
CAS No.:327613-57-0
- RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp) Peptides
Catalog No.:BCC5349
CAS No.:99896-85-2
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
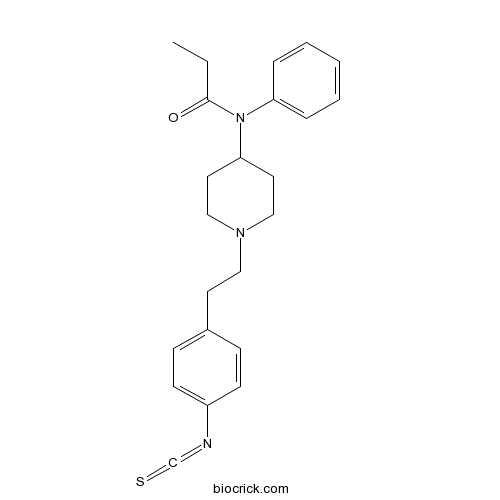
| Cas No. | 85951-63-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 84008 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H27N3OS | M.Wt | 393.55 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Fentanyl isothiocyanate | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in ethanol and to 10 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | N-[1-[2-(4-isothiocyanatophenyl)ethyl]piperidin-4-yl]-N-phenylpropanamide | ||
| SMILES | CCC(=O)N(C1CCN(CC1)CCC2=CC=C(C=C2)N=C=S)C3=CC=CC=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VDKBIFPJULZUPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H27N3OS/c1-2-23(27)26(21-6-4-3-5-7-21)22-13-16-25(17-14-22)15-12-19-8-10-20(11-9-19)24-18-28/h3-11,22H,2,12-17H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective and irreversible δ-opioid agonist (EC50 = 8 nM); acts by alkylating the receptor. |

FIT Dilution Calculator

FIT Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.541 mL | 12.7049 mL | 25.4097 mL | 50.8195 mL | 63.5243 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5082 mL | 2.541 mL | 5.0819 mL | 10.1639 mL | 12.7049 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2541 mL | 1.2705 mL | 2.541 mL | 5.0819 mL | 6.3524 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0508 mL | 0.2541 mL | 0.5082 mL | 1.0164 mL | 1.2705 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0254 mL | 0.127 mL | 0.2541 mL | 0.5082 mL | 0.6352 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- GR 125487 sulfamate
Catalog No.:BCC7142
CAS No.:859502-43-5
- AGN 205728
Catalog No.:BCC5418
CAS No.:859498-05-8
- Acetyl meldrum's acid
Catalog No.:BCC8805
CAS No.:85920-63-4
- 4-O-Methylhonokiol
Catalog No.:BCN8474
CAS No.:68592-15-4
- 6-Iodonordihydrocapsaicin
Catalog No.:BCC5860
CAS No.:859171-97-4
- Lincomycin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC9011
CAS No.:859-18-7
- prim-O-Glucosylangelicain
Catalog No.:BCN4409
CAS No.:85889-15-2
- 1,3-Dipropyl-8-phenylxanthine
Catalog No.:BCC6664
CAS No.:85872-53-3
- Marsdenoside F
Catalog No.:BCN4564
CAS No.:858360-61-9
- Vialinin A
Catalog No.:BCC2367
CAS No.:858134-23-3
- 3-O-Benzyl estrone
Catalog No.:BCC8638
CAS No.:858-98-0
- (-)-Quinpirole hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6917
CAS No.:85798-08-9
- BMS-690514
Catalog No.:BCC1430
CAS No.:859853-30-8
- Anemosapogenin
Catalog No.:BCN2454
CAS No.:85999-40-2
- Carbazole
Catalog No.:BCN6903
CAS No.:86-74-8
- Benzoyleneurea
Catalog No.:BCC8865
CAS No.:86-96-4
- Cyclovirobuxine
Catalog No.:BCN5965
CAS No.:860-79-7
- AZD7762
Catalog No.:BCC2555
CAS No.:860352-01-8
- Fmoc-Cys(Acm)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3473
CAS No.:86060-81-3
- Fmoc-Lys(Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3525
CAS No.:86060-82-4
- Fmoc-Asp-OBzl
Catalog No.:BCC3087
CAS No.:86060-83-5
- Fmoc-Gly-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3499
CAS No.:86060-85-7
- Fmoc-Ala-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3035
CAS No.:86060-86-8
- Fmoc-Val-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3571
CAS No.:86060-87-9
The FIT Game III: Reducing the Operating Expenses of a Game-Based Approach to Increasing Healthy Eating in Elementary Schools.[Pubmed:28375645]
Games Health J. 2017 Apr;6(2):111-118.
OBJECTIVE: Previously published versions of the healthy eating "FIT Game" were administered by teachers in all grades at elementary schools. The present study evaluated whether the game would retain its efficacy if teachers were relieved of this task; presenting instead all game materials on visual displays in the school cafeteria. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Participants were 572 children attending two Title 1 elementary schools (grades K-5). Following a no-intervention baseline period in which fruit and vegetable consumption were measured from food waste, the schools played the FIT Game. In the game, the children's vegetable consumption influenced events in a good versus evil narrative presented in comic book-formatted episodes in the school cafeteria. When daily vegetable-consumption goals were met, new FIT Game episodes were displayed. Game elements included a game narrative, competition, virtual currency, and limited player autonomy. The two intervention phases were separated by a second baseline phase (within-school reversal design). Simulation Modeling Analysis (a bootstrapping technique appropriate to within-group time-series designs) was used to evaluate whether vegetable consumption increased significantly above baseline levels in the FIT Game phases (P < 0.05). RESULTS: Vegetable consumption increased significantly from 21.3 g during the two baseline phases to 42.5 g during the FIT Game phases; a 99.9% increase. The Game did not significantly increase fruit consumption (which was not targeted for change), nor was there a decrease in fruit consumption. CONCLUSION: Labor-reductions in the FIT Game did not reduce its positive impact on healthy eating.
Mu-, delta- and kappa-opioid receptor-mediated inhibition of neurotransmitter release and adenylate cyclase activity in rat brain slices: studies with fentanyl isothiocyanate.[Pubmed:2906610]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep 13;154(2):169-78.
We investigated the effects of [D-Ala2,D-Leu5]enkephalin (DADLE). [D-Ala2,MePhe4,Gly-ol5]enkephalin (DAGO), [D-Pen2,D-Pen5]enkephalin (DPDPE) (0.01-1 microM) and bremazocine (0.001-0.3 microM) on the electrically evoked release of radiolabelled neurotransmitters and on the dopamine (DA)-stimulated cyclic AMP efflux from superfused rat brain slices. The differential inhibitory effects of these agonists on the evoked neurotransmitter release indicate that the opioid receptors mediating presynaptic inhibition of [3H]noradrenaline (NA, cortex), [14C]acetylcholine (ACh, striatum) and [3H]DA (striatum) release represent mu, delta and kappa receptors, respectively. In agreement with this classification, preincubation (60 min) of the slices with the delta-opioid receptor-selective irreversible ligand, fentanyl isothiocyanate (FIT, 0.01-1 microM), antagonized the inhibitory effects of DADLE and DPDPE on striatal [14C]ACh release only. On the other hand, the D-1 DA receptor-stimulated cyclic AMP efflux from striatal slices appeared to be inhibited by activation of mu as well as of delta receptors. In this case, the reversible mu antagonist, naloxone (0.1 microM), fully antagonized the inhibitory effect of the mu agonist, DAGO, without changing the effect of the delta agonist DPDPE but was ineffective as an antagonist in slices pretreated with FIT (1 microM). The inhibitory effect of DAGO on the electrically evoked [3H]NA release was antagonized by naloxone whether the receptors were irreversibly blocked by FIT or not. These data not only further support the existence of independent presynaptic mu-, delta- and kappa-opioid receptors in rat brain but also evidence strongly that mu and delta receptors mediating the inhibition of DA-sensitive adenylate cyclase could share a common binding site (for naloxone and FIT) and, therefore, may represent constituents of a functional opioid receptor complex.
Evidence that the delta-selective alkylating agent, fit, alters the mu-noncompetitive opiate delta binding site.[Pubmed:2991807]
Neuropeptides. 1985 Jun;6(3):227-37.
Considerable evidence supports the notion that the prototypic delta agonist [3H]D-ala2-D-leu5-enkephalin labels two binding sites on brain membranes in vitro. Recent studies have demonstrated that treatment of brain membranes with the delta-selective, site-directed, alkylating agent, FIT (Rice et al., Science 220, 314-316, 1983) results in a membrane preparation devoid of detectable higher affinity [3H]D-ala2-D-leu5-enkephalin binding sites, but contain residual lower affinity binding sites at which mu-ligands are apparent noncompetitive inhibitors (Rothman et al., Neuropeptides 4:210-215, 1984). In this paper we extend these data by showing that although FIT eliminates the higher affinity binding site, it also alters the properties of the residual lower affinity binding sites.
Irreversible ligands with high selectivity toward delta and mu opiate receptors.[Pubmed:6132444]
Science. 1983 Apr 15;220(4594):314-6.
Alkylating agents that display strong selectivity for opiate receptor types delta or mu were prepared by appropriate modification of the structures of the strong analgesics fentanyl, etonitazene, and endoethenotetrahydrooripavine. The availability of these substances should facilitate studies of the structural basis of receptor specificity and of the physiologic roles of these receptors.


