CyclovirobuxineCAS# 860-79-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

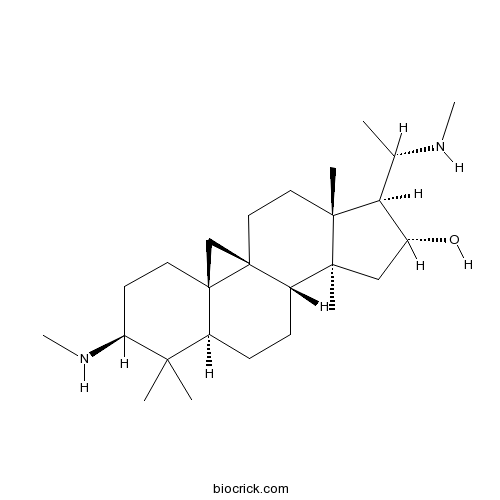
Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 860-79-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 260439 | Appearance | White cryst. |
| Formula | C26H46N2O | M.Wt | 402.66 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 20 mg/mL (49.66 mM) in Ethanol | ||
| SMILES | CC(C1C(CC2(C1(CCC34C2CCC5C3(C4)CCC(C5(C)C)NC)C)C)O)NC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GMNAPBAUIVITMI-ABNIRSKTSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H46N2O/c1-16(27-6)21-17(29)14-24(5)19-9-8-18-22(2,3)20(28-7)10-11-25(18)15-26(19,25)13-12-23(21,24)4/h16-21,27-29H,8-15H2,1-7H3/t16-,17+,18-,19-,20-,21-,23+,24-,25+,26-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Cyclovirobuxine D(CVB-D) has vasorelaxant effect, it has been widely used for treatment of cardiac insufficiency and arrhythmias in China, the antiarrhythmic and proarrhythmic potential of this drug might be concerned with prolongation of action potential duration and QT interval. CVB-D can induce autophagy in the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line by attenuating the phosphorylation of Akt and mTOR , CVB-D-induced autophagy and decrease in cell viability could be blocked by 3-methyladenine, a well-established autophagy inhibitor. |
| Targets | Nrf2 | Akt | mTOR |
| In vitro | Cyclovirobuxine D induces autophagy-associated cell death via the Akt/mTOR pathway in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.[Pubmed: 24758922]J Pharmacol Sci. 2014;125(1):74-82. Epub 2014 Apr 24.Autophagy is a highly regulated and multi-step biological process that serves to remove damaged cytoplasmic components and organelles. It has been suggested that the activation of autophagy may be a promising therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment by triggering cell death.
Comparison of the vasorelaxant effects of cyclovirobuxine D and its derivatives in rat aorta rings[Reference: WebLink]Chinese Journal of New Drugs, 2012, 21(3):240-5.To compare the vasorelaxant effects of Cyclovirobuxine D (CVB-D) and its derivatives in isolated rat thoracic aorta rings.
|
| In vivo | Beneficial effect of Cyclovirobuxine D on heart failure rats following myocardial infarction.[Pubmed: 21575690]Fitoterapia. 2011 Sep;82(6):868-77.The effect of Cyclovirobuxine D, an active ingredient from Buxus microphylla, was investigated in the potential prevention of cardiac dysfunction in rats with congestive heart failure.
|
| Kinase Assay | Experimental and theoretical investigation on the interaction between cyclovirobuxine D and human serum albumin.[Pubmed: 24691369]Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2014 Jul 15;128:552-8.Cyclovirobuxine D is an active compound extracted from the plant Buxux microphylla, and widely available as medications; however, its abuse may casts potential detrimental effects on human health. By using multispectroscopic techniques and molecular modeling, the interaction of Cyclovirobuxine D with human serum albumin was investigated. The fluorescence results manifested that static type was the operative mechanism for the interaction with human serum albumin. The structural investigation of the complexed HSA through CD, three-dimensional, FT-IR and synchronous fluorescence shown the polypeptide chain of HSA partially destabilizing. Docking studies revealed the molecule to be bound in the subdomain IIA. Finally, we investigated the distance between the bound ligand and Trp-214 of human serum albumin. |
| Cell Research | Cyclovirobuxine D Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy by Suppression of Oxidative Damage and Mitochondrial Biogenesis Impairment.[Pubmed: 26075032]Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:151972.The clinical application of doxorubicin (DOX) is compromised by its cardiac toxic effect. Cyclovirobuxine D (CVB-D) is a steroid alkaloid extracted from a traditional Chinese medicine, Buxus microphylla.
|
| Animal Research | Ameliorated effects of cyclovirobuxine D on oxidative stress and energy metabolism in experimental cardiac injured rats induced by sympathetic overactivity in vivo[Pubmed: 25566659]Zhong Yao Cai. 2014 Jul;37(7):1213-7.To investigate the ameliorated effect of CVB-D on oxidative stress and energy metabolism in experimental cardiac injuried rats induced by sympathetic overactivity in vivo.
|

Cyclovirobuxine Dilution Calculator

Cyclovirobuxine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4835 mL | 12.4174 mL | 24.8348 mL | 49.6697 mL | 62.0871 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4967 mL | 2.4835 mL | 4.967 mL | 9.9339 mL | 12.4174 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2483 mL | 1.2417 mL | 2.4835 mL | 4.967 mL | 6.2087 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0497 mL | 0.2483 mL | 0.4967 mL | 0.9934 mL | 1.2417 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0248 mL | 0.1242 mL | 0.2483 mL | 0.4967 mL | 0.6209 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Benzoyleneurea
Catalog No.:BCC8865
CAS No.:86-96-4
- Carbazole
Catalog No.:BCN6903
CAS No.:86-74-8
- Anemosapogenin
Catalog No.:BCN2454
CAS No.:85999-40-2
- BMS-690514
Catalog No.:BCC1430
CAS No.:859853-30-8
- FIT
Catalog No.:BCC7082
CAS No.:85951-63-9
- GR 125487 sulfamate
Catalog No.:BCC7142
CAS No.:859502-43-5
- AGN 205728
Catalog No.:BCC5418
CAS No.:859498-05-8
- Acetyl meldrum's acid
Catalog No.:BCC8805
CAS No.:85920-63-4
- 4-O-Methylhonokiol
Catalog No.:BCN8474
CAS No.:68592-15-4
- 6-Iodonordihydrocapsaicin
Catalog No.:BCC5860
CAS No.:859171-97-4
- Lincomycin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC9011
CAS No.:859-18-7
- prim-O-Glucosylangelicain
Catalog No.:BCN4409
CAS No.:85889-15-2
- AZD7762
Catalog No.:BCC2555
CAS No.:860352-01-8
- Fmoc-Cys(Acm)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3473
CAS No.:86060-81-3
- Fmoc-Lys(Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3525
CAS No.:86060-82-4
- Fmoc-Asp-OBzl
Catalog No.:BCC3087
CAS No.:86060-83-5
- Fmoc-Gly-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3499
CAS No.:86060-85-7
- Fmoc-Ala-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3035
CAS No.:86060-86-8
- Fmoc-Val-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3571
CAS No.:86060-87-9
- Fmoc-Leu-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3510
CAS No.:86060-88-0
- Fmoc-Ile-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3506
CAS No.:86060-89-1
- Fmoc-Pro-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3539
CAS No.:86060-90-4
- Fmoc-Phe-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3536
CAS No.:86060-92-6
- Fmoc-Tyr(tBu)-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3568
CAS No.:86060-93-7
Cyclovirobuxine D Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy by Suppression of Oxidative Damage and Mitochondrial Biogenesis Impairment.[Pubmed:26075032]
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:151972.
The clinical application of doxorubicin (DOX) is compromised by its cardiac toxic effect. Cyclovirobuxine D (CVB-D) is a steroid alkaloid extracted from a traditional Chinese medicine, Buxus microphylla. Our results showed that CVB-D pretreatment markedly attenuated DOX-induced cardiac contractile dysfunction and histological alterations. By using TUNEL assay and western blot analysis, we found that CVB-D pretreatment reduced DOX-induced apoptosis of myocardial cells and mitochondrial cytochrome c release to cytosol. CVB-D pretreatment ameliorated DOX-induced cardiac oxidative damage including lipid peroxidation and protein carbonylation and a decrease in the ratio of reduced glutathione (GSH) to oxidized glutathione (GSSG). Moreover, CVB-D was found to prevent DOX-induced mitochondrial biogenesis impairment as evidenced by preservation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1alpha) and nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF1), as well as mitochondrial DNA copy number. These findings demonstrate that CVB-D protects against DOX-induced cardiomyopathy, at least in part, by suppression of oxidative damage and mitochondrial biogenesis impairment.
Beneficial effect of Cyclovirobuxine D on heart failure rats following myocardial infarction.[Pubmed:21575690]
Fitoterapia. 2011 Sep;82(6):868-77.
The effect of Cyclovirobuxine D, an active ingredient from Buxus microphylla, was investigated in the potential prevention of cardiac dysfunction in rats with congestive heart failure. Heart failure was induced by left coronary artery occlusion and verified using echocardiography. Cyclovirobuxine D was administered for 30 days (0.5, 1.0 and 2.0mg/kg, ig) and mortality, cardiac function, hemodynamics, microcirculation, histology and ultrastructure assessments were observed. Results from the present study suggest that Cyclovirobuxine D is beneficial for heart failure induced by myocardial infarction and supports the potential for Cyclovirobuxine D as a new therapy for heart failure.
[Ameliorated effects of cyclovirobuxine D on oxidative stress and energy metabolism in experimental cardiac injured rats induced by sympathetic overactivity in vivo].[Pubmed:25566659]
Zhong Yao Cai. 2014 Jul;37(7):1213-7.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the ameliorated effect of CVB-D on oxidative stress and energy metabolism in experimental cardiac injuried rats induced by sympathetic overactivity in vivo. METHODS: SD rats were randomly divided into five groups as following: control group, model group, Vitamin E 150 mg/kg group, CVB-D low dose and high dose groups, respectively. The rat experimental cardiac injury model was established by exposed to norepinephrine (NE) 3 mg/kg by ip for 16 d. The drugs were administrated to rat for 16 d by ig. The body weight of rats were monitored during all of the experimental period. At the designing ending-time point the indexes were assayed as following: cardiac index, hydroxyproline, histopathologically examination, oxidative stress ( MDA, SOD, CAT, GSH-Px and T-AOC) and energy metabolism indicatricle ( Na+, K(+) -ATPase, and Ca2+, Mg(2+) -ATPase). RESULTS: After exposed with NE for 16 d, the rats of model group was appeared dysfunction of oxidative stress and energy metabolism such as decreasing body weight, increasing cardiac index and hydroxyproline in cardiac tissue, decreasing Na+, K(+) -ATPase and Ca(2+), Mg(2+) -ATPase activities, and deteriorating the oxidative stress. Treated with CVB-D could ameliorate all of the exacerbated indexes. CONCLUSION: CVB-D has protective effect against oxidative stress and energy metabolism in rats of experimental myocardial injury induced by sympathetic overactivity.
Cyclovirobuxine D induces autophagy-associated cell death via the Akt/mTOR pathway in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.[Pubmed:24758922]
J Pharmacol Sci. 2014;125(1):74-82. Epub 2014 Apr 24.
Autophagy is a highly regulated and multi-step biological process that serves to remove damaged cytoplasmic components and organelles. It has been suggested that the activation of autophagy may be a promising therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment by triggering cell death. In this study, we reported that Cyclovirobuxine D (CVB-D), an alkaloid component in a traditional Chinese herb, could induce autophagy in the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. CVB-D inhibited the viability of MCF-7 cells in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. Activation of autophagy was characterized by transmission electron microscopy, monodansylcadaverine staining, and expression of autophagy marker microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3). After CVB-D treatment, a clear accumulation of autophagosomes was observed accompanied with elevated LC3 fluorescent puncta. Western blot analysis revealed that CVB-D significantly promoted the conversion from LC3-I to LC3-II and the expression of autophagy-related protein 5 (ATG5), which are both essential for autophagosome formation. On the other hand, CVB-D-induced autophagy and decrease in cell viability could be blocked by 3-methyladenine, a well-established autophagy inhibitor. Moreover, CVB-D attenuated the phosphorylation of Akt and mTOR, two pivotal suppressors in autophagy pathways. These findings shed new light on the pharmacological actions and mechanism of CVB-D and may support the potential utility of autophagy inducers in cancer treatment.
Experimental and theoretical investigation on the interaction between cyclovirobuxine D and human serum albumin.[Pubmed:24691369]
Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2014 Jul 15;128:552-8.
Cyclovirobuxine D is an active compound extracted from the plant Buxux microphylla, and widely available as medications; however, its abuse may casts potential detrimental effects on human health. By using multispectroscopic techniques and molecular modeling, the interaction of Cyclovirobuxine D with human serum albumin was investigated. The fluorescence results manifested that static type was the operative mechanism for the interaction with human serum albumin. The structural investigation of the complexed HSA through CD, three-dimensional, FT-IR and synchronous fluorescence shown the polypeptide chain of HSA partially destabilizing. Docking studies revealed the molecule to be bound in the subdomain IIA. Finally, we investigated the distance between the bound ligand and Trp-214 of human serum albumin.


