Ch 55Potent RAR agonist CAS# 110368-33-7 |
- CGH 2466 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7338
CAS No.:1177618-54-0
- Istradefylline (KW-6002)
Catalog No.:BCC3798
CAS No.:155270-99-8
- 8-Aminoadenine
Catalog No.:BCC6108
CAS No.:28128-33-8
- Preladenant
Catalog No.:BCC1868
CAS No.:377727-87-2
- ANR 94
Catalog No.:BCC7815
CAS No.:634924-89-3
- Tozadenant
Catalog No.:BCC2011
CAS No.:870070-55-6
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 110368-33-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6184667 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H28O3 | M.Wt | 364.47 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in ethanol and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
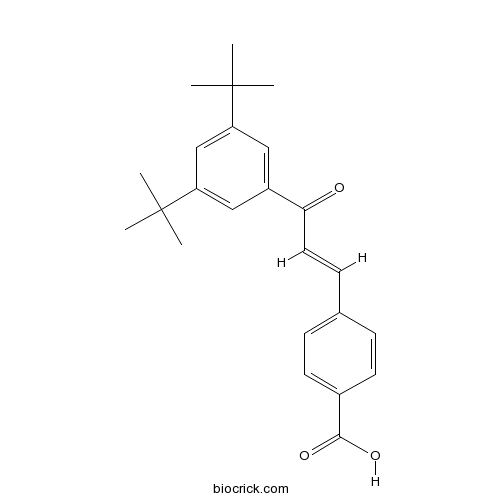
| Chemical Name | 4-[(E)-3-(3,5-ditert-butylphenyl)-3-oxoprop-1-enyl]benzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)C1=CC(=CC(=C1)C(=O)C=CC2=CC=C(C=C2)C(=O)O)C(C)(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FOUVTBKPJRMLPE-FMIVXFBMSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H28O3/c1-23(2,3)19-13-18(14-20(15-19)24(4,5)6)21(25)12-9-16-7-10-17(11-8-16)22(26)27/h7-15H,1-6H3,(H,26,27)/b12-9+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Highly potent synthetic retinoid that has high affinity for RAR-α and RAR-β receptors and low affinity for cellular retinoic acid binding protein (CRABP). Inhibits rabbit tracheal epithelial cell differentiation by inhibiting transglutaminase and increasing cholesterol sulfate (EC50 values are 0.02 and 0.03 nM respectively). Induces differentiation of embryonic carcinoma F9 and melanoma S91 cells (EC50 values are 0.26 and 0.5 nM respectively) and inhibits the induction of ornithine decarboxylase activity in 3T6 fibroblasts (EC50 = 1 nM). |

Ch 55 Dilution Calculator

Ch 55 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7437 mL | 13.7186 mL | 27.4371 mL | 54.8742 mL | 68.5928 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5487 mL | 2.7437 mL | 5.4874 mL | 10.9748 mL | 13.7186 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2744 mL | 1.3719 mL | 2.7437 mL | 5.4874 mL | 6.8593 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0549 mL | 0.2744 mL | 0.5487 mL | 1.0975 mL | 1.3719 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0274 mL | 0.1372 mL | 0.2744 mL | 0.5487 mL | 0.6859 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- S 32826
Catalog No.:BCC7678
CAS No.:1103672-43-0
- Bavisant dihydrochloride hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1404
CAS No.:1103522-80-0
- CGS 19755
Catalog No.:BCC6986
CAS No.:110347-85-8
- FD-838
Catalog No.:BCN6396
CAS No.:110341-78-1
- α-Bungarotoxin
Catalog No.:BCC7264
CAS No.:11032-79-4
- Santalol
Catalog No.:BCN8352
CAS No.:11031-45-1
- CI 966 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7010
CAS No.:110283-66-4
- Bacoside A
Catalog No.:BCC8127
CAS No.:11028-00-5
- Agnuside
Catalog No.:BCN5990
CAS No.:11027-63-7
- Amrubicin
Catalog No.:BCC3640
CAS No.:110267-81-7
- Ganoderenic acid E
Catalog No.:BCN8241
CAS No.:110241-23-1
- Ganoderic acid N
Catalog No.:BCN2438
CAS No.:110241-19-5
- 3-O-Methyltagitinin F
Catalog No.:BCN5991
CAS No.:110382-37-1
- 2,3-Dihydroheveaflavone
Catalog No.:BCN4019
CAS No.:110382-42-8
- Meclizine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC9017
CAS No.:1104-22-9
- Higenamine HCl
Catalog No.:BCN2831
CAS No.:11041-94-4
- Gelsemiol
Catalog No.:BCN5992
CAS No.:110414-77-2
- Dolastatin 10
Catalog No.:BCC4056
CAS No.:110417-88-4
- ML-7 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1770
CAS No.:110448-33-4
- BYK 204165
Catalog No.:BCC2449
CAS No.:1104546-89-5
- Crotastriatine
Catalog No.:BCN2101
CAS No.:11051-94-8
- 6,11-Di-O-acetylalbrassitriol
Catalog No.:BCN7273
CAS No.:110538-20-0
- Scutebarbatine F
Catalog No.:BCN5377
CAS No.:910099-78-4
- Albrassitriol
Catalog No.:BCN7274
CAS No.:110557-39-6
Clinicopathological features of serum TTV DNA-positive non-A-G liver diseases in Japan.[Pubmed:11551837]
Hepatol Res. 2001 Oct;21(2):169-180.
This study was undertaken to detect TTV DNA in serum samples from patients with non-A, non-B, non-C, non-E, and non-G (non-A-G) liver diseases and from blood donors, and to investigate the clinicopathological features of TTV infection including its prevalence and influence on liver disease. The study population consisted of 20 patients with non-A-G liver diseases (nine with chronic hepatitis (CH), six with liver cirrhosis (LC), and five with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), as well as 47 blood donors. Detection of TTV DNA was conducted with 200 &mgr;l of serum by the nested polymerase chain reaction. The detection rate of TTV DNA by subject category was Ch 55.9; LC 66.7; HCC 60%; and blood donors 28%. Regarding blood biochemistry, TTV DNA-positive patients tended to show higher levels of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase, as well as lower levels of platelet counts. Long-term follow-up revealed that TTV DNA-positive patients exhibited characteristic, multiple peaks of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels. The histologic findings in the livers of TTV DNA-positive patients with CH consisted of moderate necro-inflammatory reactions. In conclusion, it is possible that the TTV genotype 1b infection caused liver injury.
Functional studies of newly synthesized benzoic acid derivatives: identification of highly potent retinoid-like activity.[Pubmed:2836439]
J Cell Physiol. 1988 May;135(2):179-88.
Three newly synthesized benzoic acid derivatives (terephthalic acid anilides, chalcone carboxylic acid, and azobenzene carboxylic acid), with a certain structural similarity to retinoic acid, were examined for their retinoid-like bioactivity and their capacity to bind to cellular retinoid binding proteins. Two in vitro systems were used to evaluate their retinoid-like bioactivity: inhibition of adipose conversion of ST 13 murine preadipose cells and growth promotion of murine sarcoma virus (MSV)-transformed 3T3 cells in serum-free culture. All three compounds tested inhibited ST 13 adipose conversion at nanomolar concentrations in a manner similar to classical retinoids such as retinoic acid. The growth-stimulating activity of these compounds on MSV-transformed 3T3 cells was one to two orders of magnitude greater than that of retinoic acid. Simultaneous treatment with these compounds and retinoic acid produced only a barely detectable additive effect, suggesting a common mechanism of action, whereas unrelated mitogens, thrombin, and insulin worked synergistically in combination with retinoic acid. None of the compounds competed with retinol for binding to cellular retinol binding protein. However, two of the three competed with retinoic acid for binding to cellular retinoic acid binding protein. This study provides evidence that the newly synthesized compounds should be included among the retinoids and that their strong biological activity will undoubtedly contribute to the biological and medical application of retinoids.
New benzoic acid derivatives with retinoid activity: lack of direct correlation between biological activity and binding to cellular retinoic acid binding protein.[Pubmed:2884032]
Cancer Res. 1987 Jul 1;47(13):3523-7.
In this paper the biological activity of several newly synthesized benzoic acid derivatives of the Am- and Ch- series, which are structurally different from retinoic acid and arotinoids, was examined. These compounds inhibit squamous cell differentiation of rabbit tracheal epithelial cells in vitro as indicated by the inhibition of transglutaminase Type I and cholesterol 3-sulfate levels. In contrast to the inhibition of differentiation in rabbit tracheal cells, these compounds induce differentiation of mouse embryonal carcinoma F9 and human promyelocytic leukemia HL60 cells. The Am- and Ch- series of compounds also affect several parameters of cell proliferation. These agents are very potent inhibitors of growth of melanoma S91 cells and inhibit the induction of ornithine decarboxylase activity by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate in 3T6 fibroblasts. These results show that the Am- and Ch- derivatives elicit in several cell systems the same cellular responses as retinoic acid. We propose, therefore, that they exhibit mechanism(s) of action similar to those of retinoids. Comparison of the biological response with the binding capacity to the cellular retinoic acid-binding protein shows a lack of a direct correlation.


