Polygonum hydropiper
Polygonum hydropiper
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Polygonum hydropiper
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
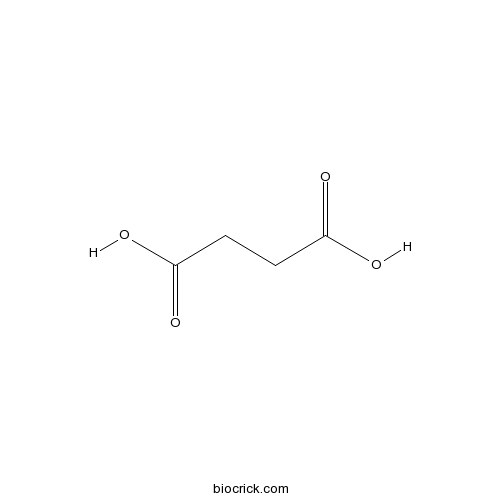
BCN5890
Succinic acid110-15-6
Instructions
-
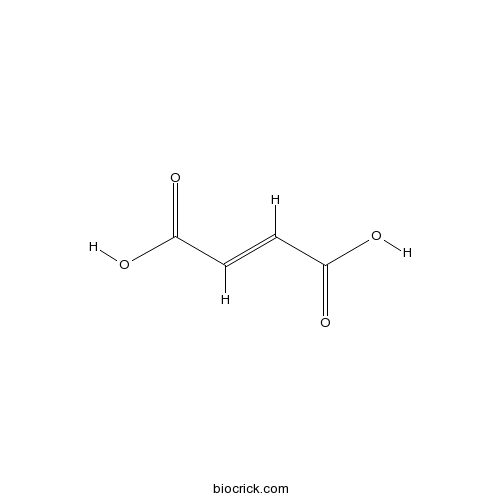
BCN5989
Fumaric acid110-17-8
Instructions
-
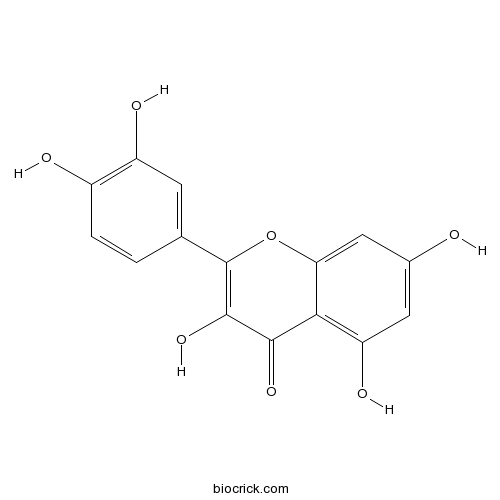
BCN6049
Quercetin117-39-5
Instructions
-
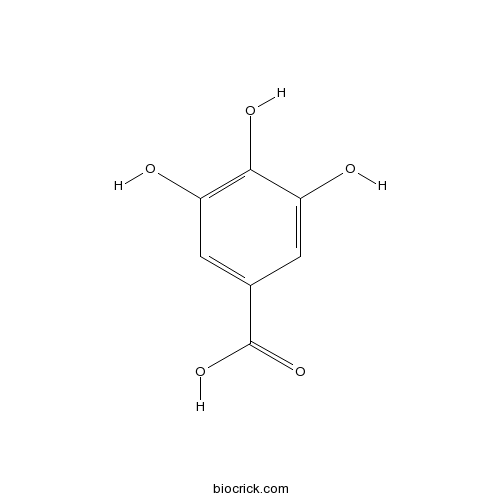
BCN1668
Gallic acid149-91-7
Instructions
-
BCN5906
Chlorogenic acid327-97-9
Instructions
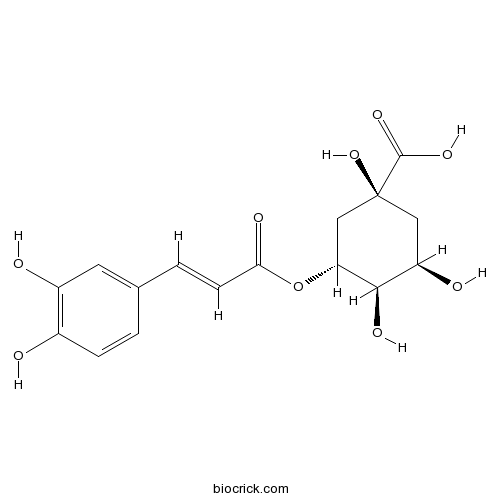
-
BCN5570
Hyperoside482-36-0
Instructions
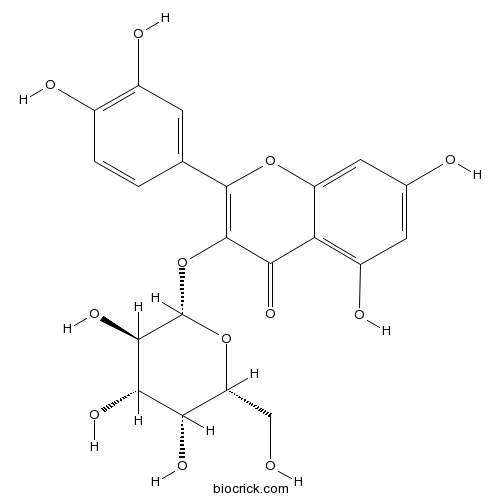
-
BCN5636
Taraxerone514-07-8
Instructions
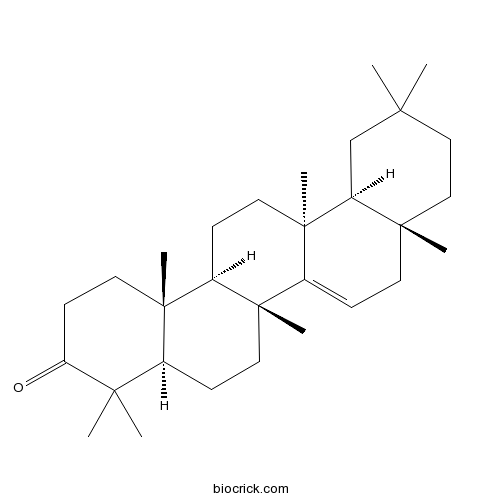
-
BCN5665
Quercitrin522-12-3
Instructions
Carotenoids, tocopherols, organic acids, charbohydrate and mineral content in different medicinal plant extracts.[Pubmed: 30074902]
Nettle (Urtica dioica L.), tansy (Tanacetum vulgare L.), bladder campion (Silene vulgaris (Moench) Garcke, waterpepper (Polygonum hydropiper L.), common centaury (Centaurium erythraea Pers.) and rose hip fruit (Rosa canina L. cv. Plovdiv 1) were used for preparation of different water extracts (infusion, decoction and microwave extract) and ethanol (tincture) extracts. Carotenoids (lutein, lycopene and β-carotene), tocopherols (α-, γ- and δ-), organic acids (ascorbic, malic, fumaric and citric), five macro- and three microelements, sugars and uronic acids content in the obtained extracts were analyzed. Among the investigated plants, stinging nettle, bladder campion and rose hip fruit were evaluated as most potential with respect to bioactive compounds and microelements. The results showed that the selected six medicinal plants and their extracts can be presented as sources of dietary fibers and micronutrients, which may encourage further application as food supplements and beverages as well as to motivate plant use as a dietary alternative in different foods. The present study is a first detailed analysis with respect to sugar content of decoction, infusion and tincture of S. vulgaris.


