Millettia pachycarpa
Millettia pachycarpa
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Millettia pachycarpa
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
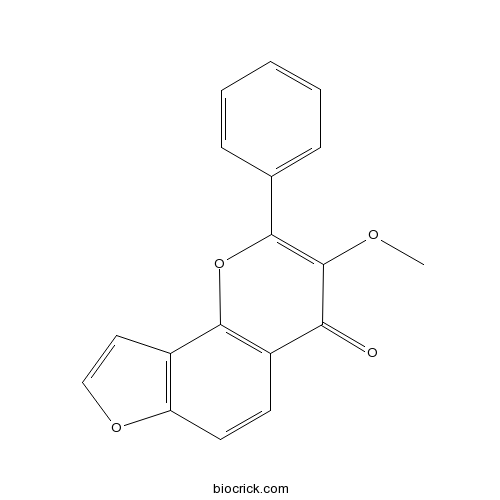
BCN8370
Karanjin521-88-0
Instructions
-
BCX1469
4-Hydroxylonchocarpin56083-03-5
Instructions

Millepachine, a potential topoisomerase II inhibitor induces apoptosis via activation of NF-κB pathway in ovarian cancer.[Pubmed: 27447570]
Millepachine (MIL) was a novel chalcone that was separated from Millettia pachycarpa Benth (Leguminosae). We found MIL induced apoptosis through activating NF-κB pathway both in SK-OV-3 and A2780S cells. Western blot showed that MIL increased the levels of IKKα, p-IKKα/β, p-IκBα and NF-κB (p65) proteins, and decreased the expression of IκBα protein. Immunohistochemistry analysis indicated that translocation of NF-κB into the nucleus increased in both ovarian cancer cells. EMSA assay proved MIL enhanced NF-κB DNA-binding activity in the nuclear. That specific NF-κB inhibitors alleviated MIL-induced apoptosis suggested NF-κB activation showed a pro-apoptotic function in SK-OV-3 and A2780S cells. Since NF-κB could be activated by double strand breaks and showed a pro-apoptotic function in the DNA damage response, SCGE assay and western blot revealed that MIL caused DNA strand breaks and significantly increased the level of p-ATM protein and further increased the levels of p-IKKα/β and NF-κB (p65) protein in SK-OV-3 and A2780S cells, while a specific ATM inhibitor could alleviated these effects. Moreover, Topoisomerase II drug screening kit and computer modeling assay were used to prove that MIL induced the production of linear DNA and inhibited the activity of topoisomerase II through binding with Topoisomerase II-Cleaved DNA complex to stabilize the complex. Taken together, our results identified that MIL exhibited anti-tumor activity through inhibiting topoisomerase II activity to induce tumor cells DNA damage, and MIL-activated NF-κB pathway showed a pro-apoptotic function in response to DNA damage.
Millettia pachycarpa exhibits anti-inflammatory activity through the suppression of LPS-induced NO/iNOS expression.[Pubmed: 25004885]
The present study was designed to investigate the in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activity of flavonoids isolated from Millettia pachycarpa Benth. The seeds of M. pachycarpa Benth were extracted with ethanol and subjected to chromatographic separation for the isolation of bioactive compounds. Their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic methods. The anti-inflammatory activity of the compounds was investigated by evaluating the inhibition ability of NO production, iNOS activity and iNOS protein expression induced by LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages in vitro and the carrageenan-induced hind paw edema model in vivo. Molecular docking simulation was also employed to obtain the binding parameters in the binding pocket of iNOS. Thirteen compounds (1-13) were isolated from Chinese herbal medicine M. pachycarpa Benth. Among them, 4-hydroxylonchocarpin (6) and deguelin (7) exhibited remarkable inhibitory rates of 66.5% and 57.7%, respectively, compared with that of 52.5% of indomethacin in LPS-induced macrophages cells. 4-hydroxylonchocarpin (6) with low toxicity (IC50 > 100 μm) exhibited better inhibitory effects to positive control of 1400W on iNOS activity at the concentration of 10 μm. Western blot assay revealed that 4-hydroxylonchocarpin (6) inhibited iNOS protein expression in RAW264.7 cells and molecular docking simulation showed that 4-hydroxylonchocarpin (6) fit well into the binding pocket of iNOS. In the carrageenan-induced paw edema model, our data revealed that the anti-inflammatory potential of 4-hydroxylonchocarpin (6) at 10 mg/kg showed comparable inhibitory ability to indomethacin at 5 h while a higher concentration of 4-hydroxylonchocarpin (6) at 50 mg/kg showed higher inhibitory activity than indomethacin, which was further confirmed by plasma levels of nitrite. The overall results suggest that 4-hydroxylonchocarpin (6) might be used as a potential therapeutic agent for inflammation-associated disorders.
Evidence of apoptosis in Raillietina echinobothrida induced by methanolic extracts of three traditional medicinal plants of Northeast India.[Pubmed: 23680183]
The therapeutic benefits of medicinal plants in terms of anthelmintic properties are known since time immemorial in India, particularly among natives of the Northeast India. However, only sporadic and scarce reports on scientific validation of these plants are available. The present study was conducted on the cestode Raillietina echinobothrida, to establish whether the anthelmintic activity of Potentilla fulgens, Alpinia nigra and Millettia pachycarpa was mediated by apoptosis or not. Light microscopic observation following MTT assay revealed the highest percentage of inhibition of viability among the worms by methanol extract of M. pachycarpa (89.33%), followed by A. nigra (65%) and P. fulgens (37%). Ultrastructural observations revealed swelling of mitochondria, disruption of mitochondrial membrane, vacuolization of mitochondria, appearance of apoptotic bodies in the cytoplasm, disintegration of nuclear membrane and nucleolus were very common throughout the tegument. DAPI stained specimens showed typical morphology of apoptosis, like nuclear condensation and fragmentation in the extracts treated parasites. A decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential was also recorded in the treated groups. Confirmatory TUNEL assay and DNA fragmentation assay of the extracts treated parasites also confirmed the apoptotic nature of cell death and is concluded to be responsible for paralysis and death of the parasite.
Millepachine, a novel chalcone, induces G2/M arrest by inhibiting CDK1 activity and causing apoptosis via ROS-mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in human hepatocarcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed: 23471882]
In this study, we reported millepachine (MIL), a novel chalcone compound for the first time isolated from Millettia pachycarpa Benth (Leguminosae), induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocarcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. In in vitro screening experiments, MIL showed strong antiproliferation activity in several human cancer cell lines, especially in HepG2 cells with an IC50 of 1.51 µM. Therefore, we chose HepG2 and SK-HEP-1 cells to study MIL's antitumor mechanism. Flow cytometry showed that MIL induced a G2/M arrest and apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. Western blot demonstrated that MIL-induced G2/M arrest was correlated with the inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 1 activity, including a remarkable decrease in cell division cycle (cdc) 2 synthesis, the accumulation of phosphorylated-Thr14 and decrease of phosphorylation at Thr161 of cdc2. This effect was associated with the downregulation of cdc25C and upmodulation of checkpoint kinase 2 in response to DNA damage. MIL also activated caspase 9 and caspase 3, and significantly increased the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 and stimulated the release of cytochrome c into cytosol, suggesting MIL induced apoptosis via mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Associated with those effects, MIL also induced the generation of reactive oxygen species. In HepG2 tumor-bearing mice models, MIL remarkably and dose dependently inhibited tumor growth. Treatment of mice with MIL (20mg/kg intravenous [i.v.]) caused more than 65% tumor inhibition without cardiac damage compared with 47.57% tumor reduction by 5mg/kg i.v. doxorubicin with significant cardiac damage. These effects suggested that MIL and its easily modified structural derivative might be a potential lead compound for antitumor drug.
Cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of constituents from Millettia pachycarpa Benth.[Pubmed: 22902267]
The aim of this study is to investigate the cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of constituents from the seeds of Millettia pachycarpa Benth. Fourteen compounds (1-14) including one novel chalcone (10) were isolated as active principles from Chinese herbal medicine M. pachycarpa Benth. Their structures were identified by using spectroscopic methods. All isolates were then evaluated for their cytotoxic effects against several cancer cell lines (HepG2, C26, LL2 and B16) with cisplatin as a positive control. And their apoptosis-inducing effects were tested against HeLa-C3 cells with taxol as a positive control. Both studies showed that compounds 1, 2, 7 and 10 demonstrated significant cytotoxic and apoptotic effects against cancer cells. Moreover, in the apoptosis assay the novel chalcone (10) showed strong apoptosis inducing effects at a concentration of 2μM within 36h. It was found to be the most potent apoptotic inducer of the compounds isolated from M. pachycarpa Benth.
Enrichment and isolation of barbigerone from Millettia pachycarpa Benth. using high-speed counter-current chromatography and preparative HPLC.[Pubmed: 20187026]
Enrichment of the anti-tumor compound barbigerone along with a rotenoid derivative from Millettia pachycarpa Benth. was performed by a two-step high-speed counter-current chromatography (HSCCC) separation process. In the first step, 155.8 mg of target fraction (Fra6) was obtained from 400 mg ethyl acetate extract of M. pachycarpa Benth. with an increase in barbigerone from 5.1 to 13% via HSCCC using a solvent system of n-hexane-ethyl acetate-methanol-water (5:4:5:3, v/v) under normal phase head to tail elution. HSCCC was repeated to eliminate the major contaminant in this initial fraction 6. After a separation time of 65 min, 22.1 mg barbigerone of 87.7% purity was obtained from Fra6 with the ternary solvent system of n-hexane-methanol-water (2:2:1, v/v) under normal phase elution. Finally, preparative HPLC was employed for the further isolation of barbigerone and the rotenoid derivative. The structures were confirmed by ESI-MS, (1)H NMR and (13)C NMR.
Ultrastructural observations on tegumental surface of Raillietina echinobothrida and its alterations caused by root-peel extract of Millettia pachycarpa.[Pubmed: 18767049]
Millettia pachycarpa Benth (Leguminosae) has a usage in traditional medicine system practiced among the Lushai tribes of Mizoram, a state in North East India, who customarily consume the aqueous extract of the root peel of the plant to get rid of intestinal worm infections. The crude ethanol, methanol, and acetone fractions of the plant were assayed against Raillietina echinobothrida, the intestinal cestode parasite of domestic fowl, to authenticate the putative anthelmintic efficacy and cestocidal potential in particular of the plants. In vitro exposure of the worm to the extract at a concentration of 25 mg/mL phosphate buffered saline (at 37 degrees C +/- 1 degrees C) revealed distortion and disruption of mitochondria, nucleus, nucleolus, nuclear membrane, basal lamina, and tegumental vacuolization in the distal cytoplasm leading to scar formation in the surface. The possible use of the plant as a potential anthelmintic against cestode parasite is discussed.


