Ipomoea batatas
Ipomoea batatas
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Ipomoea batatas
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
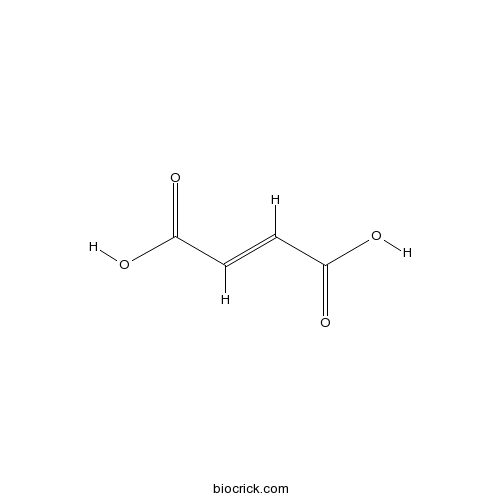
BCN5989
Fumaric acid110-17-8
Instructions
-
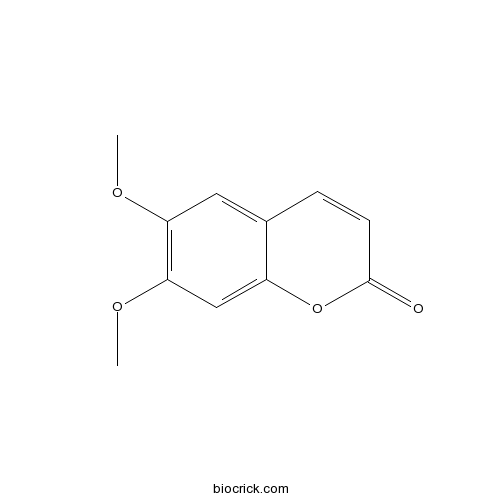
BCN6088
Scoparone120-08-1
Instructions
-
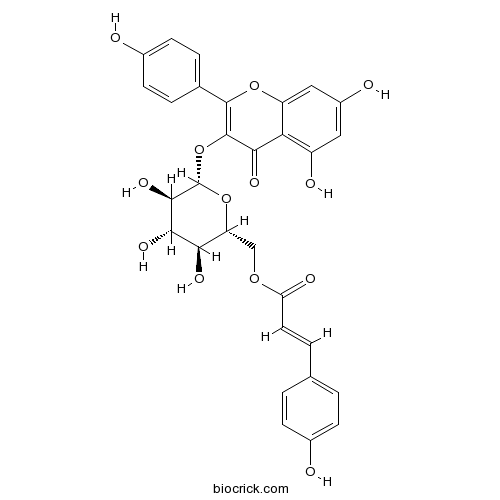
BCN4889
Tiliroside20316-62-5
Instructions
-
BCN5908
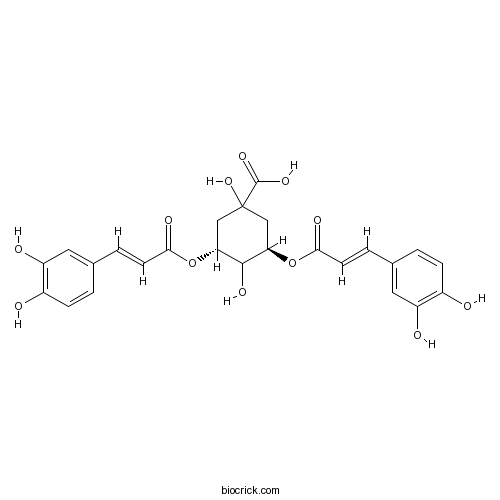
Isochlorogenic acid A2450-53-5
Instructions
-
BCN5549
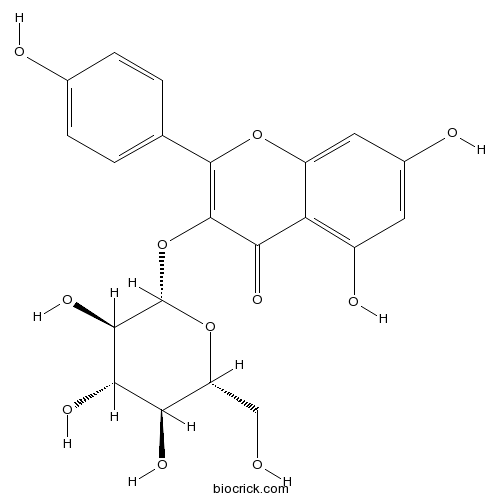
Astragalin480-10-4
Instructions
-
BCN1231
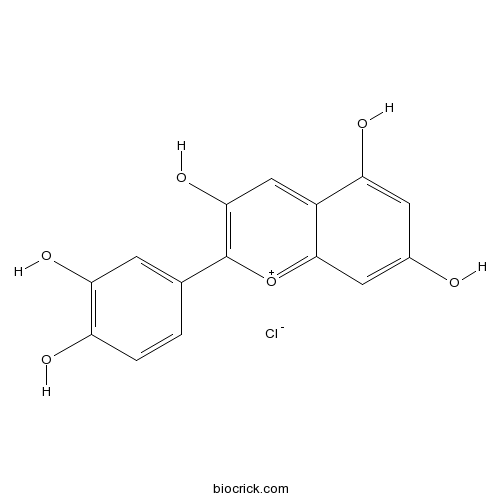
Cyanidin Chloride528-58-5
Instructions
-
BCN8390
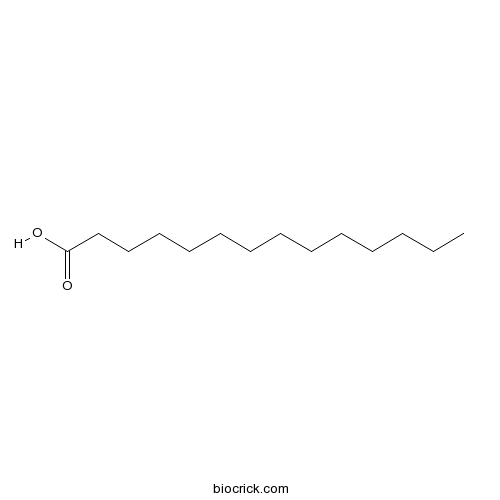
Myristic acid544-63-8
Instructions
-
BCN1230
Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside chloride7084-24-4
Instructions
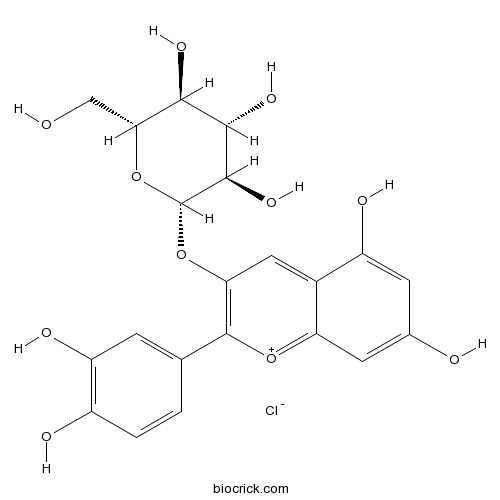
-
BCN4965
Beta-Carotene7235-40-7
Instructions
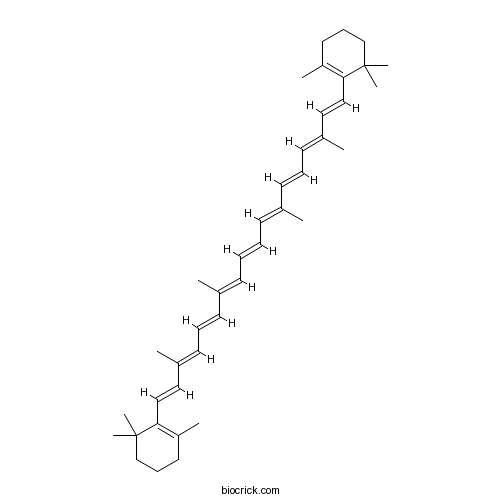
-
BCN4450
Neochlorogenic acid906-33-2
Instructions
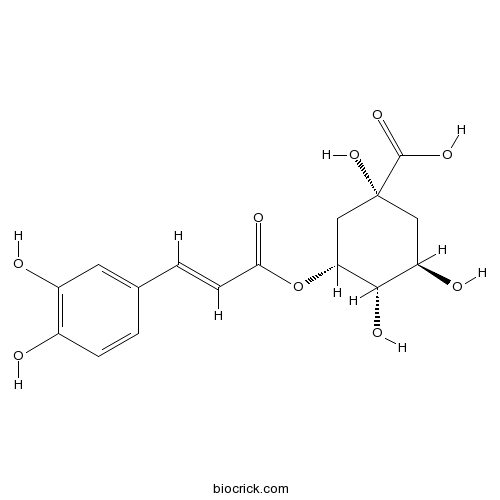
Anti-diabetic activity of aqueous extract of Ipomoea batatas L. in alloxan induced diabetic Wistar rats and its effects on biochemical parameters in diabetic rats.[Pubmed: 30058546]
Diabetes is a condition where the fasting blood glucose level elevated above the normal range (80-120mg/dL). This increase in blood glucose level may be due to the insulin deficiency i.e. insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM or type I) or due to insulin resistance i.e. non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM or type II). Diabetes leads to severe complications in the body even life treating complications e.g. nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy increased vascular permeability and delayed wound healing if left untreated. Different drugs are used for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, but synthetic drugs are costly and possess severe side effects. So, more emphasis is being placed on the use of traditional medicines because these sources have fewer side effects than the synthetics drugs and are economical. So the white skinned sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) peel-off was selected for its anti-diabetic effect as well as to see its effects on biochemical parameters. Both young (3-4 months) and old (up to 1 year) Wistar rats were selected for current study. It was found that the aqueous extract of WSSP peel-off had shown beneficial effects. In addition to the decrease in blood glucose level it also decreased protein glycation level total cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL-cholesterol. Increase in HDL-cholesterol was also observed after treating the rats with aqueous extract of Ipomoea batatas. Additionally, WSSP peel-off had also shown positive results on total protein concentration, albumin, globulin, and plasma enzymes (SGOT and SGPT). Further research would be needed in order to purify the anti-diabetic components and it should be available in compact dose form for all diabetic patients.
Ipomoea batatas L. Lam. ameliorates acute and chronic inflammations by suppressing inflammatory mediators, a comprehensive exploration using in vitro and in vivo models.[Pubmed: 30005651]
Ipomoea batatas L. Lam. is a functional food and belongs to family Convolvulaceae. It is used as an antiinflammatory, aphrodisiac, antiasthmatic, anticonvalescent, antitumor, antanemic and antidiabetic agent by local communities. This study has been planned to evaluate its antiinflammatory and antiarthritic potentials.
Preference of red mite Tetranychus ludeni Zacher (Acari: Tetranychidae) to sweet potato genotypes.[Pubmed: 29947646]
Tetranychus ludeni damages the sweet potato. Pest development can vary between plant genotypes. The objective was to identify the preference of Tetranychus ludeni for Ipomoea batatas genotypes, from the germplasm bank at the Universidade Federal dos Vales do Jequitinhonha e Mucuri (UFVJM). Natural infestations of this mite were observed on 54 sweet potato genotypes in potted, in a greenhouse. Three mite-infested leafs of each genotype were collected and analyzed. The red mite showed different population density rate in genotypes. The BD 29 genotype was found to be highly susceptible, the BD 08, BD 57, BD 17 and Espanhola genotypes were moderately susceptible, and the others forty-nine genotypes showed low susceptibility to the mite.
Developmental and reproductive response of Brachmia macroscopa (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) to three host plants.[Pubmed: 29899457]
The sweet potato leaf folder, Brachmia macroscopa Meyrick (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae), which is a significant pest of plants in the family Convolvulaceae, is rapidly expanding its range in South China and other subtropical regions. Studies were designed to examine the effects of three different host plants (sweet potato, Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.; water spinach, I. aquatica Forsskål; and morning glory, Pharbitis purpurea (L.)) on the development and life table parameters of B. macroscopa under laboratory conditions. We found that the intrinsic rates of increase of B. macroscopa were 0.17 ± 0.004, 0.21 ± 0.005 and 0.16 ± 0.004 on I. batatas, I. aquatica and P. purpurea, respectively. The highest net reproduction rate was 158.06 ± 18.22 per female reared on I. aquatica. The larvae had five instars when reared on I. batatas and I. aquatica, but required six instars on P. purpurea. The mean generation lengths of B. macroscopa ranged from 24.32 ± 0.18 days when reared on I. aquatica to 29.40 ± 0.24 days on P. purpurea. The survival of all stage and fecundity curves was intuitively manipulated using the age-stage-structured and two-sex population life table method, to enable comprehensive descriptions of the stage and population trends of B. macroscopa on the three Convolvulaceae plants. Our results indicated that I. batatas and I. aquatica were more suitable host plants than P. purpurea.


