Clerodendranthus spicatus
Clerodendranthus spicatus
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Clerodendranthus spicatus
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
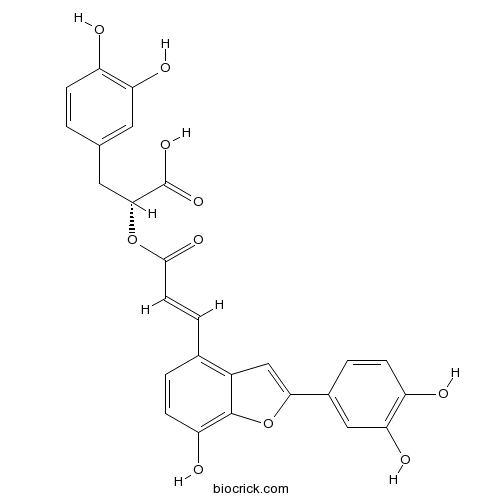
BCN5376
Salvianolic acid C115841-09-3
Instructions
-
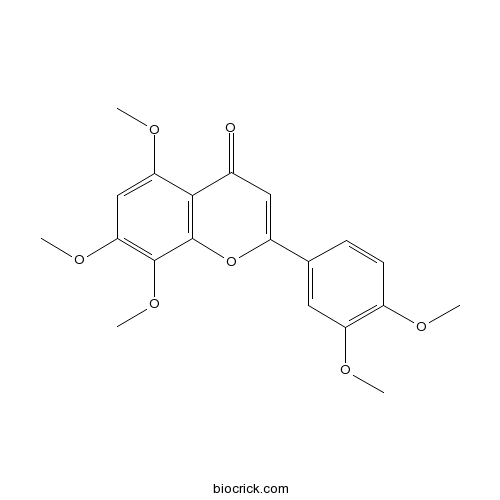
BCN2919
Isosinensetin17290-70-9
Instructions
-
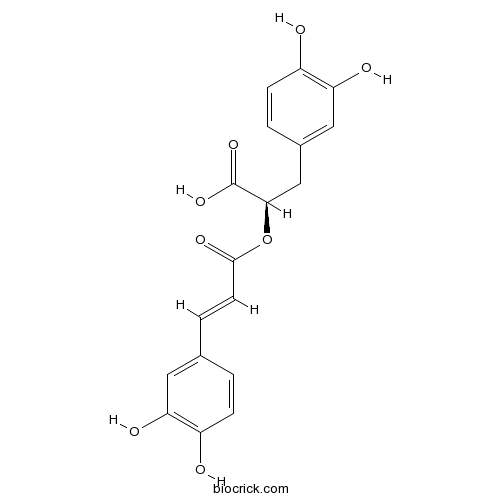
BCN5893
Rosmarinic acid20283-92-5
Instructions
-
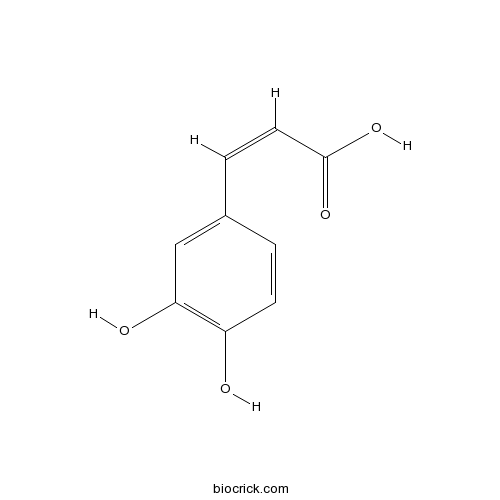
BCN5979
Caffeic acid331-39-5
Instructions
-
BCN5599
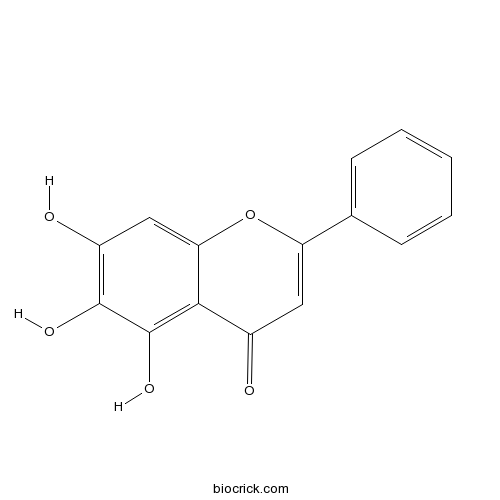
Baicalein491-67-8
Instructions
-
BCN2823
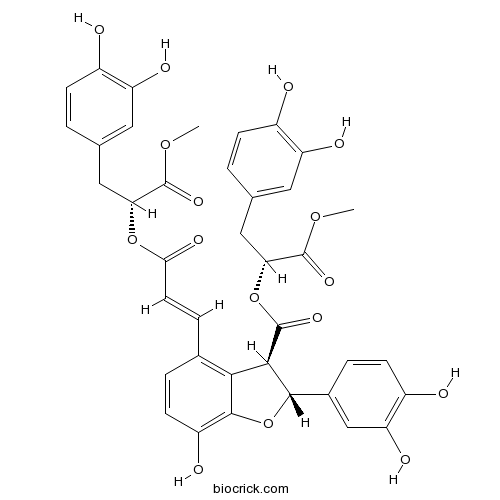
Dimethyl lithospermate B875313-64-7
Instructions
Cytotoxic and renoprotective diterpenoids from Clerodendranthus spicatus.[Pubmed: 29309828]
Three new diterpenoids, spicatusenes A-C (1-3), and eleven known ones (4-14) were isolated from the aerial parts of Clerodendranthus spicatus. Their structures were identified by spectroscopic methods. The cytotoxic activities of all the compounds against human cancer cells (HL-60, SMMC-7721, A-549, MCF-7, and SW-480) were examined and found that compounds 2, 3, 6, 8, 10, and 13 were active against one or more cancer cell lines. Besides, the renoprotective effects of all the isolates in TGF-β1-induced rat kidney fibroblasts revealed that compounds 3-7, 9, 13, and 14 were beneficial for renal fibrosis. Finally, a plausible biosynthetic pathway for 1 via a Hantzsch-type reaction was proposed.
New Diterpenoids from Clerodendranthus spicatus.[Pubmed: 28470482]
Two new diterpenoids, neoorthosiphonones B and C (1 and 2), and one known diterpenoid, were isolated from the aerial parts of Clerodendranthus spicatus. Their structures including absolute configurations were determined by comprehensive spectroscopic analyses and X-ray crystallographic methods. No compound was found to inhibit fibronectin production at the concentration of 20 μM.
New ursane-type triterpenoids from Clerodendranthus spicatus.[Pubmed: 28392270]
Five new ursane-type triterpenoids, spicatusoids A-E (1, 3-6), and three known ones (2, 7, and 8), and a known oleanane-type triterpenoid (9) were isolated from the aerial parts of Clerodendranthus spicatus. Their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic methods. In particular, the structure of 3 including its absolute configuration was confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. Cell viability of all the compounds against rat kidney fibroblast cells (NRK-49F) with or without TGF-β1 induction and human cancer cells (HL-60, SMMC-7721, A-549, MCF-7, and SW-480) was examined by using MTT or MST assays. It was found that, with exception of 1, all the tested compounds could inhibit cell proliferation in TGF-β1 induced NRK-49F cells with compounds 2 being most active.
Phenolic acid derivatives with neuroprotective effect from the aqueous extract of Clerodendranthus spicatus.[Pubmed: 28140664]
None
Clerodens E-J, antibacterial caffeic acid derivatives from the aerial part of Clerodendranthus spicatus.[Pubmed: 27593446]
Six new caffeic acid derivatives, Clerodens E-J (1-6) were isolated from the aerial part of Clerodendranthus spicatus. Their structures were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic analysis, including NMR, MS, and ECD data. Compound 1 showed moderate antibacterial activities against drug-resistant strains of bacteria in vitro.
[Phenotypic Trait Variation, Correlation and Path Analysis of Clerodendranthus spicatus].[Pubmed: 27254910]
To investigate the phenotypic trait variation range of Clerodendranthus spicatus, and to look for phenotypic traits closely related with its yield and quality, in order to provide reference for its breeding.
Four new phenolic acid with unusual bicycle [2.2.2] octane moiety from Clerodendranthus spicatus and their anti-inflammatory activity.[Pubmed: 26073946]
Four new phenolic acids, clerodens A-D (1-4) possessing an unusual bicycle [2.2.2] octane moiety were isolated from the whole plants of Clerodendranthus spicatus. Their structures were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic methods, including NMR, MS, and ECD data. All isolates were evaluated for their anti-inflammatory activities on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nitric oxide (NO) production in RAW 264.7, and compound 4 showed significant inhibitory activities with IC50 value of 6.8 μM.
Clerodendranoic acid, a new phenolic acid from Clerodendranthus spicatus.[Pubmed: 23165309]
Phenolic acid derivatives are typical constituents of Clerodendranthus spicatus which were considered to the active principles of this medicinal plant. These chemical constituents with their interesting frameworks and biological significance attracted our attention. As part of our ongoing chemical investigation of C. spicatus using various column chromatography techniques, a new phenolic compound, named clerodendranoic acid (1), was isolated from the aerial parts of C. spicatus together with five known ones, including rosmarinic acid (2), methyl rosmarinate (3), caffeic acid (4), methyl caffeate (5), ethyl caffeate (6). Their structures, including stereochemical configurations, were completely established by extensive spectroscopic methods, mainly inclvolving 1D, 2D NMR, as well as HRESIMS.


