Chrysopogon zizanioides
Chrysopogon zizanioides
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Chrysopogon zizanioides
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN8312
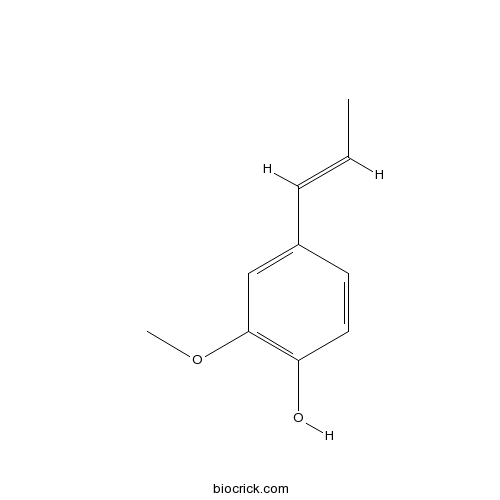
Isoeugenol97-54-1
Instructions
Comparative metabolic profiling of vetiver (Chrysopogon zizanioides) and maize (Zea mays) under lead stress.[Pubmed: 29874765]
Lead (Pb) contamination of residential soils in United States is attributed to use of Pb based paints prior to 1978 and their deterioration and accumulation in surface soils. Exposure to Pb due to ingestion and inhalation of Pb laden soil and dust causes neurological disorders, renal disorders, developmental and behavioral problems, particularly in children under the age of six. Vetiver grass is one of the leading choices for Pb remediation due to its ability to hyperaccumulate Pb, in addition to high biomass. In order to understand the effect of Pb on vetiver metabolic pathways, we compared the global metabolic changes in vetiver with that of maize, a Pb susceptible plant under Pb stress. Vetiver showed massive increase in levels of key metabolites in response to Pb, including amino acids, organic acids and coenzymes. Maize showed very modest increase in some of the same metabolites, and no change in others. The results provide the first indication of the difference in metabolic response of the hyperaccumulator, vetiver to lead stress as compared to maize.
Comparison of boron uptake and translocation in two vetiver genotypes and evaluation of boron removal efficiency of vetiver floating islands.[Pubmed: 29775106]
The objectives of this study were to identify genotypic differences in the uptake and translocation of boron (B) in vetiver (Chrysopogon zizanioides L.), a promising species in B phytoremediation, and to determine the efficiency of vetiver floating island system in B phytoremediation. Changes in plant biomass and B uptake and translocation were determined in two vetiver genotypes, Sierra and Sunshine, cultured hydroponically in a nutrient solution and exposed to six different B concentrations for 7 d and 14 d. The efficiency of B removal by Sierra (a high B accumulative genotype) grown in floating islands was also determined. Shoot B concentration differed significantly between the two genotypes but differences in root concentration were not significant. Root to shoot B transfer and B uptake ability were higher in Sierra than in Sunshine. The uptake and translocation of B was affected by B concentration and time of exposure. Sierra plants grown in floating islands were more efficient in B removal at lower B concentrations. Most of the B removed accumulated in the middle-upper sections of old leaves. Sierra is more suitable for the removal of B from wastewaters than Sunshine, especially in vetiver floating island system.
Assisted phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil from a mined site with Typha latifolia and Chrysopogon zizanioides.[Pubmed: 29031880]
None
A preliminary study to design a floating treatment wetland for remediating acid mine drainage-impacted water using vetiver grass (Chrysopogon zizanioides).[Pubmed: 28990146]
None


