Caragana jubata
Caragana jubata
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Caragana jubata
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN1061
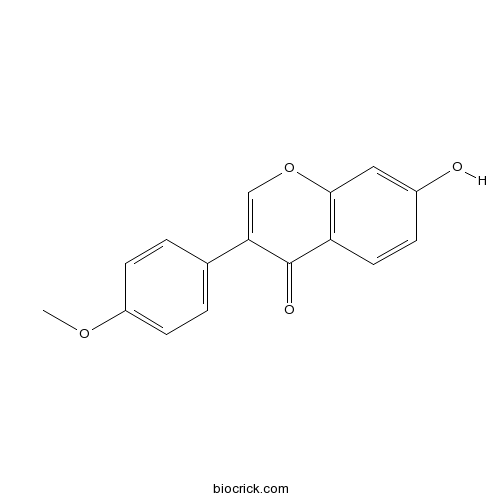
Formononetin485-72-3
Instructions
[Hepatoprotective activity of aqueous extract from Caragana jubata (Pall.) Poir. shoots in the model of acute hepatitis induced by acetaminophen in rats].[Pubmed: 29964259]
Tsel'iu issledovaniia bylo izuchenie gepatoprotektornoĭ aktivnosti rasteniia Caragana jubata (Pall.) Poir. (karagana grivastaia) na modeli ostrogo gepatita, indutsirovannogo u krys Wistar vvedeniem atsetaminofena v doze 1000 mg/kg. Ustanovleno, chto vodnoe izvlechenie C. jubata proiavlialo vyrazhennoe gepatoprotektornoe deĭstvie, sopostavimoe s preparatom sravneniia “Karsil”. Éto proiavilos' normalizatsieĭ biokhimicheskikh pokazateleĭ krovi (alaninaminotransferazy, aspartataminotransferazy, shchelochnoĭ fosfatazy, kholesterina, obshchego bilirubina) i antioksidantnoĭ aktivnosti gomogenatov pecheni, kotoruiu opredeliali khemiliuminestsentnym metodom, osnovannym na okislenii liuminola, indutsirovannom 2,2¢-azobis(2-amidinopropanom). Pri gistologicheskom issledovanii vyiavlena normalizatsiia morfofunktsional'nykh pokazateleĭ pecheni krys, kotorye poluchali vodnoe izvlechenie karagany grivastoĭ.
[Screening of active fractions with antithrombotic effect from Caragana jubata].[Pubmed: 28905571]
The antithrombotic effect of Caragana jubata (Pall.)Poir.ethanolic extract (TE)was evaluated by inferior vena cava thrombosis in rats and acute pulmonary thrombosis in mice. To search for the bioactive fractions of TE, comparison on acute pulmonary thrombosis was made between the two main fractions of TE (TE-1 and TE-2). Besides, pharmacological effects of TE, TE-1 and TE-2 on bleeding time and clotting time were also studied. Reference substances combined with UPLC/DAD-q-TOF-MS were applied to identify the main six compounds and other chemical constituents of the TE. The results showed that TE could significantly reduce the rat thrombosis weight in all doses (P<0.01) and improve the protective rate to mice in medium and high doses (P<0.05). TE-2 showed a stronger effect on protecting the mice from paralysis or death and prolonging the bleeding time and clotting time than TE-1. Chemical constituents in TE mainly include isoflavones, pterocarpans and stilbenoids. Constituents in TE-2 were mainly isoflavones and pterocarpans, while those in TE-1 were mainly stilbenoids, which could be inferred that all of these three kinds of constituents may be responsible for the antithrombotic effects of Caragana jubata.
2-Cys peroxiredoxin responds to low temperature and other cues in Caragana jubata, a plant species of cold desert of Himalaya.[Pubmed: 24477582]
A 2-Cys peroxiredoxin cDNA (CjPrx) was isolated and characterized from Caragana jubata, a temperate/alpine plant species of high altitude cold desert of Himalaya and Eurasia. The cDNA obtained was 1,064 bp long consisting of an open reading frame of 789 bp encoding 262 amino acids. The calculated molecular mass of the mature protein was 28.88 kDa and pI was 5.84. Deduced amino acid sequence of CjPrx shared a high degree homology with 2-CysPrx proteins from other plants. CjPrx had both the PRX_type 2-Cys domain and thioredoxin-like superfamily domains. CjPrx contained 26.72% α-helices, 6.87% β-turns, 20.61% extended strands and 45.80% random coils, and was a hydrophilic protein. Expression of CjPrx was modulated by low temperature, methyl jasmonate (MJ), salicylic acid and drought stress, but no significant change was observed in response to abscisic acid treatment. Among all the treatments, a strong up-regulation of CjPrx was observed in response to MJ treatment.
[Characteristics of stemflow for typical alpine shrubs in Qilian Mountain].[Pubmed: 22097356]
Taking the typical alpine shrubs Potentilla fruticosa, Salix cupularis, Hippophae rhamnoides, and Caragana jubata in Qilian Mountain as test objects, a field investigation from June 1 to October 31, 2010 was conducted on the variation characteristics of the shrub stemflow, and analyzed the affecting effects of rainfall intensity and canopy structure morphology. The stemflow generated when the rainfall in early period was 2.1 mm, with an average of 3.4%, 3.2%, 8.0%, and 4.2% of the gross rainfall for P. fruticosa, S. cupularis, H. rhamnoides, and C. jubata, respectively. There was a significant positive linear correlation between the stemflow and rainfall intensity. With increasing rainfall, the stemflow percentage showed a trend of increase-decrease-increase. Stemflow played an important role in supplying water to the shrub rhizosphere, and the average funneling ratio was 59, 30, 110, and 49 for P. fruticosa, S. cupularis, H. rhamnoides, and C. jubata, respectively. The stemflow percentage had a significant exponential relationship with the maximum rain intensity in 10 minutes (I10). When the I10 was more than 6.0 mm x h(-1), the stemflow of H. rhamnoides and C. jubata showed a persistently increasing trend, while that of P. fruticosa and S. cupularis tended to be stable. Canopy structure morphology had complicated effects on the stemflow. In the same rainfall intensities, the height and crown projection area of the shrubs were the important factors affecting the generation of stemflow.
Identification and expression analysis of CjLTI, a novel low temperature responsive gene from Caragana jubata.[Pubmed: 21701826]
Using rapid amplification of cDNA ends, a full length cDNA (CjLTI) was cloned from apical buds of Caragana jubata, a plant species that grows under extreme cold. The cDNA obtained was 573 bp long consisting of an open reading frame of 351 bp encoding 116 amino acids. Homology analysis did not exhibit significant similarity with any sequence at NCBI database, therefore it was deduced as a novel gene. Secondary structure analysis suggested that the deduced CjLTI contained 25.86% α-helices, 4.31% β-turns, 6.90% extended strands, and 62.93% random coils. The hydropathy profile suggested CjLTI to be a hydrophobic protein having characteristic features of signal peptides at N-terminus. The gene exhibited down-regulation at 5 min of exposure to low temperature (LT, 4 ± 3 °C) followed by a strong up-regulation after 15 min and onwards. Methyl jasmonate (MJ) lead to up-regulation of CjLTI starting at 5 min onwards. The gene exhibited up- and down-regulation of expression pattern in response to abscisic acid (ABA) and salicylic acid (SA). Mild drought stress slightly up-regulated gene expression and at severe drought (up to 115% reduction in leaf water potential) slight down-regulation of gene expression was observed. These results suggested CjLTI to be a LT responsive gene wherein MJ, ABA and SA pathways might be involved in regulating the gene expression.
Lipoxygenase in Caragana jubata responds to low temperature, abscisic acid, methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid.[Pubmed: 21640803]
Lipoxygenase (LOX) catalyses oxygenation of free polyunsaturated fatty acids into oxylipins, and is a critical enzyme of the jasmonate signaling pathway. LOX has been shown to be associated with biotic and abiotic stress responses in diverse plant species, though limited data is available with respect to low temperature and the associated cues. Using rapid amplification of cDNA ends, a full-length cDNA (CjLOX) encoding lipoxygenase was cloned from apical buds of Caragana jubata, a temperate plant species that grows under extreme cold. The cDNA obtained was 2952bp long consisting of an open reading frame of 2610bp encoding 869 amino acids protein. Multiple alignment of the deduced amino acid sequence with those of other plants demonstrated putative LH2/ PLAT domain, lipoxygenase iron binding catalytic domain and lipoxygenase_2 signature sequences. CjLOX exhibited up- and down-regulation of gene expression pattern in response to low temperature (LT), abscisic acid (ABA), methyl jasmonate (MJ) and salicylic acid (SA). Among all the treatments, a strong up-regulation was observed in response to MJ. Data suggests an important role of jasmonate signaling pathway in response to LT in C. jubata.
Characterization of gene expression of QM from Caragana jubata, a plant species that grows under extreme cold.[Pubmed: 19757181]
Caragana [Caragana jubata (Pall.) Poir] is a temperate plant that thrives well under extremes of cold in high altitude of Himalaya and hence the plant is expected to be a source of genes that might play an important role in tolerance to low temperature (LT). In order to identify LT inducible gene(s), differential display of mRNA (DD) was performed using the apical buds growing under snow as well as growing in the near vicinity without snow, and a LT inducible QM gene (CjQM) homologue was identified. Realizing the importance of QM gene (which encodes human Wilms' tumor suppressor QM protein) in aggregation of 40 and 60S ribosomal subunit and that not much has been reported on this gene in plant systems in relation to its relationship with LT, full length cDNA of CjQM was cloned through rapid amplification of cDNA ends. The gene (977 bp), encoded by small gene family, had an open reading frame of 651 bp and was found to be intronless. The gene exhibited up-regulation within 20 min of exposure to LT and abscisic acid (ABA), but no significant change in gene expression was observed in response to drought stress (DS), salicylic acid (SA) and methyl jasmonate (MJ) application. Up-regulation of CjQM was obtained in the tissues growing in situ under snow. Non-responsiveness of CjQM towards DS, SA and MJ, but up-regulation in response to LT and ABA suggested a specific regulation of the gene in Caragana under varied cues.


