Ampelopsis grossedentata
Ampelopsis grossedentata
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Ampelopsis grossedentata
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
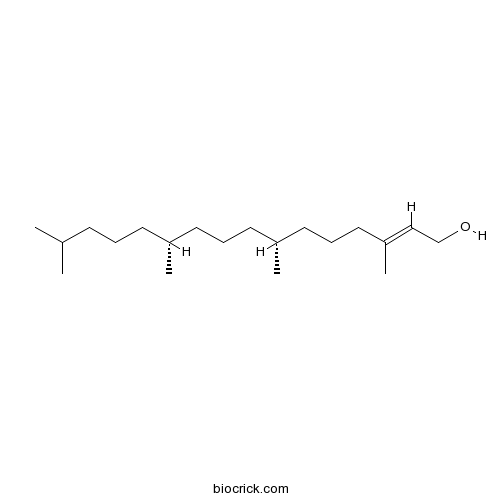
BCN1673
Phytol150-86-7
Instructions
-
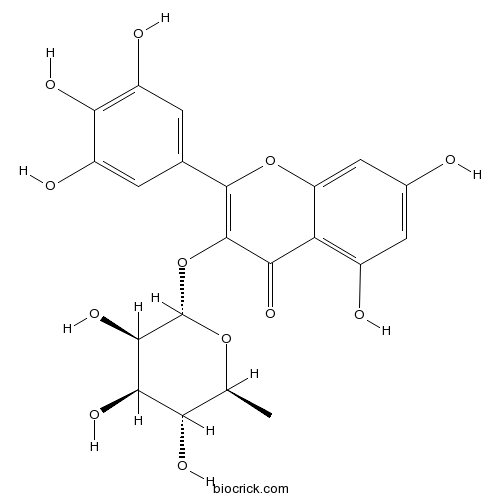
BCN1136
Myricitrin17912-87-7
Instructions
-
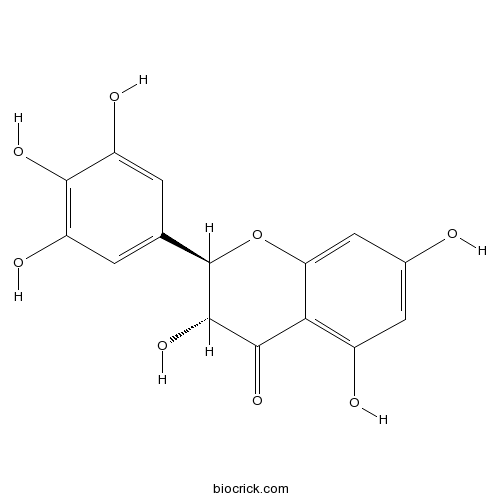
BCN5160
Ampelopsin27200-12-0
Instructions
-
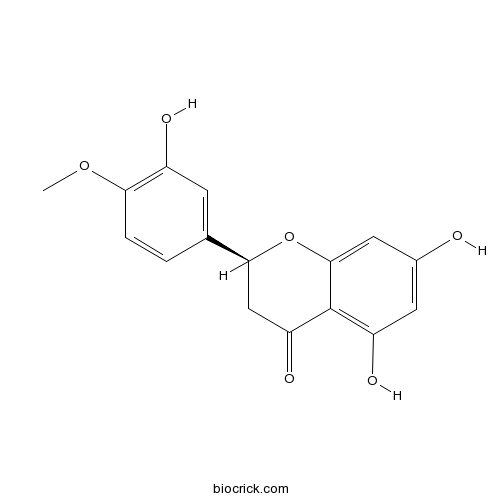
BCN5657
Hesperetin520-33-2
Instructions
-
BCN5692
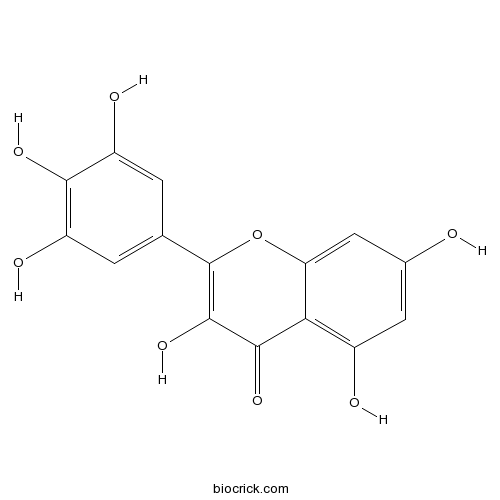
Myricetin529-44-2
Instructions
-
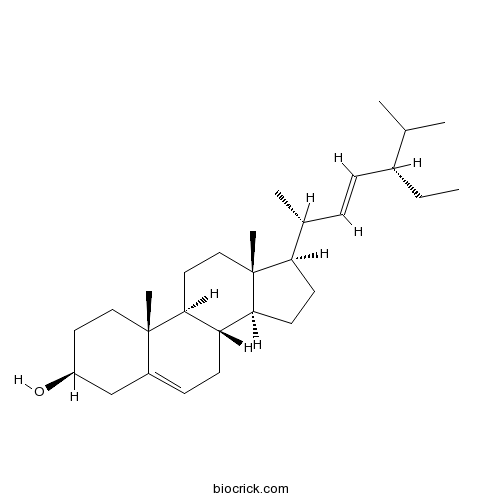
BCN4376
Stigmasterol83-48-7
Instructions
Ampelopsis grossedentata supplementation effectively ameliorates the glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.[Pubmed: 30089792]
Some animal and cellular experiments showed that ampelopsis grossedentata (APL) was helpful to improve insulin resistance or glucose uptake.
Dihydromyricetin inhibits caerulin-induced TRAF3-p38 signaling activation and acute pancreatitis response.[Pubmed: 30055802]
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a common inflammatory disease in gastrointestinal tract. Our previous study has shown that caerulin induces TNF receptor-associated factor 3 (TRAF3)-p38 signaling activation and pro-inflammatory response in macrophages, causing damage to co-cultured pancreatic acinar cells. Dihydromyricetin (DHM) is a flavonoid extracted from Ampelopsis grossedentata, which has displayed anti-inflammation and anti-oxidant functions. Our results here show that DHM potently inhibited caerulin-induced expression and productions of multiple pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-17) in murine bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs). DHM significantly inhibited caerulin-induced TRAF3 protein stabilization, TRAF3-mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 (MKK3) association and following MKK3-p38 activation in BMDMs. Significantly, DHM was ineffective against caerulin in TRAF3-silenced BMDMs. Importantly, DHM supplement attenuated the cytotoxicity of caerulin-activated BMDMs to co-cultured pancreatic acinar cells, resulting in significantly decreased acinar cell death and apoptosis. In vivo, DHM co-administration largely attenuated pancreatic and systemic inflammation in caerulin-injected AP mice. Together, DHM inhibits caerulin-induced TRAF3-p38 signaling activation and AP response. DHM could be further studied as a potential anti-AP agent.
Dihydromyricetin Inhibits Lead-Induced Cognitive Impairments and Inflammation by the Adenosine 5'-Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway in Mice.[Pubmed: 29975840]
Dihydromyricetin (DHM), a natural flavonoid derived from the medicinal and edible plant Ampelopsis grossedentata, exhibits antioxidant, antiapoptosis, antitumor, and anti-inflammatory bioactivities. This study evaluated the effects of DHM on Pb-induced neurotoxicity and explored the underlying mechanisms. DHM significantly ameliorated behavioral impairments of Pb-induced mice. It decreased the levels of lipid peroxidation and protein carbonyl and increased the activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase in the brains. DHM suppressed Pb-induced apoptosis, as indicated by the decreased levels of Bax and cleaved caspase-3. DHM also decreased inflammatory cytokines in the brains of Pb-treated mice. DHM decreased amyloid-beta (Aβ) level and nuclear factor-κB nuclear translocation. Moreover, DHM induced the adenosine 5'-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation and inhibited the activation of p38, Toll-like receptor 4, myeloid differentiation factor 88, and glycogen synthase kinase-3. Collectively, this is the first report indicating that DHM could improve Pb-induced cognitive functional impairment by preventing oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation and that the protective effect was mediated partly through the AMPK pathway.
Interactions of Dihydromyricetin, a Flavonoid from Vine Tea (Ampelopsis grossedentata) with Gut Microbiota.[Pubmed: 29660761]
None
Protective effect of dihydromyricetin on LPS-induced acute lung injury.[Pubmed: 29522258]
Dihydromyricetin (DHM), a bioactive flavonoid component isolated from Ampelopsis grossedentata, is known to have anti-inflammatory effect, but the effect of DHM on acute lung injury (ALI) is largely unknown. Here, we investigated the effect of DHM on ALI and the underlying mechanism by bioinformatic analyses and animal experiments. We found that pretreatment with DHM ameliorated lung pathological changes and suppressed the inflammation response in lung tissues after LPS challenge. The potential targets of DHM were predicted by DDI-CPI and DRAR-CPI tools and analyzed using the STRING server to predict the functionally related signaling pathways, such as MAPK signaling. Molecular docking calculations indicated that DHM could be embedded tightly into the binding pocket of ERK, JNK, and p38. Furthermore, the activation of MAPK signaling induced by LPS was inhibited by DHM. In conclusion, these findings suggest that DHM may exert its protective effect on ALI by inhibiting MAPK signaling. The present study supports a potential clinical application for DHM in treating ALI and provides a novel design that combines in silico methods with in vivo experiments for drug research.


