Albizia julibrissin
Albizia julibrissin
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Albizia julibrissin
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
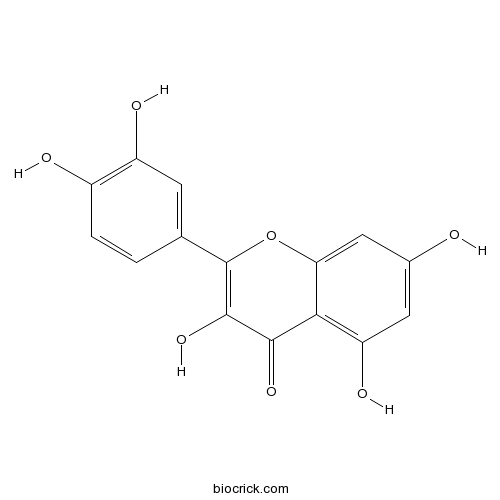
BCN6049
Quercetin117-39-5
Instructions
-
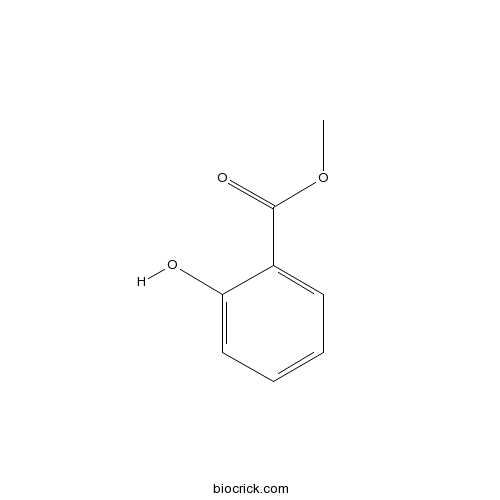
BCN5372
Methyl salicylate119-36-8
Instructions
-
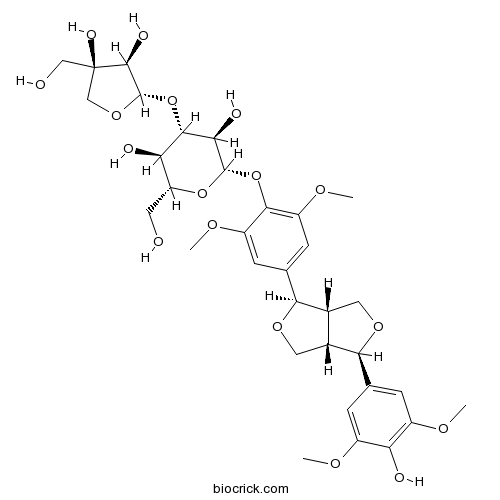
BCN1578
(-)-Syringaresnol-4-O-beta-D-apiofuranosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucopyranoside136997-64-3
Instructions
-
BCC8957
Episyringaresinol 4'-O-β-D-glncopyranoside137038-13-2
Instructions
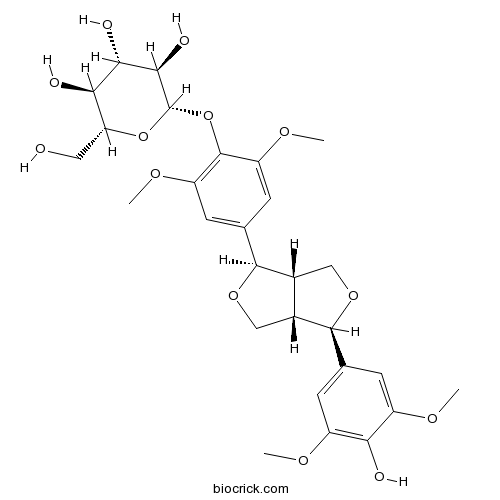
-
BCN6283
Amentoflavone1617-53-4
Instructions
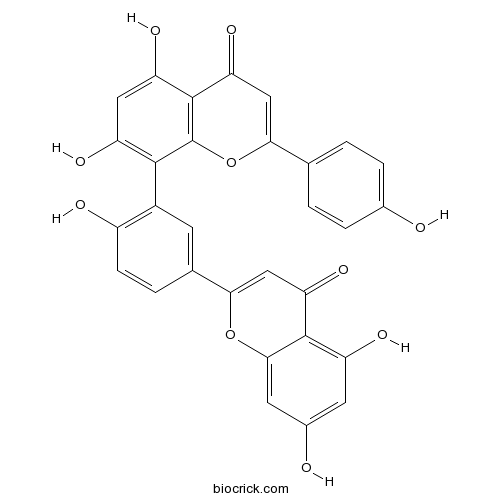
-
BCN5550
Taxifolin480-18-2
Instructions
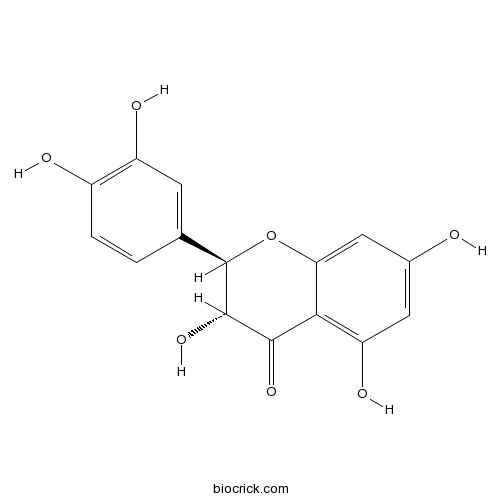
-
BCN5551
Isorhamnetin480-19-3
Instructions
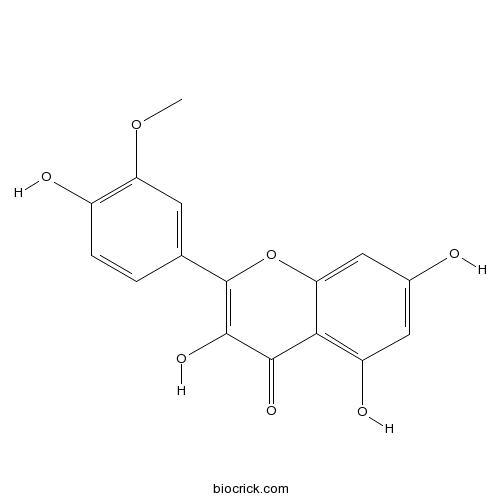
-
BCN5564
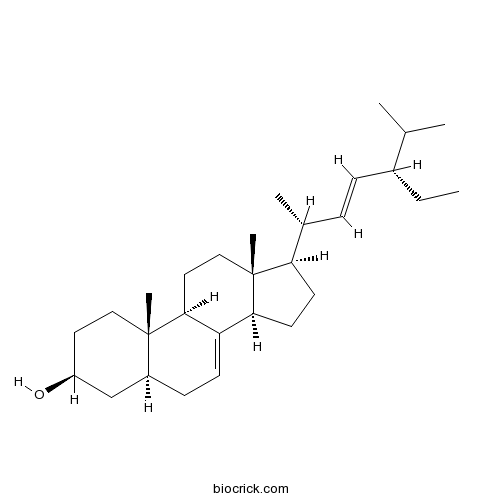
alpha-Spinasterol481-18-5
Instructions
-
BCN5569
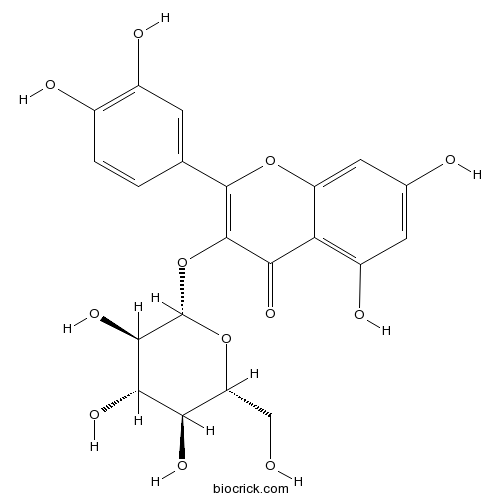
Isoquercitrin482-35-9
Instructions
-
BCN5573
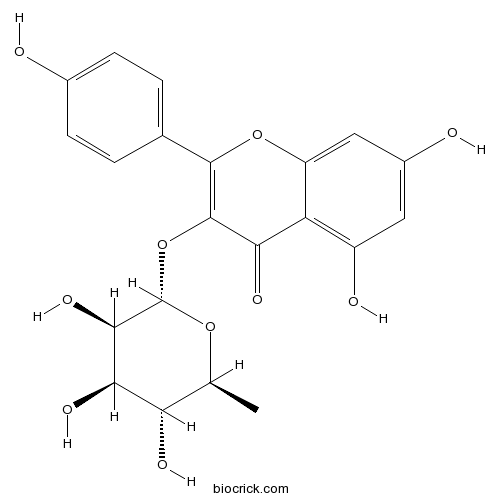
Afzelin482-39-3
Instructions
-
BCN5600
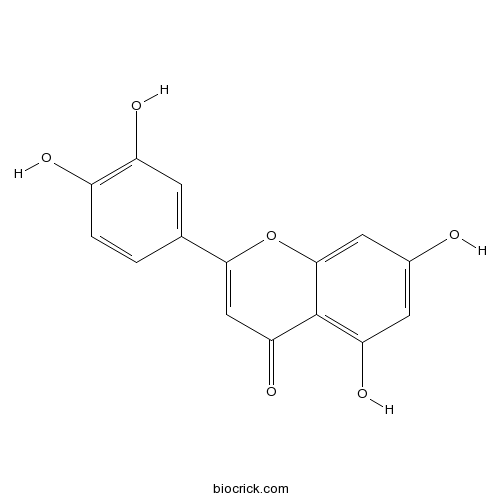
Luteolin491-70-3
Instructions
-
BCN5653
Kaempferol520-18-3
Instructions
-
BCN5656
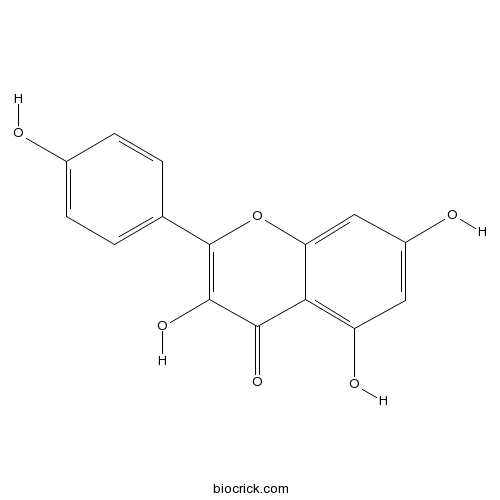
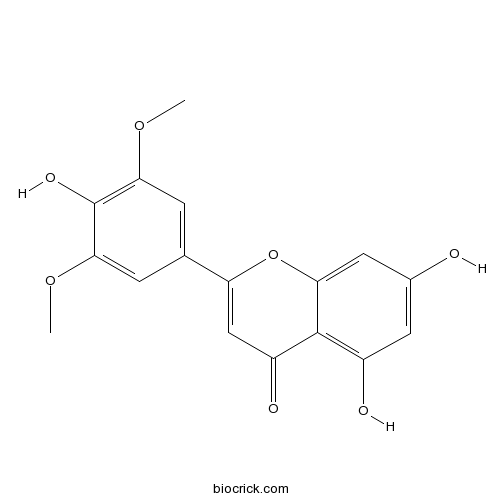
Tricin520-32-1
Instructions
-
BCN5658
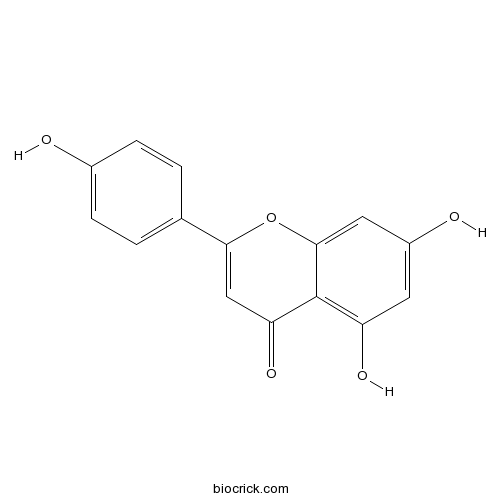
Apigenin520-36-5
Instructions
-
BCN5665
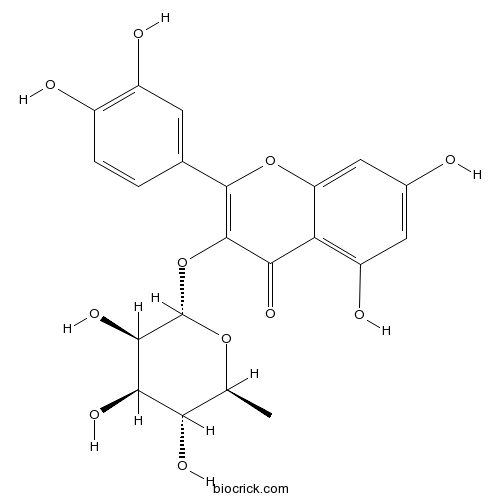
Quercitrin522-12-3
Instructions
-
BCN5725
Lupeol545-47-1
Instructions
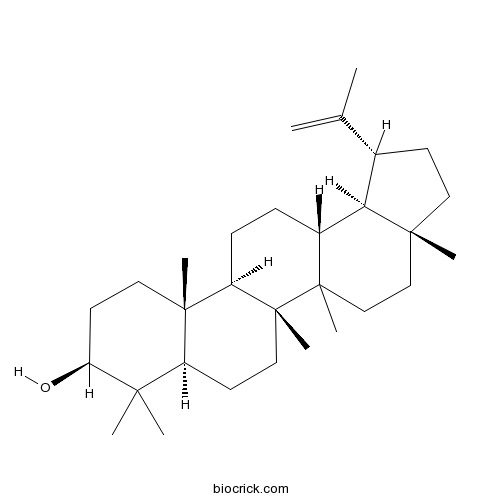
-
BCN2224
Riboflavine83-88-5
Instructions
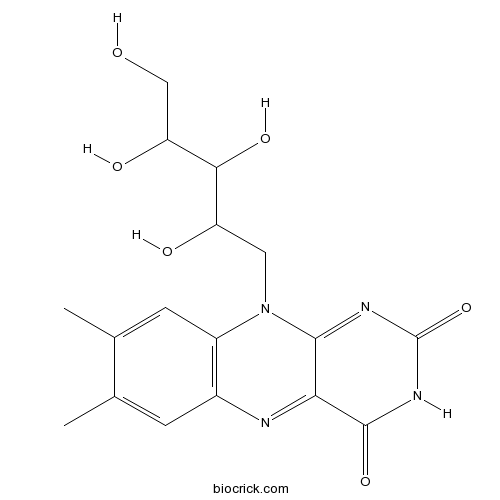
-
BCN4512
Isoliquiritigenin961-29-5
Instructions
Three new triterpenoid saponins from Albizia julibrissin.[Pubmed: 29756490]
None
Attenuation of brain mitochondria oxidative damage by Albizia julibrissin Durazz: neuroprotective and antiemetic effects.[Pubmed: 29250976]
Medicinal plants, as new drugs, are considered for treatment of insomnia, anxiety, depression, confusion, nausea, and vomiting symptoms. The current study aimed to evaluate the neuroprotective and antiemetic effects of Albizia. julibrissin Durazz. flower extract in the chickens. Emesis was induced by copper sulfate and ipecac (60 and 600 mg/kg, orally, respectively) and the methanolic extract (50, 100, and 200 mg/kg) were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.). Mitochondrial function, lipid peroxidation (LPO), protein carbonyl (PC) content, and catalase activity as biomarkers of oxidative damage were evaluated in the brain mitochondria. All doses of extract showed significant (p < 0.001) antiemetic activity against induced emesis by copper sulfate and ipecac. Brain mitochondria function (by 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg of extract) were increased 48%, 85%, and 90% against emesis induced by ipecac and 32%, 18%, and 24% against emesis induced by copper sulfate, respectively. LPO and PC contents were significantly decreased after the administration of extract in emesis induced by copper sulfate and ipecac. A significant decrease (p < 0.01) of CAT activity was observed in the extract (200 mg/kg) group in emesis induced by copper sulfate in chickens brain mitochondria. The present study suggests that the extract had antiemetic effects against emesis induced by copper sulfate and ipecac in young chickens via peripheral and central mechanisms. Neuroprotective effect of the extract could be due to the increase in bioactive compounds, plasma antioxidants, or direct free radical scavenging that could prevent lipid and protein alteration and impede the formation of oxidative damage.
[Anti-tumor target identification and molecular mechanism study of total saponins from Albizia julibrissin].[Pubmed: 29235276]
Dried stem bark from Albizia julibrissin(AJ) is a common traditional Chinese herb with several therapy effects including insomnia, anxiety and anti-tumor. Recently, the anti-tumor effect and mechanism studies of AJ have drawn much attention; however, there are still some troubles in chemical composition separation, which leads to the difficulties in pharmacological research of AJ. In this study, we firstly confirmed the proliferation inhibitory effect of total saponins from AJ(TSAJ)on human hepatocarcinoma(HepG2) cells, and also tested the apoptosis induction effect of TSAJ. Then, we successfully captured the potential target proteins from HepG2 lysates by using TSAJ-modified solid beads, and identified the target proteins by LC-MS/MS. Finally, we confirmed 5 target proteins including Exportin-2, Beta-actin-like protein 2, Myosin-9, Protein transport protein Sec61 subunit beta,and Cytochrome c oxidase copper chaperone, which are responsible forcell apoptosis, proliferation, differentiation andmigration. In summary, our findings elucidate the potential anti-tumor mechanism of TSAJ from the direct target proteins, and provide a new insight for exploring the pharmacological mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine.
Cytotoxic oleanane triterpenoid saponins from Albizia julibrissin.[Pubmed: 28764915]
None
D-Pinitol in Fabaceae: an Oviposition Stimulant for the Common Grass Yellow Butterfly, Eurema mandarina.[Pubmed: 27714574]
The common grass yellow butterfly, Eurema mandarina (formerly Eurema hecabe mandarina) (Lepidoptera, Pieridae), recently has been separated taxonomically from a subtropical population of Eurema hecabe in Japan. This species is widely distributed in the temperate region of Japan, and feeds mainly on various ligneous plants within the Fabaceae. We attempted to identify an oviposition stimulant for E. mandarina from its primary hosts, Albizia julibrissin and Lespedeza cuneata. In both hosts, crude extract and an aqueous fraction elicited oviposition responses from gravid females. A polar subfraction of the aqueous fraction also stimulated high oviposition-stimulatory activity, comparable to the original aqueous fraction, suggesting that E. mandarina females use water-soluble compounds for host recognition. Subsequent activity-directed fractionation by ion exchange chromatography indicated that one of the key substances was contained in the neutral/amphoteric fraction. Chemical analyses revealed that the active fractions of both hosts contained D-(+)-pinitol as the major component. We examined female responses to authentic D-pinitol and found that it induced oviposition responses at concentrations greater than 0.1 %. Since this cyclitol is omnipresent in Fabaceae, we conclude that D-pinitol plays a role in mediating oviposition of E. mandarina on fabaceous plants.
Ensifer glycinis sp. nov., a rhizobial species associated with species of the genus Glycine.[Pubmed: 27125987]
Rhizobial strains from root nodules of Astragalus mongholicus and soybean (Glycine max) were characterized phylogenetically as members of the genus Ensifer (formerly named Sinorhizobium), based on 16S rRNA gene sequence comparisons. Results based upon concatenated sequence analysis of three housekeeping genes (recA, atpD and glnII, ≤ 93.8 % similarities to known species) and average nucleotide identity (ANI) values of whole genome sequence comparisons (ranging from 89.6 % to 83.4 % to Ensifer fredii and Ensifer saheli, respectively) indicated the distinct positions of these novel strains within the genus Ensifer. Phylogeny of symbiotic genes (nodC and nifH) of three novel strains clustered them with rhizobial species Ensifer fredii and Ensifer sojae, both isolated from nodules of Glycine max. Cross-nodulation tests showed that the representative strain CCBAU 23380T could form root nodules with nitrogen fixation capability on Glycine soja, Albizia julibrissin, Vigna unguiculata and Cajanus cajan, but failed to nodulate Astragalus mongholicus, its original host legume. Strain CCBAU 23380T formed inefficient nodules on G. max, and it did not contain 18 : 0, 18 : 1ω7c 11-methyl or summed feature 1 fatty acids, which differed from other related strains. Failure to utilize malonic acid as a carbon source distinguished strain CCBAU 23380T from the type strains of related species. The genome size of CCBAU 23380T was 6.0 Mbp, comprising 5624 predicted genes with DNA G+C content of 62.4 mol%. Based on the results above, a novel species, Ensifer glycinis sp. nov., is proposed, with CCBAU 23380T (=LMG 29231T =HAMBI 3645T) as the type strain.


