Adinandra nitida
Adinandra nitida
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Adinandra nitida
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN7864
Camellianin A109232-77-1
Instructions
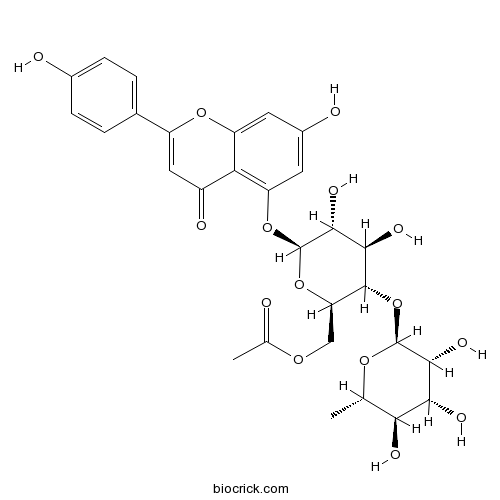
-
BCN3872
Camelliaside B131573-90-5
Instructions
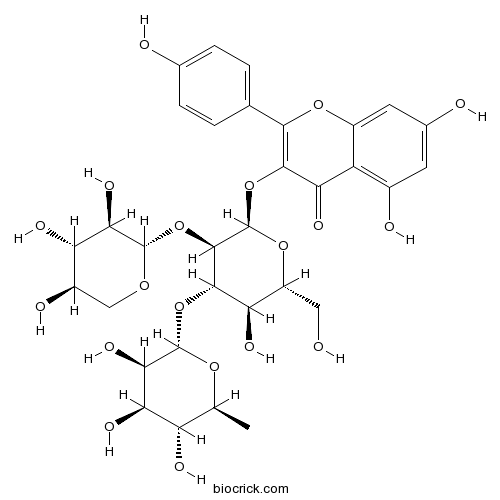
-
BCN3871
Camelliaside A135095-52-2
Instructions
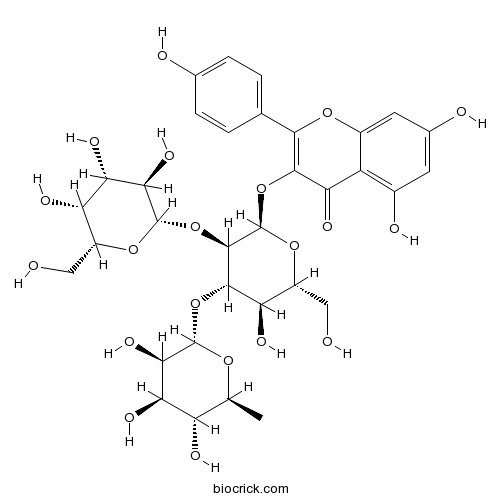
Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution study of camellianin A and its major metabolite in rats by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 26117310]
Camellianin A is a major active constituent of Adinandra nitida. A LC-MS/MS method for the determination of camellianin A and its metabolite (camellianin B) in rat plasma and tissues was developed and applied to a pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution study. Samples were separated on a Waters HSS T3 column with a mobile phase consisted of methanol and water (containing 0.1% formic acid). MS/MS detection was carried out on a triple-quadruple mass spectrometer under negative ESI mode. Pharmacokinetics study showed that camellianin A was rapidly eliminated with a t1/2 of 92.6±41.4h and CL of 3.19±0.471L/min/kg. Additionally, camellianin A showed a low oral bioavailability of 2.99% and a narrow tissue distribution; however, camellianin B was proved to have a wide tissue distribution with brain penetration. The data presented in this study provides useful information for the further applications of A. nitida and camellianin A.
[Simultaneous determination of five flavonoid compounds in leaves of Adinandra nitida by HPLC-PAD].[Pubmed: 21141488]
To established a novel HPLC-PAD method for the simultaneous determination of five compounds (camellianin A, camellianin B, apigenin, quercitrin, epicatechin) in leaves of Adinandra nitida.
Antioxidant and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activities of ethanol extract and pure flavonoids from Adinandra nitida leaves.[Pubmed: 20738217]
Adinandra nitida Merr. ex. H.L. Li (Theaceae) is an indigenous plant in south China. Its leaves have been reported to have many curative effects such as reducing blood pressure, as well as antibacterial, antioxidant, and analgesic properties, which could be used in foods and medicines.
Anti-proliferative effect of camellianin A in Adinandra nitida leaves and its apoptotic induction in human Hep G2 and MCF-7 cells.[Pubmed: 20657414]
Leaves of Adinandra nitida constitute a kind of flavonoid-rich plant food. In this study, camellianin A, the main flavonoid in the leaves of Adinandra nitida,was prepared and identified by high performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array detector-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HPLC-PDA-ESI/MS). In the anticancer assay, it was found camellianin A could inhibit the proliferation of the human hepatocellular liver carcinoma Hep G2 and human breast adenocarcinoma MCF-7 cell lines in a dose-dependent manner and induce the significant increase of the G0/G1 cell population. After treated by camellianin A, phosphatidylserine of Hep G2 and MCF-7 cells could translocate significantly to the surface of the membrane. The increase of an early apoptotic population of Hep G2 and MCF-7 cells was observed. It was concluded that camellianin A not only affected the progress of the cell cycle, but also induced cells to enter into apoptosis.
[Triterpene saponins from Adinandra nitida].[Pubmed: 18717338]
To investigate the chemical constituents of the leaves of Adinandra nitida, several column chromatography methods were used to isolate the chemical constituents of this plant. The structures were elucidated on the basis of spectral data. Six compounds were isolated and identified as 2alpha, 3alpha, 19alpha-trihydroxy-olean-12-en-28-oic acid-28-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (1), arjunetin (2), sericoside (3), glucosyl tormentate (4), nigaichigoside F1 (5) and arjunglucoside I (6), separately. Compound 1 is a new compound, and compounds 2 -6 were isolated from A. nitida for the first time.
Separation and identification of compounds in Adinandra nitida by comprehensive two-dimensional liquid chromatography coupled to atmospheric pressure chemical ionization source ion trap tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 16924385]
A comprehensive two-dimensional liquid chromatographic (2D-LC) separation system based on the combination of a CN column and a Merck Chromolith Flash reversed-phase column was developed for the separation of components in Adinandra nitida, one type of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). The two dimensions were connected by a ten-port, dual-position valve controlled automatically by software written in-house. The effluents were detected by both ultraviolet and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization source ion trap tandem mass spectrometry (MS). The calculated peak capacity of the 2D-LC-MS/MS system was above 1240. More than 57 components were resolved in the methanol extract from Adinandra nitida leaves, and five of these were identified based on their relative retention times, molecular weights and MS/MS spectra.
Analysis of flavonoids in leaves of Adinandra nitida by capillary electrochromatography on monolithic columns with stepwise gradient elution.[Pubmed: 15938186]
Extracts of Adinandra nitida leaves, known as Shiyacha in China, were analyzed by monolithic columns of capillary electrochromatography (CEC). To obtain good resolution within a short time, stepwise gradient elution of CEC was employed, and the effects of experimental parameters, such as the buffer, the gradient conditions, and the mode of injection were studied systematically. Under optimized conditions, analysis could be accomplished in 25 min on a monolithic rod of macroporous poly(butyl methacrylate-co-ethylene dimethacrylate). With two identified flavonoids, epicatechin and apigenin, as markers, a quality control method for Shiyacha and its relevant products was established. The calibration curves exhibited good linear behavior over the concentration range of two orders of magnitude. On combination with an on-line concentration technique, the detection limit of flavonoids could be decreased to 25 ng for apigenin.


