Actinostemma lobatum
Actinostemma lobatum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Actinostemma lobatum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN2955
Tubeimoside II115810-12-3
Instructions
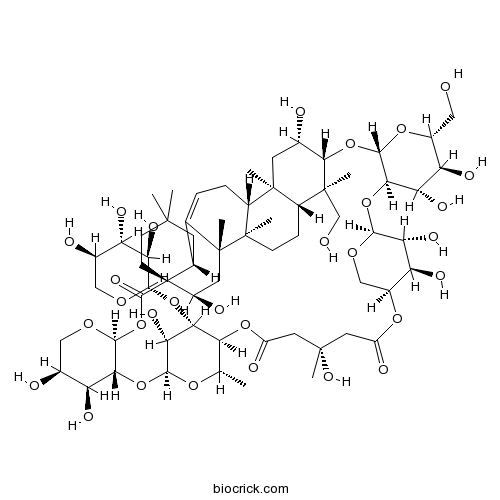
-
BCN6049
Quercetin117-39-5
Instructions
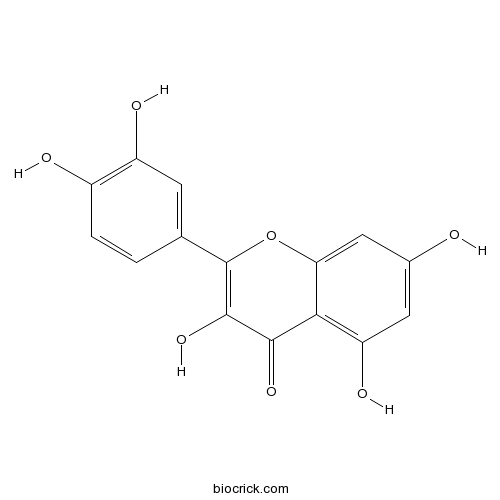
-
BCN5816
4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde123-08-0
Instructions
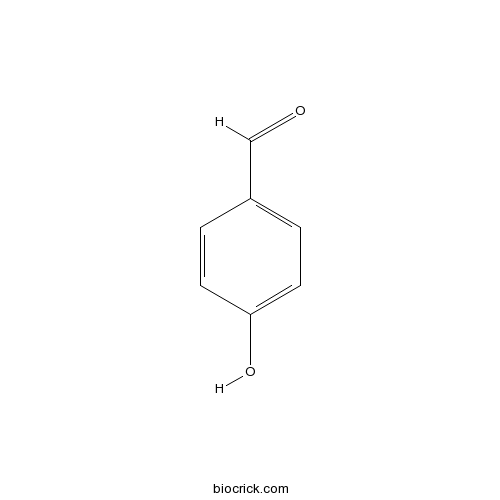
-
BCN2300
Cucurbitacin E18444-66-1
Instructions
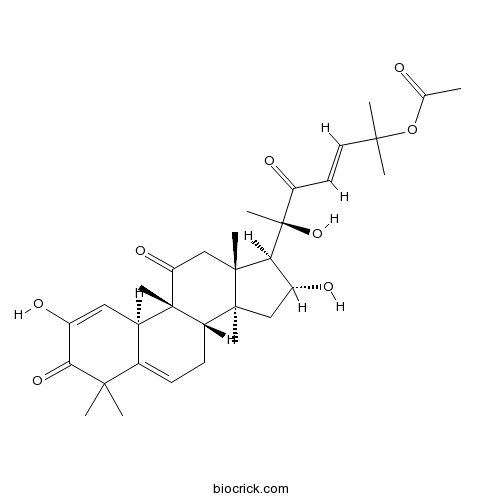
-
BCN5665
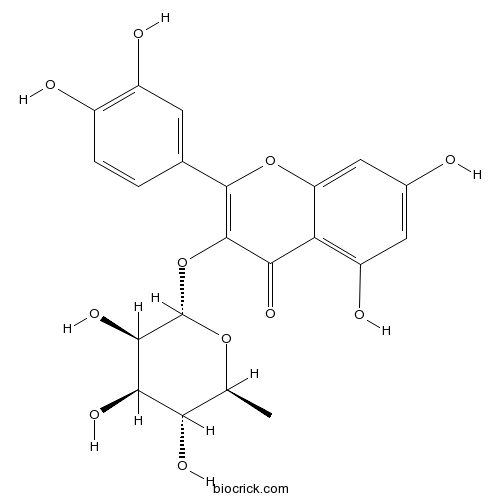
Quercitrin522-12-3
Instructions
-
BCN4537
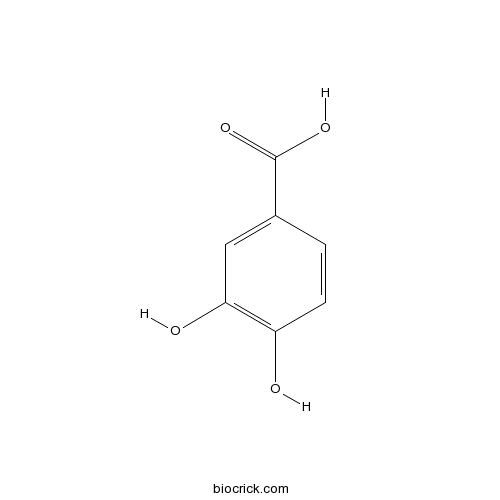
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid99-50-3
Instructions
-
BCN4546
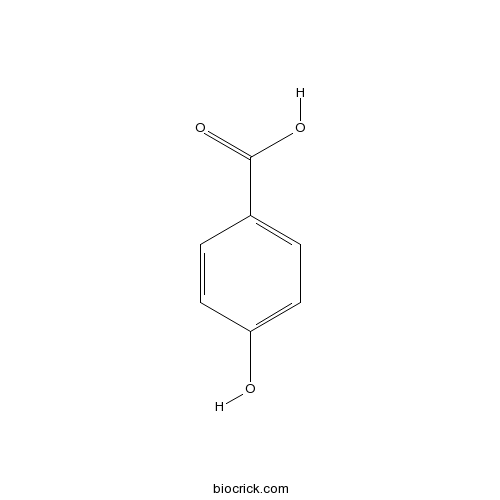
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid99-96-7
Instructions
A new cyclic bisdesmoside from Actinostemma lobatum Maxim.[Pubmed: 26062306]
A new cyclic bisdesmoside treterpene saponin, lobatoside N (1), together with four known triterpenoids, was isolated from the herb of Actinostemma lobatum Maxim. Structures were established by means of extensive spectral data analysis. Furthermore, the cytotoxic activities of the identified compounds were evaluated using HCT-116, HT-29, MCF-7 and A549 human cancer cell lines. As a result, compounds 1-5 showed significant cytotoxicities in a dose-dependent manner against the cell lines tested. Especially, compound 5 exhibited stronger activities, with IC50 value of 0.88 μM and 0.98 μM, than that of the positive control drug (Cis-platinum) against HT-29 and A549 cell lines.
Cyclic bisdesmosides from Actinostemma lobatum MAXIM (Cucurbitaceae) and their in vitro cytotoxicity.[Pubmed: 22056664]
Two new cyclic bisdesmosides elucidated as lobatoside L (1) and lobatoside M (2) and four known cyclic bisdesmosides (3-6) were isolated from Actinostemma lobatum MAXIM (Cucurbitaceae). Their structures were determined on the basis of spectroscopic analyses including IR, HR-FAB-MS, TOCSY, 1D- and 2D-NMR experiments and chemical reactions. The inhibitory effects of the six compounds on human cancer cell growth (including esophageal squamous carcinoma cell line ECA109, lung cancer cell line A549 and gastric cancer cell line MGC-803) were determined using the MTT assay. The results revealed that the six compounds exhibited cytotoxicity against all the cell lines tested, and compounds 1, 3 and 5 showed significant activities in a dose dependent manner against all the cell lines, especially for compound 1 and 5, the IC(50) values for ECA-109 cells were 8.25 μM and 3.71 μM. The results demonstrated that compounds 1 and 5's activities are 2- and 4-fold that of cisplatin.
Blockade of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa mediates the antithrombotic activity of butanol fraction of Actinostemma lobatum Maxim.[Pubmed: 18243609]
Actinostemma lobatum Maxim, a wildlife plant of Cucurbitaceae family, has been utilized for the prevention or treatment of cardiovascular diseases as a folk remedy in Korea. However, its scientific evidence remains unclear. Thus, in the present study, we examined the effects of butanol fraction of Actinostemma lobatum Maxim (BFALM) on the in vitro and in vivo antithrombotic activity and possible mechanisms were elucidated for the first time.


