Actinidia arguta
Actinidia arguta
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Actinidia arguta
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN2224
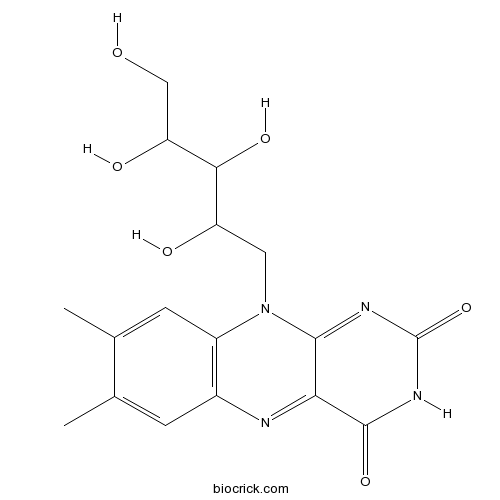
Riboflavine83-88-5
Instructions
Combined Analysis of the Fruit Metabolome and Transcriptome Reveals Candidate Genes Involved in Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Actinidia arguta.[Pubmed: 29762529]
None
Hardy kiwifruit leaves (Actinidia arguta): An extraordinary source of value-added compounds for food industry.[Pubmed: 29680033]
None
A Comparison of Food Habits Between Japanese Marten and Raccoon Dog in Western Tokyo with Reference to Fruit Use.[Pubmed: 29417891]
We studied the food habits of the Japanese marten (Martes melampus) and the raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procionoides) at the Tama Forest Science Garden, western Tokyo, Japan by fecal analysis in 2014/15. Martens were dependent on fruits throughout the year and showed less marked seasonal changes. Raccoon dogs were less dependent on fruits than martens were, and more dependent on mammals in spring, insects in summer and winter, and seeds throughout the year. Martens fed on more fruits containing tiny seeds, such as Actinidia arguta and Stachyurus praecox, whereas raccoon dogs fed on more large-seeded fruits, such as Ginkgo biloba and Diospyros kaki. Martens fed on more fruits that grew at the forest edges, whereas raccoon dogs fed on more fruits growing inside the forest.
A key structural gene, AaLDOX, is involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in all red-fleshed kiwifruit (Actinidia arguta) based on transcriptome analysis.[Pubmed: 29309888]
Study on kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis and A. deliciosa) color mainly concentrated in green and yellow-fleshed cultivars, less about molecular mechanism of red-fleshed trait formation, rarely in all red-fleshed fruit. Using 'Tianyuanhong' and 'Yongfengyihao' ('TY', a kind of all red-fleshed cultivar, from Actinidia arguta; 'YF', a kind of all green-fleshed cultivar, also from Actinidia arguta) as experimental material, we performed RNA-seq to obtain 202,742 unigenes with an average length of 603bp and N50 of 873bp via transcriptome data analysis. Of these unigenes, 72,508 (35.76%) were annotated and 997 were assigned to secondary metabolic pathways, of which 104 unigenes were involved in flavonoid and anthocyanin biosynthesis. According to the parameter log2fold-change and p-adjusted, 12 differentially expressed structural genes were selected for performing expression profiles and cluster analysis. Physiological traits including color ration, hue angle, and anthocyanin content were also investigated. From the results, we concluded AaLDOX (genes encoding leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase) maybe the key gene controlling anthocyanin biosynthesis in flesh of 'TY' kiwifruit, which promoted accumulation of anthocyanin, finally leading to the red flesh coloration.
Actinidia arguta extract attenuates inflammasome activation: Potential involvement in NLRP3 ubiquitination.[Pubmed: 29174375]
Actinidia arguta (A. arguta) has been widely used in Asian countries as a traditional medicinal herb to treat inflammation-related diseases, such as gastritis, bronchitis, and arthritis.
Biochemical and functional characterization of AcUFGT3a, a galactosyltransferase involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in the red-fleshed kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis).[Pubmed: 29057484]
Much of the diversity of anthocyanin pigmentation in plant tissues is due to the action of glycosyltransferases, which attach sugar moieties to the anthocyanin aglycone. This step can increase both their solubility and stability. We investigated the pigmentation of the outer and inner pericarps of developing fruits of the red-fleshed kiwifruit Actinidia chinensis cv. 'Hongyang'. The results show that the red color of the inner pericarp is due to anthocyanin. Based on expression analyses of structural genes, AcUFGT was shown to be the key gene involved in the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway. Expression of AcUFGT in developing fruit paralleled changes in anthocyanin concentration. Thirteen putative UFGT genes, including different transcripts, were identified in the genome of 'Hongyang'. Among these, only the expression of AcUFGT3a was found to be highly consistent with anthocyanin accumulation. Fruit infiltrated with virus-induced gene silencing showed delayed red colorations, lower anthocyanin contents and lower expressions of AcUFGT3a. At the same time, transient overexpression of AcUFGT3a in both Actinidia arguta and green apple fruit resulted in higher anthocyanin contents and deeper red coloration. In vitro biochemical assays revealed that recombinant AcUFGT3a recognized only anthocyanidins as substrate but not flavonols. Also, UDP-galactose was used preferentially as the sugar donor. These results indicate AcUFGT3a is the key enzyme regulating anthocyanin accumulation in red-fleshed kiwifruit.
The Nutritional and Health Benefits of Kiwiberry (Actinidia arguta) - a Review.[Pubmed: 28988409]
The kiwiberry (Actinidia arguta) is a new product on the market that is enjoying growing consumer acceptance around the world. This widespread interest has created increased demand for identification of the kiwiberry's nutritional health benefits. Containing over 20 essential nutrients and a range of vitamins, the kiwiberry comes near the top of fruits classed as superfoods. It is one of the richest sources of vitamin C with up to 430 mg/100 g fresh weight (FW) and is considered the richest dietary source of myo-inositol (up to 982 mg/100 g FW). The kiwiberry is also one of the richest sources of lutein (up to 0.93 mg/100 g FW) in commonly consumed fruit. Furthermore, containing up to 1301.1 mg/100 g FW phenolics and significant amounts of the essential minerals of potassium, calcium and zinc, the kiwiberry rates very highly as a 'healthy food'. The type and number of this fruit's medicinally promising nutrients have motivated ongoing investigations into its antioxidant, anti-tumour and anti-inflammatory properties. Early research has pointed to the kiwiberry being a very promising treatment for some cancers and health issues involving the gastrointestinal system, hypercholesterolemia and certain cancers. A pharmaceutical composition of A. arguta, A. kolomikta, and A. polygama extracts has already been registered for the prevention and treatment of some immune (inflammatory) mediated diseases, as well as the treatment of some non-allergic inflammatory diseases. This paper reviews and highlights the limited nutritional and therapeutic information currently available on the kiwiberry, a minor fruit possessing such major properties.


