SulfamethizoleCAS# 144-82-1 |
- Rocilinostat (ACY-1215)
Catalog No.:BCC2144
CAS No.:1316214-52-4
- LY 294002
Catalog No.:BCC3659
CAS No.:154447-36-6
- Doxorubicin
Catalog No.:BCC2082
CAS No.:23214-92-8
- E 64d
Catalog No.:BCC1127
CAS No.:88321-09-9
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 144-82-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5328 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C9H10N4O2S2 | M.Wt | 270.33 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (369.92 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
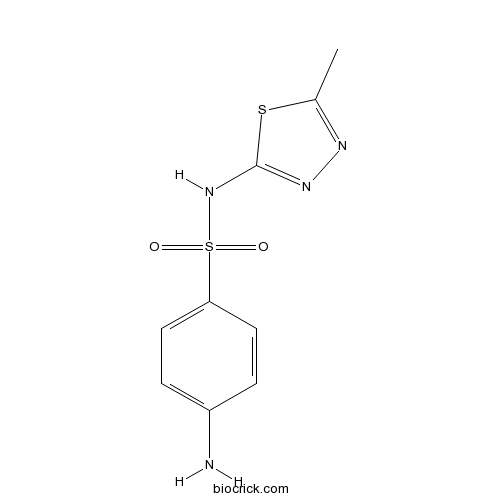
| Chemical Name | 4-amino-N-(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide | ||
| SMILES | CC1=NN=C(S1)NS(=O)(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VACCAVUAMIDAGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H10N4O2S2/c1-6-11-12-9(16-6)13-17(14,15)8-4-2-7(10)3-5-8/h2-5H,10H2,1H3,(H,12,13) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Sulfamethizole is a sulfathiazole antibacterial agent.
Target: Antibacterial
Sulfamethizole is a sulfathiazole antibacterial agent. Sulfamethizole is a competitive inhibitor of bacterial para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), a substrate of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. The inhibited reaction is necessary in these organisms for the synthesis of folic acid. Sulfamethizole, an inhibitor of dihydropteroate synthetase and the formation of folic acid, inhibited bioluminescence more than growth [1]. Treatment with sulfamethizole resulted in a significant reduction in bacterial counts in all samples from a susceptible strain (MIC, 128 micro g/ml) and a resistant strain (MIC, 512 micro g/ml). Infection with a sulII gene-positive strain (MIC, >2,048 micro g/ml) could not be treated with sulfamethizole, as no effect could be demonstrated in the urine, bladder, or kidneys [2]. References: | |||||

Sulfamethizole Dilution Calculator

Sulfamethizole Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6992 mL | 18.4959 mL | 36.9918 mL | 73.9836 mL | 92.4796 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7398 mL | 3.6992 mL | 7.3984 mL | 14.7967 mL | 18.4959 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3699 mL | 1.8496 mL | 3.6992 mL | 7.3984 mL | 9.248 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.074 mL | 0.3699 mL | 0.7398 mL | 1.4797 mL | 1.8496 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.037 mL | 0.185 mL | 0.3699 mL | 0.7398 mL | 0.9248 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Sulfamethizole
- Sulfathiazole sodium
Catalog No.:BCC5207
CAS No.:144-74-1
- Zeaxanthin
Catalog No.:BCN2380
CAS No.:144-68-3
- Oxalic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8515
CAS No.:144-62-7
- Sodium bicarbonate
Catalog No.:BCC7584
CAS No.:144-55-8
- Sodium barbital
Catalog No.:BCN2160
CAS No.:144-02-5
- CTX0294885
Catalog No.:BCC6396
CAS No.:1439934-41-4
- Jaceidin triacetate
Catalog No.:BCN6245
CAS No.:14397-69-4
- CB-839
Catalog No.:BCC5493
CAS No.:1439399-58-2
- M40
Catalog No.:BCC7686
CAS No.:143896-17-7
- Elacridar hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1547
CAS No.:143851-98-3
- CC-401 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1458
CAS No.:1438391-30-0
- 2,24-Dihydroxyursolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6244
CAS No.:143839-02-5
- Sulfapyridine
Catalog No.:BCC4729
CAS No.:144-83-2
- Sodium Nitroprusside
Catalog No.:BCC4844
CAS No.:14402-89-2
- BRD73954
Catalog No.:BCC5652
CAS No.:1440209-96-0
- Piclamilast
Catalog No.:BCC6215
CAS No.:144035-83-6
- 6-O-Syringoylajugol
Catalog No.:BCN6246
CAS No.:144049-72-9
- Febuxostat
Catalog No.:BCC2556
CAS No.:144060-53-7
- Deltarasin
Catalog No.:BCC1524
CAS No.:1440898-61-2
- Deltarasin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4270
CAS No.:1440898-82-7
- Tarasaponin VII
Catalog No.:BCN2684
CAS No.:144118-18-3
- Fmoc-Asp-OAll
Catalog No.:BCC3086
CAS No.:144120-53-6
- Fmoc-Glu-OAll
Catalog No.:BCC3490
CAS No.:144120-54-7
- Eprosartan Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4658
CAS No.:144143-96-4
Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Integrated with a Surface Acoustic Wave Technique for Detection of Sulfamethizole.[Pubmed:26704414]
Anal Chem. 2016 Jan 19;88(2):1476-84.
The synergistic effect of combining molecular imprinting and surface acoustic wave (SAW) technologies for the selective and label-free detection of Sulfamethizole as a model antibiotic in aqueous environment was demonstrated. A molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) for Sulfamethizole (SMZ) selective recognition was prepared in the form of a homogeneous thin film on the sensing surfaces of SAW chip by oxidative electropolymerization of m-phenylenediamine (mPD) in the presence of SMZ, acting as a template. Special attention was paid to the rational selection of the functional monomer using computational and spectroscopic approaches. SMZ template incorporation and its subsequent release from the polymer was supported by IR microscopic measurements. Precise control of the thicknesses of the SMZ-MIP and respective nonimprinted reference films (NIP) was achieved by correlating the electrical charge dosage during electrodeposition with spectroscopic ellipsometry measurements in order to ensure accurate interpretation of label-free responses originating from the MIP modified sensor. The fabricated SMZ-MIP films were characterized in terms of their binding affinity and selectivity toward the target by analyzing the binding kinetics recorded using the SAW system. The SMZ-MIPs had SMZ binding capacity approximately more than eight times higher than the respective NIP and were able to discriminate among structurally similar molecules, i.e., sulfanilamide and sulfadimethoxine. The presented approach for the facile integration of a sulfonamide antibiotic-sensing layer with SAW technology allowed observing the real-time binding events of the target molecule at nanomolar concentration levels and could be potentially suitable for cost-effective fabrication of a multianalyte chemosensor for analysis of hazardous pollutants in an aqueous environment.
Pharmacophore modeling, homology modeling, and in silico screening reveal mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitory activities for sotalol, glyburide, metipranolol, sulfamethizole, glipizide, and pioglitazone.[Pubmed:23545333]
J Mol Graph Model. 2013 May;42:39-49.
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a serine/threonine kinase and member of the PI3K-related kinase (PIKK) family. It plays a central role in integrating signals from metabolism, energy homeostasis, cell cycle, and stress response. Aberrant PI3K/mTOR activation is commonly observed in diseases such as cancer, diabetes and Alzheimer's disease. Accordingly, we developed common feature binding hypotheses for a set of 6 potent mTOR antagonists. The generated models were validated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses. To gain better insight into ligand-mTOR interactions, a homology model for the kinase domain of mTOR was built using the crystallographic structure of PI3Kgamma as template. The optimal pharmacophore model was further improved based on detailed docking studies of potent training compound in the homology model. The modified binding model was employed as 3D search query to screen our in-house-built database of established drugs. Subsequent in vitro screening of captured hits showed that six of them have submicromolar to low micromolar bioactivities, namely, glyburide, metipranolol, Sulfamethizole, glipizide, pioglitazone, and sotalol.
Mineralization of sulfamethizole in photo-Fenton and photo-Fenton-like systems.[Pubmed:26901716]
Water Sci Technol. 2016;73(4):746-50.
In this investigation, UV/H2O2, UV/H2O2/Fe(2+) (photo-Fenton) and UV/H2O2/Fe(3+) (photo-Fenton-like) systems were used to mineralize Sulfamethizole (SFZ). The optimal doses of H2O2 (1-20 mM) in UV/H2O2 and iron (0.1-1 mM) in photo-Fenton and photo-Fenton-like systems were determined. Direct photolysis by UV irradiation and direct oxidation by added H2O2, Fe(2+) and Fe(3+) did not mineralize SFZ. The optimal dose of H2O2 was 10 mM in UV/H2O2 and that of iron (Fe(2+) or Fe(3+)) was 0.2 mM in both UV/H2O2/Fe(2+) and UV/H2O2/Fe(3+) systems. Under the best experimental conditions and after 60 min of reaction, the SFZ mineralization percentages in UV/H2O2, UV/H2O2/Fe(2+) and UV/H2O2/Fe(3+) systems were 16, 90 and 88%, respectively. The UV/H2O2/Fe(2+) and UV/H2O2/Fe(3+) systems effectively mineralized SFZ.
Photodegradation of sulfonamide antimicrobial compounds (sulfadiazine, sulfamethizole, sulfamethoxazole and sulfathiazole) in various UV/oxidant systems.[Pubmed:25714641]
Water Sci Technol. 2015;71(3):412-7.
This study used Na(2)S(2)O(8), NaBrO8 and H(2)O(2)to degrade sulfadiazine (SDZ), Sulfamethizole (SFZ), sulfamethoxazole (SMX) and sulfathiazole (STZ) under ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. The initial concentration of sulfonamide and oxidant in all experiments was 20 mg/L and 5 mM, respectively. The degradation rate for sulfonamides satisfies pseudo-first-order kinetics in all UV/oxidant systems. The highest degradation rate for SDZ, SFZ, SMX and STZ was in the UV/Na(2)S(2)O(8), UV/NaBrO(3), UV/Na(2)S(2)O(8) and UV/H(2)O(2) system, respectively. In the UV/Na(2)S(2)O(8) system, the photodegradation rate of SDZ, SFZ, SMX and STZ was 0.0245 min(-)(1), 0.0096 min(-)(1), 0.0283 min(-)(1) and 0.0141 min(-)(1), respectively; moreover, for the total organic carbon removal rate for SDZ, SFZ, SMX and STZ it was 0.0057 min(-)(1), 0.0081 min(-)(1), 0.0130 min(-)(1) and 0.0106 min(-)(1), respectively. Experimental results indicate that the ability of oxidants to degrade sulfonamide varied with pollutant type. Moreover, UV/Na(2)S(2)O(8) had the highest mineralization rate for all tested sulfonamides.


