SirtinolSIRT inhibitor CAS# 410536-97-9 |
- SRT1720 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2222
CAS No.:1001645-58-4
- WHI-P180 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4243
CAS No.:153437-55-9
- Inauhzin
Catalog No.:BCC5146
CAS No.:309271-94-1
- Tenovin-1
Catalog No.:BCC2239
CAS No.:380315-80-0
- EX 527 (SEN0014196)
Catalog No.:BCC2223
CAS No.:49843-98-3
- PHA-793887
Catalog No.:BCC2521
CAS No.:718630-59-2
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 410536-97-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5512209 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H22N2O2 | M.Wt | 394.47 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 10 mg/mL (25.35 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
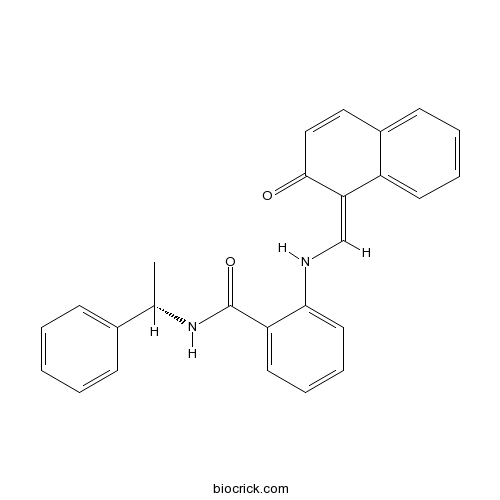
| Chemical Name | 2-[[(Z)-(2-oxonaphthalen-1-ylidene)methyl]amino]-N-[(1S)-1-phenylethyl]benzamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(C1=CC=CC=C1)NC(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2NC=C3C(=O)C=CC4=CC=CC=C43 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YUGODMKHHCZZOI-ZVTCDHROSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H22N2O2/c1-18(19-9-3-2-4-10-19)28-26(30)22-13-7-8-14-24(22)27-17-23-21-12-6-5-11-20(21)15-16-25(23)29/h2-18,27H,1H3,(H,28,30)/b23-17-/t18-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Cell-permeable, selective sirtuin deacetylase inhibitor (IC50 values are 38, 68 and 131 μM at SIRT2, Sir2p and SIRT1 respectively) that has no effect on HDAC1 activity. Significantly decreases growth and viability of PCa and HEK293T cells in vitro. |

Sirtinol Dilution Calculator

Sirtinol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.535 mL | 12.6752 mL | 25.3505 mL | 50.7009 mL | 63.3762 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.507 mL | 2.535 mL | 5.0701 mL | 10.1402 mL | 12.6752 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2535 mL | 1.2675 mL | 2.535 mL | 5.0701 mL | 6.3376 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0507 mL | 0.2535 mL | 0.507 mL | 1.014 mL | 1.2675 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0254 mL | 0.1268 mL | 0.2535 mL | 0.507 mL | 0.6338 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Sirtinol is an inhibitor of SIRT with IC50 value of 48.6µM (24 h) and 43.5µM (48 h) in MCF-7 cells [1].
Sirtinol significantly reduces the growth of MCF-7 cells in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. Meanwhile, the expression level of SIRT1 is notably decreased by sirtinol results in an induction of acetylated p53. It is found that sirtinol decreases the the expression of cell cycle-regulated proteins such as cyclin B1, cyclin D1, CDK2 and CDK6 and subsequently induces G1 phase arrest which indicates cell apoptosis. Furthermore, sirtinol is also demonstrated to induce autophagy in MCF-7 cells. Other in vitro assays show that sirtinol inhibits SIRT2 (amino acids 18–340) with IC50 value of 45µM while it does not inhibit HDAC1 at 50 and 100µM [1, 2].
References:
[1] Wang J, Kim TH, Ahn MY, Lee J, Jung JH, Choi WS, Lee BM, Yoon KS, Yoon S, Kim HS. Sirtinol, a class III HDAC inhibitor, induces apoptotic and autophagic cell death in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2012 Sep;41(3):1101-9.
[2] Grozinger CM, Chao ED, Blackwell HE, Moazed D, Schreiber SL. Identification of a class of small molecule inhibitors of the sirtuin family of NAD-dependent deacetylases by phenotypic screening. J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 19;276(42):38837-43.
- Palovarotene
Catalog No.:BCC4185
CAS No.:410528-02-8
- H-D-Ala-OBzl.TosOH
Catalog No.:BCC2850
CAS No.:41036-32-2
- Desacetylcinobufotalin
Catalog No.:BCC8166
CAS No.:4099-30-3
- Medioresinol
Catalog No.:BCN5462
CAS No.:40957-99-1
- Glycitein
Catalog No.:BCN5896
CAS No.:40957-83-3
- Taxiresinol
Catalog No.:BCN4637
CAS No.:40951-69-7
- VU0152100
Catalog No.:BCC4053
CAS No.:409351-28-6
- JNJ 16259685
Catalog No.:BCC7332
CAS No.:409345-29-5
- 3,4-Dimethoxycinnamyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCN6499
CAS No.:40918-90-9
- Sinoacutine
Catalog No.:BCN5461
CAS No.:4090-18-0
- H-Tyr-OEt.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3125
CAS No.:4089-07-0
- 3,5-Dihydroxy-1,7-bis(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)heptane
Catalog No.:BCN7494
CAS No.:408324-01-6
- Timosaponin A3
Catalog No.:BCN4999
CAS No.:41059-79-4
- Lipiferolide
Catalog No.:BCN5463
CAS No.:41059-80-7
- Neobavaisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN3194
CAS No.:41060-15-5
- Skullcapflavone I
Catalog No.:BCN5464
CAS No.:41060-16-6
- Steviolbioside
Catalog No.:BCN6800
CAS No.:41093-60-1
- Memantine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC9018
CAS No.:41100-52-1
- Platyphyllonol
Catalog No.:BCN5465
CAS No.:41137-85-3
- Hirsutanonol
Catalog No.:BCN5466
CAS No.:41137-86-4
- Hirsutenone
Catalog No.:BCN5467
CAS No.:41137-87-5
- Boc-Phe(4-F)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3219
CAS No.:41153-30-4
- CMPD-1
Catalog No.:BCC7274
CAS No.:41179-33-3
- erythro-Guaiacylglycerol beta-sinapyl ether 7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7348
CAS No.:412029-03-9
Sirtinol promotes PEPCK1 degradation and inhibits gluconeogenesis by inhibiting deacetylase SIRT2.[Pubmed:28127057]
Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 28;7(1):7.
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (PEPCK1) is the critical enzyme for gluconeogenesis and is linked with type II diabetes. Previous studies have found that SIRT2, a deacetylase, plays an important role in deacetylating PEPCK1 and little is known about the anti-diabetic activity of SIRT2 inhibitors. In this study, we investigated the anti-diabetic effects of Sirtinol, a SIRT2 inhibitor, on cell gluconeogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Immunoblotting analysis revealed that Sirtinol significantly decreased the protein level of PEPCK1, and was accompanied by the hyperacetylation of PEPCK1 as well as decreased glucose output in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, Sirtinol exerted little impact on endogenous PEPCK1 levels in SIRT2-knockdown cells. The in vitro experiments further confirmed the in vivo data; Sirtinol decreased liver PEPCK1 protein level and prevented pyruvate-induced blood glucose from increasing. Based on our results, the rate-limiting enzyme PEPCK1 is the primary target of Sirtinol, and the inhibition of SIRT2 activity may play an important role in cell gluconeogenesis. Thus, SIRT2 may be a novel molecular target for diabetes therapy and may thus shed light on the underlying diabetes treatment mechanisms of Sirtinol.
Sirtinol abrogates late phase of cardiac ischemia preconditioning in rats.[Pubmed:27677982]
J Physiol Sci. 2017 Jul;67(4):515-522.
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of Sirtinol, as an inhibitor of sirtuin NAD-dependent histone deacetylases, on myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury following early and late ischemia preconditioning (IPC). Rats underwent sustained ischemia and reperfusion (IR) alone or proceeded by early or late IPC. Sirtinol (S) was administered before IPC. Arrhythmias were evaluated based on the Lambeth model. Infarct size (IS) was measured using triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining. The transcription level of antioxidant-coding genes was assessed by real-time PCR. In early and late IPC groups, IS and the number of arrhythmia were significantly decreased (P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 vs IR, respectively). In S + early IPC, incidences of arrhythmia and IS were not different compared with the early IPC group. However, in S + late IPC the IS was different from the late IPC group (P < 0.05). In late IPC but not early IPC, transcription levels of catalase (P < 0.01) and Mn-SOD (P < 0.05) increased, although this upregulation was not significant in the S + late IPC group. Our results are consistent with the notion that different mechanisms are responsible for early and late IPC. In addition, sirtuin NAD-dependent histone deacetylases may be implicated in late IPC-induced cardioprotection.
Suppressive effects of sirtinol on human cytomegalovirus (hCMV) infection and hCMV-induced activation of molecular mechanisms of senescence and production of reactive oxygen species.[Pubmed:26763147]
Mech Ageing Dev. 2016 Sep;158:62-9.
Substantial evidence suggests that chronic human cytomegalovirus (hCMV) infection contributes significantly to T-cell immunosenescence and adverse health outcomes in older adults. As such, it is important to search for compounds with anti-hCMV properties. Studies have shown that resveratrol, a sirtuin activator, suppresses hCMV infection. Here we report suppressive effects of Sirtinol, a sirtuin antagonist, on hCMV infection and its cellular and molecular consequences. Human diploid fibroblast WI-38 cells were infected by hCMV Towne strain in the absence or presence of Sirtinol. hCMV replication was measured using qPCR. Senescent phenotype was determined by senescence-associated beta galactosidase (SA-beta-Gal) activity. Expression of hCMV immediate early (IE) and early (E) proteins and senescence-associated proteins (pRb and Rb, p16(INK4), and p53) and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) were assessed using standard laboratory assays. The results demonstrated that Sirtinol suppressed hCMV infection as well as hCMV-induced activation of molecular mechanisms of senescence and ROS production. While underlying molecular mechanisms remain to be elucidated, these findings indicate Sirtinol as a novel and potent anti-hCMV agent with the potential to be developed as an effective treatment for chronic hCMV infection and its cellular and molecular consequences that are important to ageing and health of older adults.
Sirtinol, a Sir2 protein inhibitor, affects stem cell maintenance and root development in Arabidopsis thaliana by modulating auxin-cytokinin signaling components.[Pubmed:28195159]
Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 14;7:42450.
In Arabidopsis thaliana, besides several key transcription factors and chromatin modifiers, phytohormones auxin and cytokinin play pivotal role in shoot and root meristem maintenance, and lateral root (LR) development. Sirtinol, a chemical inhibitor of Sir2 proteins, is known to promote some auxin induced phenotypes in Arabidopsis. However, its effect on plant stem cell maintenance or organ formation remained unaddressed. Here we show that Sirtinol affects meristem maintenance by altering the expression of key stem cell regulators, cell division and differentiation by modulating both auxin and cytokinin signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. The expression of shoot stem cell niche related genes WUSCHEL (WUS) and CLAVATA3 (CLV3) was upregulated, whereas SHOOT MERISTEMLESS (STM) was downregulated in Sirtinol treated seedlings. The expression level and domain of key root stem cell regulators PLETHORA (PLTs) and WUS-Related Homeobox 5 (WOX5) were altered in Sirtinol treated roots. Sirtinol affects LR development by disturbing proper auxin transport and maxima formation, similar to 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). Sirtinol also affects LR formation by altering cytokinin biosynthesis and signaling genes in roots. Therefore, Sirtinol affects shoot and root growth, meristem maintenance and LR development by altering the expression of cytokinin-auxin signaling components, and regulators of stem cells, meristems, and LRs.
Role of sirtuin histone deacetylase SIRT1 in prostate cancer. A target for prostate cancer management via its inhibition?[Pubmed:19075016]
J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 6;284(6):3823-32.
Prostate cancer (PCa) is a major age-related malignancy, and according to estimates from the American Cancer Society, a man's chance of developing this cancer significantly increases with increasing age, from 1 in 10,149 by age 39 to 1 in 38 by age 59 to 1 in 7 by age 70. Therefore, it is important to identify the causal connection between mechanisms of aging and PCa. Employing in vitro and in vivo approaches, in this study, we tested the hypothesis that SIRT1, which belongs to the Sir2 (silent information regulator 2) family of sirtuin class III histone deacetylases, is overexpressed in PCa, and its inhibition will have antiproliferative effects in human PCa cells. Our data demonstrated that SIRT1 was significantly overexpressed in human PCa cells (DU145, LNCaP, 22Rnu1, and PC3) compared with normal prostate epithelial cells (PrEC) at protein, mRNA, and enzymatic activity levels. SIRT1 was also found to be overexpressed in human PCa tissues compared with adjacent normal prostate tissue. Interestingly, our data demonstrated that SIRT1 inhibition via nicotinamide and Sirtinol (at the activity level) as well as via short hairpin RNA-mediated RNA interference (at the genetic level) resulted in a significant inhibition in the growth and viability of human PCa cells while having no effect on normal prostate epithelial cells. Further, we found that inhibition of SIRT1 caused an increase in FOXO1 acetylation and transcriptional activation in PCa cells. Our data suggested that SIRT1, via inhibiting FOXO1 activation, could contribute to the development of PCa. We suggest that SIRT1 could serve as a target toward developing novel strategies for PCa management.
A novel chalcone polyphenol inhibits the deacetylase activity of SIRT1 and cell growth in HEK293T cells.[Pubmed:19008647]
J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Nov;108(3):364-71. Epub 2008 Nov 13.
SIRT1 is one of seven mammalian orthologs of yeast silent information regulator 2 (Sir2), and it functions as a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)-dependent deacetylase. Recently, resveratrol and its analogues, which are polyphenols, have been reported to activate the deacetylase activity of SIRT1 in an in vitro assay and to expand the life-span of several species through Sir2 and the orthologs. To find activators or inhibitors to SIRT1, we examined thirty-six polyphenols, including stilbenes, chalcones, flavanones, and flavonols, with the SIRT1 deacetylase activity assay using the acetylated peptide of p53 as a substrate. The results showed that 3,2',3',4'-tetrahydroxychalcone, a newly synthesized compound, inhibited the SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of a p53 acetylated peptide and recombinant protein in vitro. In addition, this agent induced the hyperacetylation of endogenous p53, increased the endogenous p21CIP1/WAF1 in intact cells, and suppressed the cell growth. These results indicated that 3,2',3',4'-tetrahydroxychalcone had a stronger inhibitory effect on the SIRT1-pathway than Sirtinol, a known SIRT1-inhibitor. Our results mean that 3,2',3',4'-tetrahydroxychalcone is a novel inhibitor of SIRT1 and produces physiological effects on organisms probably through inhibiting the deacetylation by SIRT1.
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of sirtinol analogues as class III histone/protein deacetylase (Sirtuin) inhibitors.[Pubmed:16302818]
J Med Chem. 2005 Dec 1;48(24):7789-95.
In a search for potent inhibitors of class III histone/protein deacetylases (sirtuins), a series of Sirtinol analogues have been synthesized and the degree of inhibition was assessed in vitro using recombinant yeast Sir2, human SIRT1, and human SIRT2 and in vivo with a yeast phenotypic assay. Two analogues, namely, 3- and 4-[(2-hydroxy-1-naphthalenylmethylene)amino]-N-(1-phenylethyl)benzamide (i.e., m- and p-Sirtinol), were 2- to 10-fold more potent than Sirtinol against human SIRT1 and SIRT2 enzymes. In yeast in vivo assay, these two small molecules were as potent as Sirtinol. Compounds lacking the 2-hydroxy group at the naphthalene moiety or bearing several modifications at the benzene 2'-position of the aniline portion (carbethoxy, carboxy, and cyano) were 1.3-13 times less potent than Sirtinol, whereas the 2'-carboxamido analogue was totally inactive. Both (R)- and (S)-Sirtinol had similar inhibitory effects on the yeast and human enzymes, demonstrating no enantioselective inhibitory effect.
Identification of a class of small molecule inhibitors of the sirtuin family of NAD-dependent deacetylases by phenotypic screening.[Pubmed:11483616]
J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 19;276(42):38837-43.
The yeast transcriptional repressor Sir2p silences gene expression from the telomeric, rDNA, and silent mating-type loci and may play a role in higher order processes such as aging. Sir2p is the founding member of a large family of NAD-dependent deacetylase enzymes, named the sirtuins. These proteins are conserved from prokaryotes to eukaryotes, but most remain uncharacterized, including all seven human sirtuins. A reverse chemical genetic approach would be useful in identifying the biological function of sirtuins in a wide variety of experimental systems, but no cell-permeable small molecule inhibitors of sirtuins have been reported previously. Herein we describe a high throughput, phenotypic screen in cells that led to the discovery of a class of sirtuin inhibitors. All three compounds inhibited yeast Sir2p transcriptional silencing activity in vivo, and yeast Sir2p and human SIRT2 deacetylase activity in vitro. Such specific results demonstrate the utility and robustness of this screening methodology. Structure-activity relationship analysis of the compounds identified a key hydroxy-napthaldehyde moiety that is necessary and sufficient for inhibitory activity. Preliminary studies using one of these compounds suggest that inhibition of sirtuins interferes with body axis formation in Arabidopsis.


