Methyl protodioscinCAS# 54522-52-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

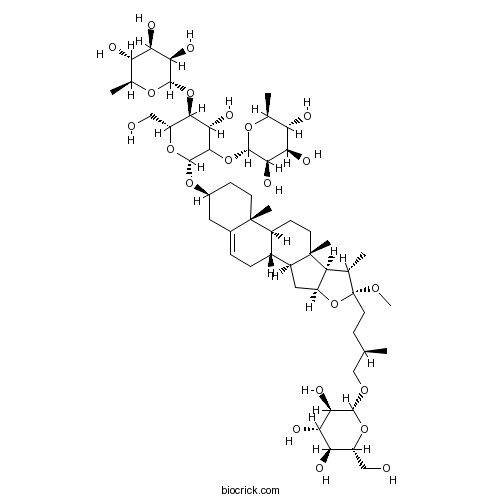
Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 54522-52-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 171347 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C52H86O22 | M.Wt | 1063.23 |
| Type of Compound | Steroids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Methylprotodioscin; CCRIS 4125; | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| SMILES | CC1C2C(CC3C2(CCC4C3CC=C5C4(CCC(C5)OC6C(C(C(C(O6)CO)OC7C(C(C(C(O7)C)O)O)O)O)OC8C(C(C(C(O8)C)O)O)O)C)C)OC1(CCC(C)COC9C(C(C(C(O9)CO)O)O)O)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HSSJYSJXBOCKQM-LXNCCRCLSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C52H86O22/c1-21(20-66-46-40(61)39(60)36(57)31(18-53)70-46)10-15-52(65-7)22(2)33-30(74-52)17-29-27-9-8-25-16-26(11-13-50(25,5)28(27)12-14-51(29,33)6)69-49-45(73-48-42(63)38(59)35(56)24(4)68-48)43(64)44(32(19-54)71-49)72-47-41(62)37(58)34(55)23(3)67-47/h8,21-24,26-49,53-64H,9-20H2,1-7H3/t21-,22+,23+,24+,26+,27-,28+,29+,30+,31-,32-,33+,34+,35+,36-,37-,38-,39+,40-,41-,42-,43+,44-,45?,46-,47+,48+,49-,50+,51+,52-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Methyl protodioscin has anti-thrombosis, antiosteoporotic, anti-myocardial infarction, and cytotoxic activities. Methyl protodioscin shows strong cytotoxicity against most cell lines from solid tumors with GI50 ≤10.0 microM, but moderate cytotoxicity is shown against leukemia cell lines with GI50 10-30 microM. It potentially increase HDL cholesterol while reducing LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, it also can treat diverse inflammatory pulmonary diseases. |
| Targets | LDL | Caspase | Bcl-2/Bax |
| In vitro | Methyl protodioscin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in A549 human lung cancer cells.[Pubmed: 25210320]Pharmacogn Mag. 2014 Jul;10(39):318-24.Methyl protodioscin (MPD) is a furostanol bisglycoside with antitumor properties. It has been shown to reduce proliferation, cause cell cycle arrest.
The present study elucidates the mechanism underlying MPD's apoptotic effects, using the A549 human lung cancer cell line.
The cytotoxicity of methyl protodioscin against human cancer cell lines in vitro.[Pubmed: 12901285]Cancer Invest. 2003 Jun;21(3):389-93.Methyl protodioscin (NSC-698790) was a furostanol saponin isolated from the rhizome of Dioscorea collettii var. hypoglauca (Dioscoreaceae), a Chinese herbal remedy for the treatment of cervical carcinoma, carcinoma of the urinary bladder, and renal tumors for centuries.
|
| In vivo | Dioscin and methylprotodioscin isolated from the root of Asparagus cochinchinensis suppressed the gene expression and production of airway MUC5AC mucin induced by phorbol ester and growth factor.[Pubmed: 25981923 ]Phytomedicine. 2015 May 15;22(5):568-72.The root of Asparagus cochinchinensis (Lour.) Merr. has been utilized as mucoregulators and expectorants for controlling the airway inflammatory diseases in folk medicine.
We investigated whether dioscin and Methyl protodioscin isolated from the root of Asparagus cochinchinensis (Lour.) Merr. suppress the gene expression and production of airway MUC5AC mucin induced by phorbol ester and growth factor.
|
| Kinase Assay | Methyl protodioscin increases ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux while inhibiting gene expressions for synthesis of cholesterol and triglycerides by suppressing SREBP transcription and microRNA 33a/b levels.[Pubmed: 25733328]Atherosclerosis. 2015 Apr;239(2):566-70.Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) regulate homeostasis of LDL, HDL and triglycerides. This study was aimed to determine if inhibition of SREBPs by Methyl protodioscin (MPD) regulates downstream gene and protein expressions of lipid metabolisms.
|
| Cell Research | In vivo antiosteoporotic activity of a fraction of Dioscorea spongiosa and its constituent, 22-O-methylprotodioscin.[Pubmed: 15114498]Planta Med. 2004 Mar;70(3):220-6.Methyl protodioscin (NSC-698790) was a furostanol saponin isolated from the rhizome of Dioscorea collettii var. hypoglauca (Dioscoreaceae), a Chinese herbal remedy for the treatment of cervical carcinoma, carcinoma of the urinary bladder, and renal tumors for centuries.
|
| Animal Research | Therapeutic Effects of Methyl Protodioscin for Myocardial Infarction in Rats[Reference: WebLink]Effects of Methyl Protodioscin on In-Vivo and In-Vitro Thrombosis and Blood Viscosity in Rats[Reference: WebLink]Traditional Chinese Drug Research & Clinical Pharmacology,2008, 19(1):3-5.To investigate the effects of Methyl protodioscin (MPD ) on in-vitro and in-vivo thrombosis and blood viscosity in rats.
Traditional Chinese Drug Research & Clinical Pharmacology,2008, 19(1):1-3.To study the therapeutic effects of Methyl protodioscin (MPD ) on myocardial infarction in rats.
|

Methyl protodioscin Dilution Calculator

Methyl protodioscin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.9405 mL | 4.7027 mL | 9.4053 mL | 18.8106 mL | 23.5133 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.1881 mL | 0.9405 mL | 1.8811 mL | 3.7621 mL | 4.7027 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.0941 mL | 0.4703 mL | 0.9405 mL | 1.8811 mL | 2.3513 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0188 mL | 0.0941 mL | 0.1881 mL | 0.3762 mL | 0.4703 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0094 mL | 0.047 mL | 0.0941 mL | 0.1881 mL | 0.2351 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Methyl protodioscin(NSC-698790) is a furostanol bisglycoside with antitumor properties; shows to reduce proliferation, cause cell cycle arrest. IC50 value: Target: in vitro: MPD showed growth inhibitory effects in A549 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The significant G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptotic effect were also seen in A549 cells treated with MPD. MPD-induced apoptosis was accompanied by a significant reduction of mitochondrial membrane potential, release of mitochondrial cytochrome c to cytosol, activation of caspase-3, downregulation of Bcl-2, p-Bad, and upregulation of Bax [1]. In THP-1 macrophages, MPD increases levels of ABCA1 mRNA and protein in dose- and time-dependent manners, and apoA-1-mediated cholesterol efflux. MPD also decreases the gene expressions of HMGCR, FAS and ACC for cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis [2].
References:
[1]. Bai Y, et al. Methyl protodioscin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in A549 human lung cancer cells. Pharmacogn Mag. 2014 Jul;10(39):318-24.
[2]. Ma W, et al. Methyl protodioscin increases ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux while inhibiting gene expressions for synthesis of cholesterol and triglycerides by suppressing SREBP transcription and microRNA 33a/b levels. Atherosclerosis. 2015 Apr;239
- H-Leu-CMK.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2971
CAS No.:54518-92-2
- 5-Aminolevulinic acid HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4883
CAS No.:5451-09-2
- Erythrodiol
Catalog No.:BCN5726
CAS No.:545-48-2
- Lupeol
Catalog No.:BCN5725
CAS No.:545-47-1
- Uvaol
Catalog No.:BCN5724
CAS No.:545-46-0
- 5-Glutinen-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN5723
CAS No.:545-24-4
- Jolkinolide E
Catalog No.:BCN3772
CAS No.:54494-34-7
- 3alpha-dihydrocadambine
Catalog No.:BCN8151
CAS No.:54483-84-0
- JNJ 10181457 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7842
CAS No.:544707-20-2
- UBP 282
Catalog No.:BCC7171
CAS No.:544697-47-4
- MRS 1845
Catalog No.:BCC7198
CAS No.:544478-19-5
- c-di-AMP
Catalog No.:BCC8054
CAS No.:54447-84-6
- Methyl protogracillin
Catalog No.:BCN8177
CAS No.:54522-53-1
- Nicardipine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4685
CAS No.:54527-84-3
- QNZ (EVP4593)
Catalog No.:BCC2249
CAS No.:545380-34-5
- AMG 9810
Catalog No.:BCC7329
CAS No.:545395-94-6
- Quercetin-3-O-glucose-6'-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN6545
CAS No.:54542-51-7
- Doxercalciferol
Catalog No.:BCC4902
CAS No.:54573-75-0
- Conessine
Catalog No.:BCC7352
CAS No.:546-06-5
- Alantolactone
Catalog No.:BCN1033
CAS No.:546-43-0
- α-Thujone
Catalog No.:BCC8271
CAS No.:546-80-5
- Columbin
Catalog No.:BCN2622
CAS No.:546-97-4
- Boc-Lys(2-Cl-Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3416
CAS No.:54613-99-9
- URB597
Catalog No.:BCC2324
CAS No.:546141-08-6
The cytotoxicity of methyl protodioscin against human cancer cell lines in vitro.[Pubmed:12901285]
Cancer Invest. 2003 Jun;21(3):389-93.
Methyl protodioscin (NSC-698790) was a furostanol saponin isolated from the rhizome of Dioscorea collettii var. hypoglauca (Dioscoreaceae), a Chinese herbal remedy for the treatment of cervical carcinoma, carcinoma of the urinary bladder, and renal tumors for centuries. To systematically evaluate its potential anticancer activity, Methyl protodioscin was tested cytotoxicity in vitro against human cancer cell lines by the NCI's (National Cancer Institute) anticancer drug screen. As a result, Methyl protodioscin showed strong cytotoxicity against most cell lines from solid tumors with GI50 < or = 10.0 microM, especially selectively against one colon cancer line (HCT-15) and one breast cancer line (MDA-MB-435) with GI50 < 2.0 microM but moderate cytotoxicity was shown against leukemia cell lines with GI50 10-30 microM. The data are consistent with the fact that the rhizome of D. collettii var. hypoglauca has been employed for the treatment of solid tumors rather than leukemia in China for centuries. Based on an analysis using the COMPARE computer program with Methyl protodioscin as a seed compound, no compounds in the NCI's anticancer drug screen database have cytotoxicity patterns similar to those of Methyl protodioscin, indicating a potential novel mechanism of anticancer action.
In vivo antiosteoporotic activity of a fraction of Dioscorea spongiosa and its constituent, 22-O-methylprotodioscin.[Pubmed:15114498]
Planta Med. 2004 Mar;70(3):220-6.
The antiosteoporotic activity of the 90 % EtOH fraction of the water extract of rhizomes of Dioscorea spongiosa and methylprotodioscin, its major constituent, were examined in the model of postmenopausal bone loss using ovariectomized (OVX) rats or mice. After 6 weeks treatment, the proximal tibia of rats or mice and the distal femora of mice were scanned by peripheral quantitative computed tomography (pQCT). Both the 90 % EtOH fraction (100 mg/kg/d) and methylprotodioscin (50 mg/kg/d) significantly inhibited bone loss in bone mineral content (BMC) and bone mineral density (BMD) in total, cancellous and cortical bones, and the decrease in bone strength indexes induced by OVX, without side effect on the uterus.
Dioscin and methylprotodioscin isolated from the root of Asparagus cochinchinensis suppressed the gene expression and production of airway MUC5AC mucin induced by phorbol ester and growth factor.[Pubmed:25981923]
Phytomedicine. 2015 May 15;22(5):568-72.
BACKGROUND: The root of Asparagus cochinchinensis (Lour.) Merr. has been utilized as mucoregulators and expectorants for controlling the airway inflammatory diseases in folk medicine. HYPOTHESIS/PURPOSE: We investigated whether dioscin and methylprotodioscin isolated from the root of Asparagus cochinchinensis (Lour.) Merr. suppress the gene expression and production of airway MUC5AC mucin induced by phorbol ester and growth factor. STUDY DESIGN: Confluent NCI-H292 cells were pretreated with dioscin or methylprotodioscin for 30 min and then stimulated with EGF or PMA for 24 h. The MUC5AC mucin gene expression was measured by RT-PCR. Production of MUC5AC mucin protein was measured by ELISA. RESULTS: (1) Dioscin and methylprotodioscin suppressed the expression of MUC5AC mucin gene induced by EGF or PMA; (2) dioscin suppressed the production of MUC5AC mucin induced by either EGF at 10(-5) M (p < 0.05) and 10(-6) M (p < 0.05) or PMA at 10(-4) M (p < 0.05), 10(-5) M (p < 0.05) and 10(-6) M (p < 0.05); (3) methylprotodioscin also suppressed the production of MUC5AC mucin induced by either EGF at 10(-4) M (p < 0.05) or PMA at 10(-4) M (p < 0.05). CONCLUSION: These results suggest that dioscin and methylprotodioscin isolated from the root of Asparagus cochinchinensis suppress the gene expression and production of MUC5AC mucin, by directly acting on airway epithelial cells, and the results are consistent with the traditional use of Asparagus cochinchinensis as remedy for diverse inflammatory pulmonary diseases.
Methyl protodioscin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in A549 human lung cancer cells.[Pubmed:25210320]
Pharmacogn Mag. 2014 Jul;10(39):318-24.
BACKGROUND: Methyl protodioscin (MPD) is a furostanol bisglycoside with antitumor properties. It has been shown to reduce proliferation, cause cell cycle arrest. OBJECTIVE: The present study elucidates the mechanism underlying MPD's apoptotic effects, using the A549 human lung cancer cell line. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The human pulmonary adenocarcinoma cell line A549 was obtained from the Cell Bank of the Animal Experiment Center, North School Region, Sun Yat-Sen University. All of the cells were grown in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA), penicillin (10,000 U/l), and streptomycin (100 mg/l) at 37 degrees C in a 5% CO2 humidified atmosphere. The induction of apoptosis was observed in flow cytometry and fluorescent staining experiments. RESULTS: MPD showed growth inhibitory effects in A549 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The significant G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptotic effect were also seen in A549 cells treated with MPD. MPD-induced apoptosis was accompanied by a significant reduction of mitochondrial membrane potential, release of mitochondrial cytochrome c to cytosol, activation of caspase-3, downregulation of Bcl-2, p-Bad, and upregulation of Bax. CONCLUSION: Our results show that the induction of apoptosis by MPD involves multiple molecular pathways and strongly suggest that Bcl-2 family proteins signaling pathways. In addition, mitochondrial membrane potential, mitochondrial cytochrome c and caspase-3 were also closely associated with MPD-induced apoptotic process in human A549 cells.
Methyl protodioscin increases ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux while inhibiting gene expressions for synthesis of cholesterol and triglycerides by suppressing SREBP transcription and microRNA 33a/b levels.[Pubmed:25733328]
Atherosclerosis. 2015 Apr;239(2):566-70.
Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) regulate homeostasis of LDL, HDL and triglycerides. This study was aimed to determine if inhibition of SREBPs by Methyl protodioscin (MPD) regulates downstream gene and protein expressions of lipid metabolisms. In THP-1 macrophages, MPD increases levels of ABCA1 mRNA and protein in dose- and time-dependent manners, and apoA-1-mediated cholesterol efflux. The underlying mechanisms for the effects is that MPD inhibits the transcription of SREBP1c and SREBP2, and decreases levels of microRNA 33a/b hosted in the introns of SREBPs, which leads to reciprocally increase ABCA1 levels. In HepG2 cells, MPD shows the same effects as these observed in THP-1 macrophages. MPD also decreases the gene expressions of HMGCR, FAS and ACC for cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis. MPD further promotes LDL receptor through reducing the PCSK9 level. Collectively, the study demonstrates that MPD potentially increase HDL cholesterol while reducing LDL cholesterol and triglycerides.


