FlavopiridolPan-cdk inhibitor CAS# 146426-40-6 |
- LY2835219
Catalog No.:BCC1113
CAS No.:1231930-82-7
- Roscovitine (Seliciclib,CYC202)
Catalog No.:BCC1105
CAS No.:186692-46-6
- Nu 6027
Catalog No.:BCC1154
CAS No.:220036-08-8
- SNS-032 (BMS-387032)
Catalog No.:BCC1152
CAS No.:345627-80-7
- AT7519 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1376
CAS No.:902135-91-5
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 146426-40-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5459219 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H20ClNO5 | M.Wt | 401.85 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | L868275; HMR-1275; Alvocidib | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 33.33 mg/mL (82.94 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
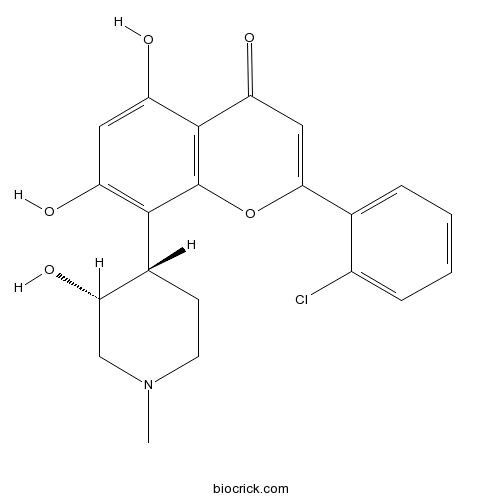
| Chemical Name | 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-8-[(3R,4S)-3-hydroxy-1-methylpiperidin-4-yl]chromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CN1CCC(C(C1)O)C2=C(C=C(C3=C2OC(=CC3=O)C4=CC=CC=C4Cl)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BIIVYFLTOXDAOV-PXAZEXFGSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H20ClNO5/c1-23-7-6-12(17(27)10-23)19-14(24)8-15(25)20-16(26)9-18(28-21(19)20)11-4-2-3-5-13(11)22/h2-5,8-9,12,17,24-25,27H,6-7,10H2,1H3/t12-,17+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Flavopiridol is a broad inhibitor of CDK, competing with ATP to inhibit CDKs including CDK1, CDK2, CDK4 with IC50s of 30, 170, 100 nM, respectively.In Vitro:Flavopiridol (2 μM) robustly induces a distinct pattern of ER stress in CLL cells that contributes to cell death through IRE1-mediated activation of ASK1 and possibly downstream caspases[1]. Flavopiridol results in potent upregulation of a number of PRGs in treatments lasting 4-24 h. Flavopiridol has and immediate and long-term effect on the expression of several PRGs. In serum starved cells re-stimulated with serum, flavopiridol also inhibits the expression of these genes, but subsequently, JUNB, GADD45B and EGR1 are upregulated in the presence of flavopiridol[2]. References: | |||||

Flavopiridol Dilution Calculator

Flavopiridol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4885 mL | 12.4425 mL | 24.8849 mL | 49.7698 mL | 62.2123 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4977 mL | 2.4885 mL | 4.977 mL | 9.954 mL | 12.4425 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2488 mL | 1.2442 mL | 2.4885 mL | 4.977 mL | 6.2212 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0498 mL | 0.2488 mL | 0.4977 mL | 0.9954 mL | 1.2442 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0249 mL | 0.1244 mL | 0.2488 mL | 0.4977 mL | 0.6221 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Flavopiridol is a potent and selective inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) with IC50 values of ~41 nM for CDK1, CDK2, CDK4, CDK6 and 300 nM for CDK7, respectively [1].
CDKs are a family of protein kinases regulating the cell cycle and play an important role in transcription, mRNA processing, and cell differentiation.
Analysis of the crystal structure suggested flavopiridol binded to the ATP-binding pocket of CDK2. In MCF-7 breast cancer cells, flavopiridol reduced the mRNA level of cyclin D1 protein and cyclin D3 protein [1]. In 23 human tumor cell models, flavopiridol significantly inhibited human bone marrow colony formation between 10 and 100 ng/ml [2].
In prostate cancer xenograft PRXFI369, flavopinidol (10 mg/kg/day) had antitumor activity of optimal test/control (T/C) of 33% and a growth delay of 30 days. Also, it reduced tumor volume by 85%. In prostate cancer xenograft PRXFI337, the optimal T/C was 27% and the growth delay was 17 days [2].
References:
[1]. Senderowicz AM. The cell cycle as a target for cancer therapy: basic and clinical findings with the small molecule inhibitors flavopiridol and UCN-01. Oncologist, 2002, 7 Suppl 3: 12-9.
[2]. Drees M, Dengler WA, Roth T, et al. Flavopiridol (L86-8275): selective antitumor activity in vitro and activity in vivo for prostate carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res, 1997, 3(2): 273-279.
[3]. Carlson BA, Dubay MM, Sausville EA, et al. Flavopiridol induces G1 arrest with inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 2 and CDK4 in human breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res, 1996, 56(13): 2973-2978.
- Lactose
Catalog No.:BCN8387
CAS No.:14641-93-1
- Desmethylrocaglamide
Catalog No.:BCN7735
CAS No.:146408-78-8
- SR 48692
Catalog No.:BCC7763
CAS No.:146362-70-1
- N-Methyllidocaine iodide
Catalog No.:BCC6905
CAS No.:1462-71-1
- Chlorajapolide F
Catalog No.:BCN6425
CAS No.:1461760-59-7
- R-(-)-Deprenyl hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5196
CAS No.:14611-52-0
- Z-Arg(Z)2-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3574
CAS No.:14611-34-8
- Pulchinenoside E1
Catalog No.:BCN8185
CAS No.:146100-02-9
- Dihydromarein
Catalog No.:BCN8406
CAS No.:
- MSDC-0160
Catalog No.:BCC5343
CAS No.:146062-49-9
- Tauroursodeoxycholic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6953
CAS No.:14605-22-2
- SC 51089
Catalog No.:BCC7773
CAS No.:146033-02-5
- Camaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN1650
CAS No.:146450-83-1
- Pralatrexate
Catalog No.:BCC2304
CAS No.:146464-95-1
- 1-Methylpsilocin
Catalog No.:BCC7536
CAS No.:1465-16-3
- Complanatoside A
Catalog No.:BCN6282
CAS No.:146501-37-3
- WR 1065
Catalog No.:BCC2417
CAS No.:14653-77-1
- Tyrphostin AG 1296
Catalog No.:BCC1195
CAS No.:146535-11-7
- Fmoc-Gly(allyl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3156
CAS No.:146549-21-5
- 2-Cyclopropyl-3-[(diphenylphosphinyl)methyl]-4-(4-fluorophenyl)quinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8572
CAS No.:146578-99-6
- 2,6-Dimethoxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1651
CAS No.:1466-76-8
- Dantrolene, sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6673
CAS No.:14663-23-1
- H-Trp(Boc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3115
CAS No.:146645-63-8
- SR 2640 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7180
CAS No.:146662-42-2
Intrathecal Administration of Flavopiridol Promotes Regeneration in Experimental Model of Spinal Cord Injury.[Pubmed:27476919]
Turk Neurosurg. 2016;26(6):922-929.
AIM: Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a serious condition of the central nervous system and it affects the quality of life and even hampers the day-to-day activity of the patient. In the current study, we investigated the efficacy of intrathecal administration of Flavopiridol in an experimental animal model of SCI. The study also aimed at exploring the physiological effects of Flavopiridol on neurons, astrocytes and cell cycle regulatory proteins. MATERIAL AND METHODS: In vitro scratch wound experiments were performed on female Sprague-Dawley rats (n=23). A complete hemisection to the right of T10 was made, and Flavopiridol solution (200 mM, 0.8 nmol Flavopiridol/animal) was delivered topically to the lesion site. Cell viability assay, in vitro scratch injury assay, cell cycle analysis using flow cytometry and behavioural assessments were performed. RESULTS: The local delivery of Flavopiridol reduced cavity formation and improved regeneration of neurons with improvement in physiological performance. Flavopiridol also inhibited the migration and proliferation of astrocytes, and at the same time, promoted the survival of neurons. CONCLUSION: Intrathecal administration of Flavopiridol can be a promising treatment strategy in patients with SCI and it needs to be validated in patient setting.
Exposure-Response Analysis of Alvocidib (Flavopiridol) Treatment by Bolus or Hybrid Administration in Newly Diagnosed or Relapsed/Refractory Acute Leukemia Patients.[Pubmed:28174232]
Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Jul 15;23(14):3592-3600.
Purpose: To elucidate any differences in the exposure-response of alvocidib (Flavopiridol) given by 1-hour bolus or a hybrid schedule (30-minute bolus followed by a 4-hour infusion) using a Flavopiridol/cytosine arabinoside/mitoxantrone sequential protocol (FLAM) in patients with acute leukemia. The hybrid schedule was devised to be pharmacologically superior in chronic leukemia based on unbound exposure.Experimental Design: Data from 129 patients in three FLAM studies were used for pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling. Newly diagnosed (62%) or relapsed/refractory (38%) patients were treated by bolus (43%) or hybrid schedule (57%). Total and unbound Flavopiridol concentrations were fit using nonlinear mixed-effect population pharmacokinetic methodologies. Exposure-response relationships using unbound Flavopiridol AUC were explored using recursive partitioning.Results: Flavopiridol pharmacokinetic parameters were estimated using a two-compartment model. No pharmacokinetic covariates were identified. Flavopiridol fraction unbound was 10.9% and not different between schedules. Partitioning found no association between dosing schedule and clinical response. Clinical response was associated with AUC >/= 780 h*ng/mL for newly diagnosed patients and AUC >/= 1,690 h*ng/mL for relapsed/refractory patients. Higher exposures were not associated with increases in severe adverse events (>/= grade 3).Conclusions: Pharmacokinetic modeling showed no difference in Flavopiridol plasma protein binding for bolus versus hybrid dosing. Further trials in newly diagnosed patients with acute leukemia should utilize the bolus FLAM regimen at the MTD of 50 mg/m(2)/day. Trials in relapsed/refractory patients should use the hybrid dosing schedule at the MTD (30/60 mg/m(2)/day) to achieve the higher exposures required for maximal efficacy in this population. Clin Cancer Res; 23(14); 3592-600. (c)2017 AACR.
Effects of flavopiridol on critical regulation pathways of CD133high/CD44high lung cancer stem cells.[Pubmed:27787370]
Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Oct;95(43):e5150.
BACKGROUND: Flavopiridol a semisynthetic flavone that inhibits cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and has growth-inhibitory activity and induces a blockade of cell-cycle progression at G1-phase and apoptosis in numerous human tumor cell lines and is currently under investigation in phase II clinical trials. Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are comprised of subpopulation of cells in tumors that have been proposed to be responsible for recurrence and resistance to chemotherapy. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of Flavopiridol in cancer stem cell cytoskeleton, cell adhesion, and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in CSCs. METHODS: The cells were treated with Flavopiridol to determine the inhibitory effect. Cell viability and proliferation were determined by using the WST-1 assay. Caspase activity and immunofluorescence analyses were performed for the evaluation of apoptosis, cell cytoskeleton, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers. The effects of Flavopiridol on the cell cycle were also evaluated. Flow cytometric analysis was used to detect the percentages of CSCs subpopulation. We analyzed the gene expression patterns to predict cell cycle and cell cytoskeleton in CSCs by RT-PCR. RESULTS: Flavopiridol-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis at the IC50 dose, resulting in a significant increase expression of caspases activity. Cell cycle analyses revealed that Flavopiridol induces G1 phase cell cycle arrest. Flavopiridol significantly decreased the mRNA expressions of the genes that regulate the cell cytoskeleton and cell cycle components and cell motility in CSCs. CONCLUSION: Our results suggest that Flavopiridol has activity against lung CSCs and may be effective chemotherapeutic molecule for lung cancer treatment.
Flavopiridol: An Old Drug With New Perspectives? Implication for Development of New Drugs.[Pubmed:27171480]
J Cell Physiol. 2017 Feb;232(2):312-322.
Glioblastoma, the most common brain tumor, is characterized by high proliferation rate, invasion, angiogenesis, and chemo- and radio-resistance. One of most remarkable feature of glioblastoma is the switch toward a glycolytic energetic metabolism that leads to high glucose uptake and consumption and a strong production of lactate. Activation of several oncogene pathways like Akt, c-myc, and ras induces glycolysis and angiogenesis and acts to assure glycolysis prosecution, tumor proliferation, and resistance to therapy. Therefore, the high glycolytic flux depends on the overexpression of glycolysis-related genes resulting in an overproduction of pyruvate and lactate. Metabolism of glioblastoma thus represents a key issue for cancer research. Flavopiridol is a synthetic flavonoid that inhibits a wide range of Cyclin-dependent kinase, that has been demonstrate to inactivate glycogen phosphorylase, decreasing glucose availability for glycolysis. In this work the study of glucose metabolism upon Flavopiridol treatment in the two different glioblastoma cell lines. The results obtained point towards an effect of Flavopiridol in glycolytic cells, thus suggesting a possible new use of this compound or Flavopiridol-derived formulations in combination with anti-proliferative agents in glioblastoma patients. J. Cell. Physiol. 232: 312-322, 2017. (c) 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.


