Flavokawain CCAS# 37308-75-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

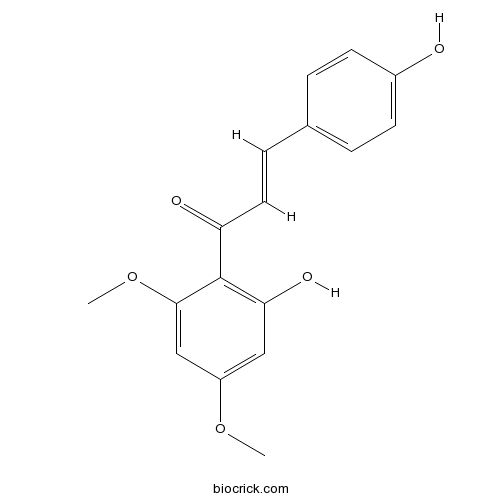
Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 37308-75-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6293081 | Appearance | Yellow-orange powder |
| Formula | C17H16O5 | M.Wt | 300.3 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Flavokawin C;56798-34-6 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in chloroform and methan | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=C(C(=C1)OC)C(=O)C=CC2=CC=C(C=C2)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UXUFMIJZNYXWDX-VMPITWQZSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H16O5/c1-21-13-9-15(20)17(16(10-13)22-2)14(19)8-5-11-3-6-12(18)7-4-11/h3-10,18,20H,1-2H3/b8-5+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Flavokawain C is a melanogenesis inhibitor, it inhibited melanogenesis with IC50 values of 6.9 uM. Flavokawain C has anti-tumor activity, it inhibited cell cycle and promoted apoptosis, associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress and regulation of MAPKs and Akt signaling pathways in HCT 116 human colon carcinoma cells.Flavokawain B and flavokawain C are melanogenesis inhibitors, they inhibit melanogenesis with IC50 values of 7.7uM and 6.9 uM, respectively. Flavokawain C inhibits cell cycle and promotes apoptosis, associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress and regulation of MAPKs and Akt signaling pathways in HCT 116 human colon carcinoma cells. |
| Targets | NADPH-oxidase | AChR | MAPK | Akt |
| In vitro | The flavokawains: uprising medicinal chalcones[Reference: WebLink]Cancer Cell International 2013, 13:102Plant-based compounds have been in the spotlight in search of new and promising drugs. Flavokawains B and C, melanogenesis inhibitors, isolated from the root of Piper methysticum and synthesis of analogs.[Pubmed: 25597012]Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Feb 15;25(4):799-802.The ethanolic extract of the root of Piper methysticum was found to inhibit melanogenesis in MSH-activated B16 melanoma cells. |
| Cell Research | Flavokawain C Inhibits Cell Cycle and Promotes Apoptosis, Associated with Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Regulation of MAPKs and Akt Signaling Pathways in HCT 116 Human Colon Carcinoma Cells.[Pubmed: 26859847 ]PLoS One. 2016 Feb 9;11(2):e0148775.Flavokawain C (FKC) is a naturally occurring chalcone which can be found in Kava (Piper methysticum Forst) root. The present study evaluated the effect of FKC on the growth of various human cancer cell lines and the underlying associated mechanisms. |

Flavokawain C Dilution Calculator

Flavokawain C Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.33 mL | 16.65 mL | 33.3 mL | 66.6001 mL | 83.2501 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.666 mL | 3.33 mL | 6.66 mL | 13.32 mL | 16.65 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.333 mL | 1.665 mL | 3.33 mL | 6.66 mL | 8.325 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0666 mL | 0.333 mL | 0.666 mL | 1.332 mL | 1.665 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0333 mL | 0.1665 mL | 0.333 mL | 0.666 mL | 0.8325 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- H-D-Tyr-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3135
CAS No.:3728-20-9
- Sennoside D
Catalog No.:BCN1005
CAS No.:37271-17-3
- Sennoside C
Catalog No.:BCN1004
CAS No.:37271-16-2
- TCS OX2 29
Catalog No.:BCC7670
CAS No.:372523-75-6
- Wilfordine
Catalog No.:BCN3083
CAS No.:37239-51-3
- Wilfortrine
Catalog No.:BCN3085
CAS No.:37239-48-8
- Wilforgine
Catalog No.:BCN5427
CAS No.:37239-47-7
- Sieber Linker
Catalog No.:BCC2835
CAS No.:3722-51-8
- PIK-75
Catalog No.:BCC1163
CAS No.:372196-77-5
- Citromycin
Catalog No.:BCN7459
CAS No.:37209-30-6
- Capsidiol
Catalog No.:BCC8140
CAS No.:37208-05-2
- L-Citruline
Catalog No.:BCN2692
CAS No.:372-75-8
- 3-Quinuclidinone
Catalog No.:BCC8642
CAS No.:3731-38-2
- Decloxizine
Catalog No.:BCC5529
CAS No.:3733-63-9
- Cephaeline Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8307
CAS No.:3738-70-3
- DS2
Catalog No.:BCC7748
CAS No.:374084-31-8
- Boc-DL-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3050
CAS No.:3744-87-4
- Istaroxime hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1661
CAS No.:374559-48-5
- Kisspeptin 10 (human)
Catalog No.:BCC7415
CAS No.:374675-21-5
- Metastin (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5761
CAS No.:374683-24-6
- DHP Linker
Catalog No.:BCC2830
CAS No.:3749-36-8
- Amikacin
Catalog No.:BCC5206
CAS No.:37517-28-5
- 2-Chlorocinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5036
CAS No.:3752-25-8
- LY451395
Catalog No.:BCC5377
CAS No.:375345-95-2
Induction of Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest by Flavokawain C on HT-29 Human Colon Adenocarcinoma via Enhancement of Reactive Oxygen Species Generation, Upregulation of p21, p27, and GADD153, and Inactivation of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins.[Pubmed:28808400]
Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Jul;13(Suppl 2):S321-S328.
Chalcones have been shown to exhibit anti-cancer properties by targeting multiple molecular pathways. It was, therefore, of interest to investigate Flavokawain C (FKC), a naturally occurring chalcone, which can be isolated from Kava (Piper methysticum Forst) root extract. The aim of this study was to investigate the inhibitory effect of FKC on the growth of HT-29 cells and its underlying mechanism of action. Cell viability of HT-29 cells was assessed by Sulforhodamine B assay after FKC treatment. Induction of apoptosis was examined by established morphological and biochemical assays. ROS generation was determined by dichlorofluorescein fluorescence staining, and superoxide dismutase activity was measured using the spectrophotometric method. Western blotting was used to examine the changes in the protein levels. FKC markedly decreased the cell viability of HT-29 cells and the cells showed dramatic changes in cellular and nuclear morphologies with typical apoptotic features. The induction of apoptosis correlated well with the externalization of phosphatidylserine, DNA fragmentation, decreased mitochondrial membrane potential, activation of caspases, and PARP cleavage. This was associated with an increase in reactive oxygen species and a decrease in SOD activity. The protein levels of XIAP, c-IAP1, and c-IAP2 were downregulated, whereas the GADD153 was upregulated after FKC treatment. FKC induced cell cycle arrest at the G1 and G2/M phases via upregulation of p21 and p27 in a p53-independent manner. Our results provide evidence that FKC has the potential to be developed into chemotherapeutic drug for the treatment of colon adenocarcinoma. SUMMARY: Flavokawain C inhibited the growth of HT-29 human colon adenocarcinoma cellsFlavokawain C induced apoptosis in HT-29 cells, associated with an increase in reactive oxygen species and a decrease in SOD activityFlavokawain C induced cell cycle arrest at the G1 and G2/M phases via upregulation of p21 and p27 in HT-29 cellsHT-29 cells treated with Flavokawain C caused downregulation of XIAP, c-IAP1, and c-IAP2, and upregulation of GADD153. Abbreviations used: FKC: Flavokawain C; SRB: Sulforhodamine B; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; PARP: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; IAPs: Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins; TUNEL: Transferase dUTP nick end labeling; Annexin V-FITC: Annexin V conjugated with fluorescein isothicyanate.
Phenols displaying tyrosinase inhibition from Humulus lupulus.[Pubmed:26162028]
J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016 Oct;31(5):742-7.
Tyrosinase is the rate-limiting enzyme for the production of melanin and other pigments via the oxidation of l-tyrosine. The methanol extract from Humulus lupulus showed potent inhibition against mushroom tyrosinase. The bioactivity-guided fractionation of this methanol extract resulted in the isolation of seven flavonoids (1-7), identified as xanthohumol (1), 4'-O-methylxanthohumol (2), xanthohumol C (3), Flavokawain C (4), xanthoumol B (5), 6-prenylnaringenin (6) and isoxanthohumol (7). All isolated flavonoids (1-7) effectively inhibited the monophenolase (IC50s = 15.4-58.4 microM) and diphenolase (IC50s = 27.1-117.4 microM) activities of tyrosinase. Kinetic studies using Lineweaver-Burk and Dixon-plots revealed that chalcones (1-5) were competitive inhibitors, whereas flavanones (6 and 7) exhibited both mixed and non-competitive inhibitory characteristics. In conclusion, this study is the first to demonstrate that the phenolic phytochemicals of H. lupulus display potent inhibitory activities against tyrosinase.
Flavokawains B and C, melanogenesis inhibitors, isolated from the root of Piper methysticum and synthesis of analogs.[Pubmed:25597012]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Feb 15;25(4):799-802.
The ethanolic extract of the root of Piper methysticum was found to inhibit melanogenesis in MSH-activated B16 melanoma cells. Flavokawains B and C were isolated from this extract based on their anti-melanogenesis activity and found to inhibit melanogenesis with IC50 values of 7.7muM and 6.9muM, respectively. Flavokawain analogs were synthesized through a Claisen-Schmidt condensation of their corresponding acetophenones and benzaldehydes and were evaluated in terms of their tyrosinase inhibitory and anti-melanogenesis activities. Compound 1b was the most potent of these with an IC50 value of 2.3muM in melanogenesis inhibition assays using MSH-activated B16 melanoma cells.
Flavokawain C Inhibits Cell Cycle and Promotes Apoptosis, Associated with Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Regulation of MAPKs and Akt Signaling Pathways in HCT 116 Human Colon Carcinoma Cells.[Pubmed:26859847]
PLoS One. 2016 Feb 9;11(2):e0148775.
Flavokawain C (FKC) is a naturally occurring chalcone which can be found in Kava (Piper methysticum Forst) root. The present study evaluated the effect of FKC on the growth of various human cancer cell lines and the underlying associated mechanisms. FKC showed higher cytotoxic activity against HCT 116 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner in comparison to other cell lines (MCF-7, HT-29, A549 and CaSki), with minimal toxicity on normal human colon cells. The apoptosis-inducing capability of FKC on HCT 116 cells was evidenced by cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation and increased phosphatidylserine externalization. FKC was found to disrupt mitochondrial membrane potential, resulting in the release of Smac/DIABLO, AIF and cytochrome c into the cytoplasm. Our results also revealed that FKC induced intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis via upregulation of the levels of pro-apoptotic proteins (Bak) and death receptors (DR5), while downregulation of the levels of anti-apoptotic proteins (XIAP, cIAP-1, c-FlipL, Bcl-xL and survivin), resulting in the activation of caspase-3, -8 and -9 and cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). FKC was also found to cause endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, as suggested by the elevation of GADD153 protein after FKC treatment. After the cells were exposed to FKC (60muM) over 18hrs, there was a substantial increase in the phosphorylation of ERK 1/2. The expression of phosphorylated Akt was also reduced. FKC also caused cell cycle arrest in the S phase in HCT 116 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner and with accumulation of cells in the sub-G1 phase. This was accompanied by the downregulation of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK2 and CDK4), consistent with the upregulation of CDK inhibitors (p21Cip1 and p27Kip1), and hypophosphorylation of Rb.
Comparative evaluation of cytotoxicity and antioxidative activity of 20 flavonoids.[Pubmed:18433100]
J Agric Food Chem. 2008 May 28;56(10):3876-83.
Flavonoids are common dietary components with many health benefits shown through epidemiological studies. However, the fact that flavonoids also act as pro-oxidants and mutagens makes the safety of flavonoids uncertain when used at higher doses. To give a preliminary evaluation on the correlation between beneficial and harmful effects of flavonoids, the antioxidative activity and cytotoxicity of 20 flavonoids from food and herbs were investigated in vitro. The results indicated that luteolin, hydroxygenkwanin, and kaempferol possessed significant dual properties, whereas flavokawain B, Flavokawain C, cardamonin, and uvangoletin showed a marked cytotoxicity. The relationships between structure and antioxidant and cytotoxic activity are intensively discussed. In view of the toxicity, the intake of flavonoids in large amounts should not yet be encouraged.


