DihydrokavainCAS# 587-63-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

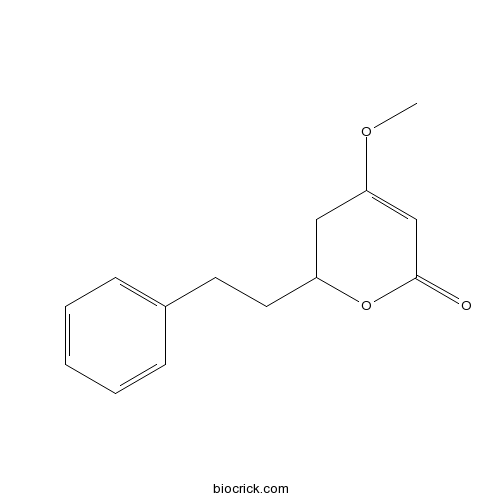
Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 587-63-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 98356 | Appearance | White-pale yellow powder |
| Formula | C14H16O3 | M.Wt | 232.27 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 7,8-Dihydrokawain; 7,8-Dihydrokavain; Marindinin | ||
| Solubility | Freely soluble in dioxane and methanol; slightly soluble in water | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-methoxy-2-(2-phenylethyl)-2,3-dihydropyran-6-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=O)OC(C1)CCC2=CC=CC=C2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VOOYTQRREPYRIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H16O3/c1-16-13-9-12(17-14(15)10-13)8-7-11-5-3-2-4-6-11/h2-6,10,12H,7-9H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Dihydrokavain may play an important role in regulation of GABAergic neurotransmission, it non-competitively inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-batrachotoxinin-A 20-alpha-benzoate to receptor site 2 of voltage-gated Na+ channels. Dihydrokavain may treat sleep disturbances, as well as stress and anxiety. |
| Targets | GABA Receptor | Sodium channel |
| In vitro | Kavalactones and dihydrokavain modulate GABAergic activity in a rat gastric-brainstem preparation.[Pubmed: 12494336]Planta Med. 2002 Dec;68(12):1092-6.
|
| Kinase Assay | Kavain, dihydrokavain, and dihydromethysticin non-competitively inhibit the specific binding of [3H]-batrachotoxinin-A 20-alpha-benzoate to receptor site 2 of voltage-gated Na+ channels.[Pubmed: 9690349]Planta Med. 1998 Jun;64(5):458-9.
|

Dihydrokavain Dilution Calculator

Dihydrokavain Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.3053 mL | 21.5267 mL | 43.0533 mL | 86.1067 mL | 107.6334 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8611 mL | 4.3053 mL | 8.6107 mL | 17.2213 mL | 21.5267 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4305 mL | 2.1527 mL | 4.3053 mL | 8.6107 mL | 10.7633 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0861 mL | 0.4305 mL | 0.8611 mL | 1.7221 mL | 2.1527 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0431 mL | 0.2153 mL | 0.4305 mL | 0.8611 mL | 1.0763 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Dihydrokavain is one of the six major kavalactones found in the kava plant; appears to contribute significantly to the anxiolytic effects of kava, based on a study in chicks.
References:
[1]. Feltenstein MW, et al. Anxiolytic properties of Piper methysticum extract samples and fractions in the chick social-separation-stress procedure. Phytother Res. 2003 Mar;17(3):210-6.
- 3,4-Dichloro-Phe-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2636
CAS No.:587-56-4
- 2-C-Methyl-D-erythritol
Catalog No.:BCC8570
CAS No.:58698-37-6
- Boc-Cys(Acm)-ONp
Catalog No.:BCC3375
CAS No.:58651-76-6
- PH-797804
Catalog No.:BCC3672
CAS No.:586379-66-0
- Boc-ON
Catalog No.:BCC2797
CAS No.:58632-95-4
- H- ß-HoGlu-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3232
CAS No.:58610-41-6
- m-Anisic acid
Catalog No.:BCC9015
CAS No.:586-38-9
- Anagrelide HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2306
CAS No.:58579-51-4
- Saikosaponin B4
Catalog No.:BCN8516
CAS No.:58558-09-1
- Saikosaponin B1
Catalog No.:BCN5917
CAS No.:58558-08-0
- Losmapimod
Catalog No.:BCC5368
CAS No.:585543-15-3
- Confluentin
Catalog No.:BCN5795
CAS No.:585534-03-8
- H-D-Cha-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2662
CAS No.:58717-02-5
- 16-Oxoprometaphanine
Catalog No.:BCN5797
CAS No.:58738-31-1
- H-D-Ser-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3098
CAS No.:5874-57-7
- Licochalcone A
Catalog No.:BCN6332
CAS No.:58749-22-7
- Licochalcone B
Catalog No.:BCN6333
CAS No.:58749-23-8
- Proparacaine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5073
CAS No.:5875-06-9
- Meranzin hydrate
Catalog No.:BCN5798
CAS No.:5875-49-0
- Haplopine
Catalog No.:BCN3921
CAS No.:5876-17-5
- Pinostilbenoside
Catalog No.:BCN5799
CAS No.:58762-96-2
- Alpha-Belladonnine
Catalog No.:BCN1894
CAS No.:5878-33-1
- ZCL278
Catalog No.:BCC3665
CAS No.:587841-73-4
- C7280948
Catalog No.:BCC6443
CAS No.:587850-67-7
Kavalactones and dihydrokavain modulate GABAergic activity in a rat gastric-brainstem preparation.[Pubmed:12494336]
Planta Med. 2002 Dec;68(12):1092-6.
Using an in vitro neonatal rat gastric-brainstem preparation, the activity of majority neurons recorded in the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) of the brainstem were significantly inhibited by GABA A receptor agonist, muscimol (30 microM), and this inhibition was reversed by selective GABA A receptor antagonist, bicuculline (10 microM). Application of kavalactones (300 microg/ml) and Dihydrokavain (300 microM) into the brainstem compartment of the preparation also significantly reduced the discharge rate of these NTS neurons (39 % and 32 %, respectively, compared to the control level), and this reduction was partially reversed by bicuculline (10 microM). Kavalactones or Dihydrokavain induced inhibitory effects were not reduced after co-application of saclofen (10 microM; a selective GABA B receptor antagonist) or naloxone (100 nM; an opioid receptor antagonist). Pretreatment with kavalactones (300 microg/ml) or Dihydrokavain (300 microM) significantly decreased the NTS inhibitory effects induced by muscimol (30 microM), approximately from 51 % to 36 %. Our results demonstrated modulation of brainstem GABAergic mechanism by kavalactones and Dihydrokavain, and suggested that these compounds may play an important role in regulation of GABAergic neurotransmission.
Kavain, dihydrokavain, and dihydromethysticin non-competitively inhibit the specific binding of [3H]-batrachotoxinin-A 20-alpha-benzoate to receptor site 2 of voltage-gated Na+ channels.[Pubmed:9690349]
Planta Med. 1998 Jun;64(5):458-9.
The mode of action of the kava pyrones, kavain, Dihydrokavain and dihydromethysticin on the specific binding of [3H]-batrachotoxinin-A 20-alpha-benzoate to epitope 2 of voltage-dependent Na+ channels was investigated by performing saturation experiments in the presence and absence of these kava pyrones. The tested compounds significantly decreased the apparent total number of binding sites (Bmax) for [3H]-batrachotoxinin-A 20-alpha-benzoate (control: 0.5 pmol/mg protein, kava pyrones: 0.2-0.27 pmol/mg protein) with little change in the equilibrium constants (KD) for [3H]-batrachotoxin-A 20-alpha-benzoate (control: 28.2 nM, kava pyrones: 24-31 nM). The results indicate for the kava pyrones a non-competitive inhibition of the specific [3H]-batrachotoxinin-A 20-alpha-benzoate binding to receptor site 2 of voltage-gated Na+ channels.


