CarbendazimCAS# 10605-21-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

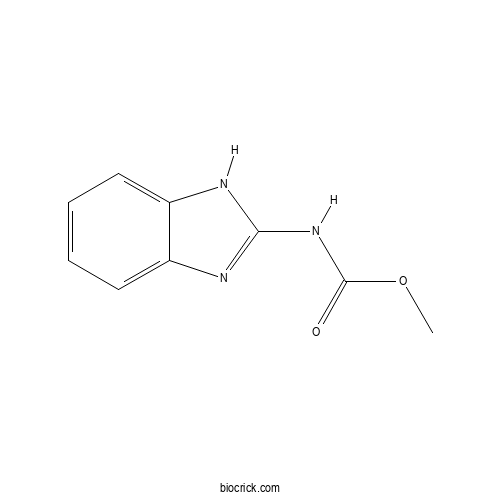
Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 10605-21-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 25429 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C9H9N3O2 | M.Wt | 191.19 |
| Type of Compound | Impurities | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | methyl N-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate | ||
| SMILES | COC(=O)NC1=NC2=CC=CC=C2N1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | TWFZGCMQGLPBSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H9N3O2/c1-14-9(13)12-8-10-6-4-2-3-5-7(6)11-8/h2-5H,1H3,(H2,10,11,12,13) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Carbendazim Dilution Calculator

Carbendazim Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.2304 mL | 26.152 mL | 52.304 mL | 104.608 mL | 130.76 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0461 mL | 5.2304 mL | 10.4608 mL | 20.9216 mL | 26.152 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.523 mL | 2.6152 mL | 5.2304 mL | 10.4608 mL | 13.076 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1046 mL | 0.523 mL | 1.0461 mL | 2.0922 mL | 2.6152 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0523 mL | 0.2615 mL | 0.523 mL | 1.0461 mL | 1.3076 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Anisyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCX0431
CAS No.:105-13-5
- Deacetylnomilinic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0430
CAS No.:35930-21-3
- Ichangin
Catalog No.:BCX0429
CAS No.:10171-61-6
- Obacunone 17-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0428
CAS No.:123564-64-7
- 3-epi-Actinidic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0427
CAS No.:143839-01-4
- (±)-Dihydrodehydrodiconiferyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCX0426
CAS No.:85165-02-2
- (-)-Isolariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCX0425
CAS No.:110268-37-6
- 21,23-Dihydro-21-hydroxy-23-oxonomilin
Catalog No.:BCX0424
CAS No.:2243600-32-8
- Procymidone
Catalog No.:BCX0423
CAS No.:32809-16-8
- Azoxystrobin
Catalog No.:BCX0422
CAS No.:131860-33-8
- 5α,6α-Epoxyergosta-8,22-diene-3β,7α-diol
Catalog No.:BCX0421
CAS No.:16250-61-6
- 20(R)-Hydroxypregn-4-en-3-one
Catalog No.:BCX0420
CAS No.:145-15-3
- (2Z,6E)-Farnesyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCX0433
CAS No.:40266-29-3
- Isolimonic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0434
CAS No.:74729-97-8
- Anibadimer A
Catalog No.:BCX0435
CAS No.:23768-65-2
- 5-Deoxyisorhoifolin
Catalog No.:BCX0436
CAS No.:2055239-29-5
- 1(10)Z,4Z-Furanodienone
Catalog No.:BCX0437
CAS No.:88010-63-3
- Thalifaronine
Catalog No.:BCX0438
CAS No.:105458-70-6
- Huazhongilexol
Catalog No.:BCX0439
CAS No.:161407-80-3
- Thalifaramine
Catalog No.:BCX0440
CAS No.:105437-16-9
- (12Z)-Labda-8(17),12-diene-14,15,16-triol
Catalog No.:BCX0441
CAS No.:1630864-26-4
- Citrusin
Catalog No.:BCX0442
CAS No.:108943-57-3
- 7-O-Galloyl-D-sedoheptulose
Catalog No.:BCX0443
CAS No.:233690-85-2
- 1,7-Di-O-Galloyl-D-sedoheptulose
Catalog No.:BCX0444
CAS No.:126622-78-4
Carboxylesterase and Cytochrome P450 Confer Metabolic Resistance Simultaneously to Azoxystrobin and Some Other Fungicides in Botrytis cinerea.[Pubmed:38634420]
J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Apr 18.
Plant pathogens have frequently shown multidrug resistance (MDR) in the field, often linked to efflux and sometimes metabolism of fungicides. To investigate the potential role of metabolic resistance in B. cinerea strains showing MDR, the azoxystrobin-sensitive strain B05.10 and -resistant strain Bc242 were treated with azoxystrobin. The degradation half-life of azoxystrobin in Bc242 (9.63 days) was shorter than that in B05.10 (28.88 days). Azoxystrobin acid, identified as a metabolite, exhibited significantly lower inhibition rates on colony and conidia (9.34 and 11.98%, respectively) than azoxystrobin. Bc242 exhibited higher expression levels of 34 cytochrome P450s (P450s) and 11 carboxylesterase genes (CarEs) compared to B05.10 according to RNA-seq analysis. The expression of P450 genes Bcin_02g01260 and Bcin_12g06380, along with the CarEs Bcin_12g06360 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, resulted in reduced sensitivity to various fungicides, including azoxystrobin, kresoxim-methyl, pyraclostrobin, trifloxystrobin, iprodione, and Carbendazim. Thus, the mechanism of B. cinerea MDR is linked to metabolism mediated by the CarE and P450 genes.
Integration of a biocompatible metal-phenolic network and fluorescence microspheres as labels for sensitive and stable detection of carbendazim with a lateral flow immunoassay.[Pubmed:38626714]
Food Chem. 2024 Apr 4;450:139260.
High fluorescence intensity microspheres such as aggregation-induced emission fluorescence microspheres (AIEFM) have improved the sensitivity of lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA). The preparation of immune probes in LFIA usually adopts the chemical coupling strategy with 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide for antibody coupling, which has the problems of low coupling efficiency, tedious coupling process, and poor repeatability. A biocompatible metal-phenolic network (MPN), which contains large amounts of phenols and galloyl groups, could easily, quickly, and stably couple with antibodies. Herein, we proposed a strategy based on MPN modification on ultrabright AIEFM surface as a novel label for the rapid detection of Carbendazim. The limit of detection of AIEFM@MPN-LFIA was 0.019 ng/mL, which was 4.9 times lower than that of AIEFM-LFIA. In spiked samples, the average recoveries of AIEFM@MPN-LFIA ranged from 80% to 118% (coefficient of variation <13.45%). Therefore, AIEFM@MPN was a promising signal label that could improve the detection performance of LFIA.
Asymmetries among soil fungicide residues, nitrous oxide emissions and microbiomes regulated by nitrification inhibitor at different moistures.[Pubmed:38626681]
J Hazard Mater. 2024 Apr 15;470:134301.
Carbendazim residue has been widely concerned, and nitrous oxide (N(2)O) is one of the dominant greenhouse gases. Microbial metabolisms are fundamental processes of removing organic pollutant and producing N(2)O. Nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) can change soil abiotic properties and microbial communities and simultaneously affect Carbendazim degradation and N(2)O emission. In this study, the comprehensive linkages among Carbendazim residue, N(2)O emission and microbial community after the DMPP application were quantified under different soil moistures. Under 90% WHC, the DMPP application significantly reduced Carbendazim residue by 54.82% and reduced soil N(2)O emission by 98.68%. The Carbendazim residue was negatively related to soil ammonium nitrogen (NH(4)(+)-N), urease activity, and ratios of Bacteroidetes, Thaumarchaeota and Nitrospirae under 90% WHC, and the N(2)O emission was negatively related to NH(4)(+)-N content and relative abundance of Acidobacteria under the 60% WHC condition. In the whole (60% and 90% WHC together), the Carbendazim residue was negatively related to the abundances of nrfA (correlation coefficient = -0.623) and nrfH (correlation coefficient = -0.468) genes. The hao gene was negatively related to the Carbendazim residue but was positively related to the N(2)O emission rate. The DMPP application had the promising potential to simultaneously reduce ecological risks of fungicide residue and N(2)O emission via altering soil abiotic properties, microbial activities and communities and functional genes. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPLICATION: Carbendazim was a high-efficiency fungicide that was widely used in agricultural production. Nitrous oxide (N(2)O) is the third most important greenhouse gas responsible for global warming. The 3, 4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) is an effective nitrification inhibitor widely used in agricultural production. This study indicated that the DMPP application reduced soil Carbendazim residues and N(2)O emission. The asymmetric linkages among the Carbendazim residue, N(2)O emission, microbial community and functional gene abundance were regulated by the DMPP application and soil moisture. The results could broaden our horizons on the utilizations DMPP in decreasing fungicide risks and N(2)O emission.
Design, synthesis, antifungal evaluation and mechanism study of novel norbornene derivatives as potential laccase inhibitors.[Pubmed:38625031]
Pest Manag Sci. 2024 Apr 16.
BACKGROUND: To discover novel fungicide candidates, five series of novel norbornene hydrazide, bishydrazide, oxadiazole, carboxamide and acylthiourea derivatives (2a-2 t, 3a-3 f, 4a-4 f, 5a-5 f and 7a-7 f) were designed, synthesized and assayed for their antifungal activity toward seven representative plant fungal pathogens. RESULTS: In the in vitro antifungal assay, some title norbornene derivatives presented good antifungal activity against Botryosphaeria dothidea, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Fusarium graminearum. Especially, compound 2b exhibited the best inhibitory activity toward B. dothidea with the median effective concentration (EC(50)) of 0.17 mg/L, substantially stronger than those of the reference fungicides boscalid and Carbendazim. The in vivo antifungal assay on apples revealed that 2b had significant curative and protective effects, both of which were superior to boscalid. In the preliminary antifungal mechanism study, 2b was able to injure the surface morphology of hyphae, destroy the cell membrane integrity and increase the intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) level of B. dothidea. In addition, 2b could considerably inhibit the laccase activity with the median inhibitory concentration (IC(50)) of 1.02 muM, much stronger than that of positive control cysteine (IC(50) = 35.50 muM). The binding affinity and interaction mode of 2b with laccase were also confirmed by molecular docking. CONCLUSION: This study presented a promising lead compound for the study on novel laccase inhibitors as fungicidal agrochemicals, which demonstrate significant anti-B. dothidea activity and laccase inhibitory activity. This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
Residue levels, processing factors and risk assessment of pesticides in ginger from market to table.[Pubmed:38608592]
J Hazard Mater. 2024 Apr 9;470:134268.
Ginger is consumed as a spice and medicine globally. However, pesticide residues in ginger and their residue changes during processing remain poorly understood. Our results demonstrate that clothianidin, Carbendazim and imidacloprid were the top detected pesticides in 152 ginger samples with detection rates of 17.11-27.63%, and these pesticides had higher average residues of 44.07-97.63 mug/kg. Although most samples contained low levels of pesticides, 66.45% of the samples were detected with pesticides, and 38.82% were contaminated with 2-5 pesticides. Peeling, washing, boiling and pickling removed different amounts of pesticides from ginger (processing factor range: 0.06-1.56, most <1). By contrast, pesticide residues were concentrated by stir-frying and drying (0.50-6.45, most >1). Pesticide residues were influenced by pesticide physico-chemical parameters involving molecular weight, melting point, degradation point and octanol-water partition coefficient by different ginger processing methods. Chronic and acute dietary risk assessments suggest that dietary exposure to pesticides from ginger consumption was within acceptable levels for the general population. This study sheds light on pesticide residues in ginger from market to processing and is of theoretical and practical value for ensuring ginger quality and safety.
Optimization and validation of high throughput methods for the determination of 132 organic contaminants in green and roasted coffee using GC-QqQ-MS/MS and LC-QqQ-MS/MS.[Pubmed:38604032]
Food Chem. 2024 Apr 4;449:139223.
Recently some major safety concerns have been raised on organic contaminants in widely consumed plants such as coffee. Hence, this study aimed to develop specifically optimized methods for determining organic contaminants, such as pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), in coffee using GC-MS/MS and LC-MS/MS. QuEChERS method was used as a base extraction method, and 27 experiments were studied using design of experiments with categorical variables (extraction buffers, cleanup sorbents, and coffee roasting degree) to find the optimum method for each matrix type. The optimum method for green coffee was acetate buffer and chitosan for clean-up, while no-buffer extraction and the PSA + C18 method were ideal for light and dark-roasted coffee. The optimized methods were validated in accordance with SANTE/11312/2021. Furthermore, ten real samples (4 green, and 6 roasted) from the markets were analysed; ortho-phenylphenol was found in all the roasted coffee samples, and Carbendazim was found in one green coffee sample.
Analysis of 207 residual pesticides in hot pepper powder using LC-MS/MS.[Pubmed:38585557]
Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023 Oct 25;33(6):1337-1350.
This study investigated the determination of 207 pesticides in hot pepper powder and found patterns of pesticide use by production from five regions, detecting a total of 50 pesticides. The LOD, LOQ and recoveries of pesticides were 0.08-2.53, 0.25-7.60 mug kg(-1), and 81.0-132.1%, respectively. The Horrat values ranged from 0.07 to 1.97. A total of 50 residual pesticides were detected in 963 hot pepper powder samples. All residual pesticide levels were below the Korean maximum residue level (MRL) and the %ADI was Carbendazim, and flubendiamide). The region where the most pesticide types were detected was Ham-pyeong with 38 types. Tebuconazole had detection rates of > 90% in all regions. In the PCA results with factor analysis, each region shows patterns of pesticide use. Four regions focus on Aphidoidea control and one region on Colletotrichum acutatum control. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s10068-023-01443-6.
Indole alkaloids isolated from the Nicotiana tabacum-derived Aspergillus fumigatus 0338 as potential inhibitors for tobacco powdery mildew and their mode of actions.[Pubmed:38582586]
Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2024 Mar;200:105814.
To explore active natural products against tobacco powdery mildew caused by Golovinomyces cichoracearum, an extract from the fermentation of endophytic Aspergillus fumigatus 0338 was investigated. The mechanisms of action for active compounds were also studied in detail. As a result, 14 indole alkaloid derivatives were isolated, with seven being newly discovered (1-7) and the remaining seven previously described (8-14). Notably, compounds 1-3 are rare linearly fused 6/6/5 tricyclic prenylated indole alkaloids, with asperversiamide J being the only known natural product of this kind. The isopentenyl substitutions at the 5-position in compounds 4 and 5 are also rare, with only compounds 1-(5-prenyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-propan-2-one (8) and 1-(6-methoxy-5-prenyl-1H-indol3-yl)-propan-2-one currently available. In addition, compounds 6 and 7 are new framework indole alkaloid derivatives bearing a 6-methyl-1,7-dihydro-2H-azepin-2-one ring. The purified compounds were evaluated for their activity against G. cichoracearum, and the results revealed that compounds 7 and 9 demonstrated obvious anti-G. cichoracearum activities with an inhibition rate of 82.6% and 85.2%, respectively, at a concentration of 250 mug/mL, these rates were better than that of the positive control agent, Carbendazim (78.6%). The protective and curative effects of compounds 7 and 9 were also better than that of positive control, at the same concentration. Moreover, the mechanistic study showed that treatment with compound 9 significantly increased the structural tightness of tobacco leaves and directly affect the conidiospores of G. cichoracearum, thereby enhancing resistance. Compounds 7 and 9 could also induce systemic acquired resistance (SAR), directly regulating the expression of defense enzymes, defense genes, and plant semaphorins, which may further contribute to increased plant resistance. Based on the activity experiments and molecular dockings, the indole core structure may be the foundation of these compounds' anti-G. cichoracearum activity. Among them, the indole derivative parent structures of compounds 6, 7, and 9 exhibit strong effects. Moreover, the methoxy substitution in compound 7 can enhance their activity. By isolating and structurally identifying the above indole alkaloids, new candidates for anti-powdery mildew chemical screening were discovered, which could enhance the utilization of N. tabacum-derived fungi in pesticide development.
Characterization of the fludioxonil and phenamacril dual resistant mutants of Fusarium graminearum.[Pubmed:38582573]
Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2024 Mar;200:105815.
Fusarium graminearum is an important fungal pathogen causing Fusarium head blight (FHB) in wheat and other cereal crops worldwide. Due to lack of resistant wheat cultivars, FHB control mainly relies on application of chemical fungicides. Both fludioxonil (a phenylpyrrole compound) and phenamacril (a cyanoacrylate fungicide) have been registered for controlling FHB in China, however, fludioxonil-resistant isolates of F. graminearum have been detected in field. To evaluate the potential risk of dual resistance of F. graminearum to both compounds, fludioxonil and phenamacril dual resistant (DR) mutants of F. graminearum were obtained via fungicide domestication in laboratory. Result showed that resistance of the DR mutants to both fludioxonil and phenamacril were genetically stable after sub-cultured for ten generations or stored at 4 degrees C for 30 days on fungicide-free PDA. Cross-resistance assay showed that the DR mutants remain sensitive to other groups of fungicides, including Carbendazim, tebuconazole, pydiflumetofen, and fluazinam. In addition, the DR mutants exhibited defects in mycelia growth, conidiation, mycotoxin deoxynivalenol (DON) production, and virulence Moreover, the DR mutants displayed increased sensitivity to osmotic stress. Sequencing results showed that amino acid point mutations S217L/T in the myosin I protein is responsible for phenamacril resistance in the DR mutants. Our results indicate that mutations leading to fludioxonil and phenamacril dual resistance could result in fitness cost for F. graminearum. Our results also suggest that the potential risk of F. graminearum developing resistance to both fludioxonil and phenamacril in field could be rather low, which provides scientific guidance in controlling FHB with fludioxonil and phenamacril.
Swellable microneedle-coupled light-addressable photoelectrochemical sensor for in-situ tracking of multiple pesticides pollution in vivo.[Pubmed:38581877]
J Hazard Mater. 2024 Apr 4;470:134216.
In vivo monitoring of multiple pesticide contamination is of great significance for evaluating the health risks of different pesticides, agricultural production safety, and ecological and environmental assessment. Here, we report a hydrogel microneedle array coupled light-addressable photoelectrochemical sensor for tracking multiple pesticide uptake and elimination in living animals and plants, holding three prominent merits: i) enables in-situ detection of in vivo pesticides, avoiding cumbersome and complex sample transportation and handling processes; ii) allows repeated in vivo sampling of the same organism, improving tracking test controllability and accuracy; iii) avoids lethal sampling, providing a better understanding of the pesticides fate in living organisms. The coupled sensor is mechanically robust for withstanding more than 0.35 N per needle and highly swellable (800 %) for timely extraction of su ffi cient in vivo solution for analysis. For proof-of-concept, it achieves in-situ detection of atrazine, acetamiprid, and Carbendazim e ffi ciently and quantitatively in artificial agarose skin models, mouse skin interstitial fluids, and plant leaves with little inflammatory reaction. This simple, highly integrated, minimally invasive, and high-throughput in vivo monitoring method is ideal for future field environmental monitoring and plant and animal disease diagnosis.
Research Progress on Benzimidazole Fungicides: A Review.[Pubmed:38542855]
Molecules. 2024 Mar 8;29(6):1218.
Benzimidazole fungicides are a class of highly effective, low-toxicity, systemic broad-spectrum fungicides developed in the 1960s and 1970s, based on the fungicidal activity of the benzimidazole ring structure. They exhibit biological activities including anticancer, antibacterial, and antiparasitic effects. Due to their particularly outstanding antibacterial properties, they are widely used in agriculture to prevent and control various plant diseases caused by fungi. The main products of benzimidazole fungicides include benomyl, Carbendazim, thiabendazole, albendazole, thiophanate, thiophanate-methyl, fuberidazole, methyl (1-[(5-cyanopentyl)amino]carbonyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl) carbamate, and Carbendazim salicylate. This article mainly reviews the physicochemical properties, toxicological properties, disease control efficacy, and pesticide residue and detection technologies of the aforementioned nine benzimidazole fungicides and their main metabolite (2-aminobenzimidazole). On this basis, a brief outlook on the future research directions of benzimidazole fungicides is presented.
Combined effects of polyethylene microplastics and carbendazim on Eisenia fetida: A comprehensive ecotoxicological study.[Pubmed:38527586]
Environ Pollut. 2024 May 1;348:123854.
Microplastic (MP) pollution is becoming an emerging environmental concern across aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. Plastic mulching and the use of pesticides in agriculture can lead to microplastics and agrochemicals in soil, which can result in unintended exposure to non-target organisms. The combined toxicity of multiple stressors represents a significant paradigm shift within the field of ecotoxicology, and its exploration within terrestrial ecosystems involving microplastics is still relatively limited. The present study investigated the combined effects of polyethylene MP (PE-MP) and the agrochemical Carbendazim (CBZ) on the earthworm Eisenia fetida at different biological levels of organization. While E. fetida survival and reproduction did not exhibit significant effects following PE-MP treatment, there was a reduction in cocoon and hatchling numbers. Notably, prolonged exposure revealed delayed toxicity, leading to substantial growth impairment. Exposure to CBZ led to significant alterations in the endpoints mentioned above. While there was a decrease in cocoon and hatchling numbers, the combined treatment did not yield significant effects on earthworm reproduction except at higher concentrations. However, lower concentrations of PE-MP alongside CBZ induced a noteworthy decline in biomass content, signifying a form of potentiation interaction. In addition, concurrent exposure led to synergistic effects, from oxidative stress to modifications in vital organs such as the body wall, intestines, and reproductive structures (spermathecae, seminal vesicles, and ovarian follicles). The comparison of multiple endpoints revealed that seminal vesicles and ovarian follicles were the primary targets during the combined exposure. The research findings suggest that there are variable and complex responses to microplastic toxicity in terrestrial ecosystems, especially when combined with other chemical stressors like agrochemicals. Despite these difficulties, the study implies that microplastics can alter earthworms' responses to agrochemical exposure, posing potential ecotoxicological risks to soil fauna.
Bacteria-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antifungal potentials against Aspergillus flavus.[Pubmed:38527060]
PLoS One. 2024 Mar 25;19(3):e0297870.
The best biocontroller Bacillus subtilis produced silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with a spherical form and a 62 nm size through green synthesis. Using UV-vis spectroscopy, PSA, and zeta potential analysis, scanning electron microscopy, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, the properties of synthesized silver nanoparticles were determined. Silver nanoparticles were tested for their antifungicidal efficacy against the most virulent isolate of the Aspergillus flavus fungus, JAM-JKB-BHA-GG20, and among the 10 different treatments, the treatment T6 [PDA + 1 ml of NP (19: 1)] + Pathogen was shown to be extremely significant (82.53%). TG-51 and GG-22 were found to be the most sensitive groundnut varieties after 5 and 10 days of LC-MS QTOF infection when 25 different groundnut varieties were screened using the most toxic Aspergillus flavus isolate JAM- JKB-BHA-GG20, respectively. In this research, the most susceptible groundnut cultivar, designated GG-22, was tested. Because less aflatoxin (1651.15 g.kg-1) was observed, treatment T8 (Seed + Pathogen + 2 ml silver nanoparticles) was determined to be much more effective. The treated samples were examined by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry for the detection of metal ions and the fungicide Carbendazim. Ag particles (0.8 g/g-1) and the fungicide Carbendazim (0.025 g/g-1) were found during Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry analysis below detectable levels. To protect plants against the invasion of fungal pathogens, environmentally friendly green silver nanoparticle antagonists with antifungal properties were able to prevent the synthesis of mycotoxin by up to 82.53%.
Transcriptomic profile in carbendazim-induced developmental defects in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos/larvae.[Pubmed:38522711]
Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2024 Jun;280:109907.
Carbendazim is a widely used fungicide to protect agricultural and horticultural crops against a wide array of fungal species. Published reports have shown that the wide usage of Carbendazim resulted in reprotoxicity, carcinogenicity, immunotoxicity, and developmental toxicity in mammalian models. However, studies related to the developmental toxicity of Carbendazim in aquatic organisms are not clear. To address this gap, an attempt was made by exposing zebrafish embryos to Carbendazim (800 mug/L) and assessing the phenotypic and transcriptomic profile at different developmental stages [24 hour post fertilization (hpf), 48 hpf, 72 hpf and 96 hpf). At 48 hpf, phenotypic abnormalities such as delay in hatching rate, deformed spinal axial curvature, and pericardial edema were observed in zebrafish larvae over its respective controls. At 72 hpf, exposure of zebrafish embryos exposed to Carbendazim resulted in scoliosis; however, unexposed larvae did not exhibit signs of scoliosis. Interestingly, the transcriptomic analysis revealed a total of 1253 DEGs were observed at selected time points, while unique genes at 24 hpf, 48 hpf, 72 hpf and 96 hpf was found to be 76.54 %, 61.14 %, 92.98 %, and 68.28 %, respectively. Functional profiling of downregulated genes revealed altered transcriptomic markers associated with phototransduction (24 hpf and 72 hpf), immune system (48 hpf), and SNARE interactions in the vesicular pathway (96 hpf). Whereas functional profiling of upregulated genes revealed altered transcriptomic markers associated with riboflavin metabolism (24 hpf), basal transcription factors (48 hpf), insulin signaling pathway (72 hpf), and primary bile acid biosynthesis (96 hpf). Taken together, Carbendazim-induced developmental toxicity could be ascribed to pleiotropic responses at the molecular level, which in turn might reflect phenotypic abnormalities.
Synergistic activation of lamellar bismuth selenide anchored functionalized carbon nanofiber for detecting hazardous carbendazim in environmental water samples.[Pubmed:38522669]
Chemosphere. 2024 May;355:141744.
Pesticides pollute natural water reservoirs through persistent accumulation. Therefore, their toxicity and degradability are serious issues. Carbendazim (CBZ) is a pesticide used against fungal infections in agricultural crops, and its overexploitation detrimentally affects aquatic ecosystems and organisms. It is necessary to design a logical, efficient, and field-deployable method for monitoring the amount of CBZ in environmental samples. Herein, a nano-engineered bismuth selenide (Bi(2)Se(3))/functionalized carbon nanofiber (f-CNF) nanocomposite was utilized as an electrocatalyst to fabricate an electrochemical sensing platform for CBZ. Bi(2)Se(3)/f-CNF exhibited a substantial electroactive surface area, high electrocatalytic activity, and high conductivity owing to the synergistic interaction of Bi(2)Se(3) with f-CNF. The structural chemical compositions and morphology of the Bi(2)Se(3)/f-CNF nanocomposite were confirmed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). Electrochemical analysis was carried out using cyclic voltammetry (CV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). The voltammetry and impedance experiments exposed that the Bi(2)Se(3)/f-CNF-modified GCE has attained adequate electrocatalytic function with amended features of electron transportation (R(ct) = 35.93 Omega) and improved reaction sites (0.082 cm(2)) accessible by CBZ moiety along with exemplary electrochemical stability (98.92%). The Bi(2)Se(3)/f-CNF nanocomposite exhibited higher sensitivity of 0.2974 muA muM(-1)cm(-2) and a remarkably low limit of detection (LOD) of 1.04 nM at a broad linera range 0.001-100 muM. The practicability of the nanocomposite was tested in environmental (tap and pond water) samples, which supports excellent signal amplification with satisfactory recoveries. Hence, the Bi(2)Se(3)/f-CNF nanocomposite is a promising electrode modifier for detecting CBZ.


