5,7-Dihydroxy-4-MethylcoumarinCAS# 2107-76-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

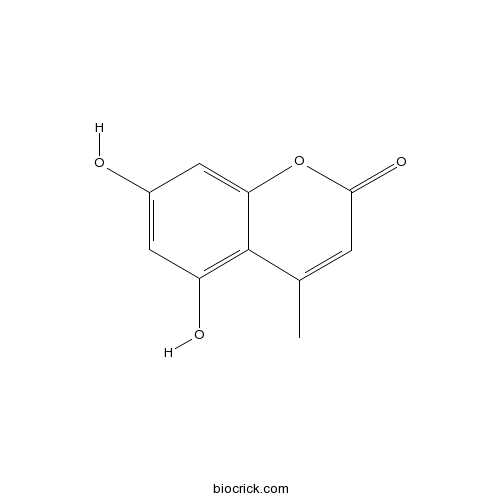
Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 2107-76-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5354284 | Appearance | White-beige powder |
| Formula | C10H8O4 | M.Wt | 192 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in chloroform and methan | ||
| Chemical Name | 5,7-dihydroxy-4-methylchromen-2-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC(=O)OC2=CC(=CC(=C12)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QNVWGEJMXOQQPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H8O4/c1-5-2-9(13)14-8-4-6(11)3-7(12)10(5)8/h2-4,11-12H,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin inhibits human neutrophil oxidative metabolism and elastase activity. 2. 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin has in vitro platelet antiaggregatory property. 3. 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin shows inhibition of the cyclooxygenase pathway. |
| Targets | ROS |

5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin Dilution Calculator

5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.2083 mL | 26.0417 mL | 52.0833 mL | 104.1667 mL | 130.2083 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0417 mL | 5.2083 mL | 10.4167 mL | 20.8333 mL | 26.0417 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5208 mL | 2.6042 mL | 5.2083 mL | 10.4167 mL | 13.0208 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1042 mL | 0.5208 mL | 1.0417 mL | 2.0833 mL | 2.6042 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0521 mL | 0.2604 mL | 0.5208 mL | 1.0417 mL | 1.3021 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- PD 168568 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7702
CAS No.:210688-56-5
- 6alpha-Hydroxylycopodine
Catalog No.:BCN7403
CAS No.:21061-92-7
- 1,11b-Dihydro-11b-hydroxymaackiain
Catalog No.:BCN3914
CAS No.:210537-05-6
- 1,11b-Dihydro-11b-hydroxymedicarpin
Catalog No.:BCN3913
CAS No.:210537-04-5
- Sitaxentan sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4495
CAS No.:210421-74-2
- Odoratin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN8089
CAS No.:210413-47-1
- Spiradine F
Catalog No.:BCN4915
CAS No.:21040-64-2
- Cinnamyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN4914
CAS No.:21040-45-9
- Z-LEHD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC5117
CAS No.:210345-04-3
- Ac-LEHD-AFC
Catalog No.:BCC2359
CAS No.:210345-03-2
- Z-WEHD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1139
CAS No.:210345-00-9
- Z-IETD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC5116
CAS No.:210344-98-2
- 7,8-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCC8290
CAS No.:2107-77-9
- CP 471474
Catalog No.:BCC2373
CAS No.:210755-45-6
- Sakakin
Catalog No.:BCN4916
CAS No.:21082-33-7
- Org 12962 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7718
CAS No.:210821-63-9
- W-84 dibromide
Catalog No.:BCC6682
CAS No.:21093-51-6
- CART (62-76) (rat, human)
Catalog No.:BCC6008
CAS No.:210978-19-1
- BMY 7378
Catalog No.:BCC5063
CAS No.:21102-95-4
- Mahanimbine
Catalog No.:BCN3174
CAS No.:21104-28-9
- SB 265610
Catalog No.:BCC5936
CAS No.:211096-49-0
- Marsformoxide B
Catalog No.:BCN6687
CAS No.:2111-46-8
- Sobetirome
Catalog No.:BCC1957
CAS No.:211110-63-3
- Rubranol
Catalog No.:BCN4917
CAS No.:211126-61-3
4-methylcoumarin derivatives inhibit human neutrophil oxidative metabolism and elastase activity.[Pubmed:23905650]
J Med Food. 2013 Aug;16(8):692-700.
Increased neutrophil activation significantly contributes to the tissue damage in inflammatory illnesses; this phenomenon has motivated the search for new compounds to modulate their effector functions. Coumarins are natural products that are widely consumed in the human diet. We have evaluated the antioxidant and immunomodulator potential of five 4-methylcoumarin derivatives. We found that the 4-methylcoumarin derivatives inhibited the generation of reactive oxygen species by human neutrophils triggered by serum-opsonized zymosan or phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate; this inhibition occurred in a concentration-dependent manner, as revealed by lucigenin- and luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence assays. Cytotoxicity did not mediate this inhibitory effect. The 7,8-dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin suppressed the neutrophil oxidative metabolism more effectively than the 6,7- and 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarins, but the 5,7- and 7,8-diacetoxy-4-methylcoumarins were less effective than their hydroxylated counterparts. An analysis of the biochemical pathways suggested that the 6,7- and 7,8-dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarins inhibit the protein kinase C-mediated signaling pathway, but 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin, as well as 5,7- and 7,8-diacetoxy-4-methylcoumarins do not significantly interfere in this pathway of the activation of the human neutrophil oxidative metabolism. The 4-methylcoumarin derivatives bearing the catechol group suppressed the elastase and myeloperoxidase activity and reduced the 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl free radical the most strongly. Interestingly, the 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin scavenged hypochlorous acid more effectively than the o-dihydroxy-substituted 4-methylcoumarin derivatives, and the diacetoxylated 4-methylcoumarin derivatives scavenged hypochlorous acid as effectively as the 7,8-dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin. The significant influence of small structural modifications in the inhibitory potential of 4-methylcoumarin derivatives on the effector functions of neutrophil makes them interesting candidates to develop new drugs for the treatment of inflammatory diseases mediated by increased neutrophil activation.
In vitro platelet antiaggregatory properties of 4-methylcoumarins.[Pubmed:22996069]
Biochimie. 2012 Dec;94(12):2681-6.
Platelets play a crucial role in physiological haemostasis. However, in coronary arteries damaged by atherosclerosis, enhanced platelet aggregation, with subsequent thrombus formation, is a precipitating factor in acute myocardial infarction. Current therapeutic approaches are able to reduce approximately one quarter of cardiovascular events, but they are associated with an increased risk of bleeding and in some resistant patients are not efficient. Some coumarins possess antiplatelet activity and, due to their additional antioxidant effects, may be promising drugs for use in combination with the present therapeutic agents. The aim of this study was to analyse a series of simple 4-methylcoumarins for their antiplatelet activity. Human plasma platelet suspensions were treated with different aggregation inducers [arachidonic acid (AA), collagen and ADP] in the presence of the 4-methylcoumarins. Complementary experiments were performed to explain the mechanism of action. 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarins, in particular those containing a lipophilic side chain at C-3, reached the activity of acetylsalicylic acid on AA-induced aggregation. Other tested coumarins were less active. Some of the tested compounds mildly inhibited either collagen- or ADP-induced aggregation. 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarins did not interfere with the function of thromboxane synthase, but were competitive antagonists of thromboxane A(2) receptors and inhibited cyclooxygenase-1 as well. 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarins appear to be promising candidates for the extension of the current spectrum of antiplatelet drugs.
Biotransformation of hydroxycoumarin derivatives by cultured suspension cells of Catharanthus roseus.[Pubmed:22764584]
Pharmazie. 2012 May;67(5):467-71.
Using 7-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin (1), 7-hydroxy-4-phenylcoumarin (2), 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin (3), 7,8-dihydroxycoumarin (4) as substrates, three new compounds, 4-methylcoumarin-7-O-beta-D-xylopyranosyl (1 --> 6) beta-D-glucopyranoside (1b), 4-phenylcoumarin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1 --> 6) beta-D-glucopyranoside (2b), 4-methylcoumarin-5,7-O-beta-D-diglucoside (3b), along with four known compounds (1a, 2a, 3a and 4a) were biosynthesized by the cell suspension cultures of Catharanthus roseus as biocatalyst. Their structures were elucidated by analysis of the physicochemical properties and 1H NMR, 13C NMR, HMBC and ESI-MS spectra. Besides, the results also showed that this novel biocatalyst system of C. roseus cell cultures has a great capacity of regio-selective glycosylation to the hydroxyl group of the exogenous substrates. Co-culture time curves on conversion were also established.
Structure-activity relationship of dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarins as powerful antioxidants: correlation between experimental & theoretical data and synergistic effect.[Pubmed:20600568]
Biochimie. 2010 Sep;92(9):1089-100.
The chain-breaking antioxidant activities of eight coumarins [7-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin (1), 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin (2), 6,7-dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin (3), 6,7-dihydroxycoumarin (4), 7,8-dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin (5), ethyl 2-(7,8-dihydroxy-4-methylcoumar-3-yl)-acetate (6), 7,8-diacetoxy-4-methylcoumarin (7) and ethyl 2-(7,8-diacetoxy-4-methylcoumar-3-yl)-acetate (8)] during bulk lipid autoxidation at 37 degrees C and 80 degrees C in concentrations of 0.01-1.0 mM and their radical scavenging activities at 25 degrees C using TLC-DPPH test have been studied and compared. It has been found that the o-dihydroxycoumarins 3-6 demonstrated excellent activity as antioxidants and radical scavengers, much better than the m-dihydroxy analogue 2 and the monohydroxycoumarin 1. The substitution at the C-3 position did not have any effect either on the chain-breaking antioxidant activity or on the radical scavenging activity of the 7,8-dihydroxy- and 7,8-diacetoxy-4-methylcoumarins 6 and 8. The comparison with DL-alpha-tocopherol (TOH), caffeic acid (CA) and p-coumaric acid (p-CumA) showed that antioxidant efficiency decreases in the following sequence: TOH>CA>3>4>6>5>2>1=7=8=p-CumA. Theoretical calculations and the "Lipinski's Rule of Five" were used for explaining the structure-activity relationships and pharmacokinetic behavior. A higher TGSO oxidation stability was observed in the presence of equimolar (1:1) binary mixtures of coumarins with TOH (1+TOH, 3+TOH and 5+TOH). However, the synergism (14%) was observed only for the binary mixture of 5 + TOH.
Rotational diffusion of dihydroxy coumarins: Effect of OH groups and their relative position on solute-solvent interactions.[Pubmed:19489576]
J Phys Chem B. 2009 Jun 25;113(25):8599-606.
The rotational dynamics of 6,7- and 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin in a series of linear alcohols have been studied by time-resolving their fluorescence anisotropy decay with the frequency up-conversion method. Through estimations of their rotational diffusion coefficients in a series of linear alcohols, it was verified that these two coumarins keep nearly the same hydrodynamic contributions to friction, which accounts for only about 35% of the observed reorientational times. Whereas the former compound has the two -OH groups bonded to adjacent carbon atoms in the aromatic frame, in the latter compound, the two hydroxyl groups are separated by enough space to develop more stable interactions involving a network of several solvent molecules. These findings show that this structural difference results in significantly slower rotational relaxation for the 5,7-dihydroxylated coumarin as a result of specific hydrogen-bonding networks as determined at B3LYP/6-311G(d,p) level of theory.
Antifungal and antibacterial activities of Mexican tarragon (Tagetes lucida).[Pubmed:19127719]
J Agric Food Chem. 2006 May 17;54(10):3521-7.
Mexican tarragon (Tagetes lucida Cv. Asteraceae: Campanulatae) is an important, nutritious plant and an effective herbal medicine. Seven coumarins, 7,8-dihydroxycoumarin (4), umbelliferone (7-hydroxycoumarin) (5), scoparone (6,7-dimethoxycoumarin) (7), esculetin (6,7-dihydroxycoumarin) (11), 6-hydroxy-7-methoxycoumarin (12), herniarin (7-methoxycoumarin) (13), and scopoletin (6-methoxy-7-hydroxycoumarin) (14), and three flavonoids, patuletin (18), quercetin (19), and quercetagetin (20), were isolated from CH2Cl2 and MeOH extracts from aerial parts of T. lucida. In addition, 6,7-diacetoxy coumarin (15), 6-methoxy-7-acetylcoumarin (16), and 6-acetoxy-7-methoxycoumarin (17) derivatives were synthesized. 8-Methoxypsoralen (1), 8-acetyl-7-hydroxycoumarin (2), 7,8-dihydroxy-6-meth-oxycoumarin (3), 6,7-dimethoxy-4-methylcoumarin (6), 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin (8), 4-hydroxycoumarin (9), 4-hydroxy-6,7-dimethylcoumarin (10), naringenin (21), glycoside-7-rhamnonaringin (22), and rutin (23) were commercially obtained (Sigma-Aldrich). All of these compounds and extracts (M1 and M2) were assayed against bacteria and fungi. The antibacterial activity was determined on Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Salmonella typhi, Salmonella sp., Shigella boydii, Shigella sp., Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterobacter agglomerans, Sarcina lutea, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, Yersinia enterolitica, Vibrio cholerae (three El Tor strains, CDC-V12, clinic case, and INDRE-206, were obtained from contaminated water), and V. cholerae (NO-O1). The evaluated fungi were Aspergillus niger, Penicillium notatum, Fusarium moniliforme, Fusarium sporotrichum, Rhizoctonia solani, and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. The most active compounds against Gram-positive and -negative bacteria were the dihydroxylated coumarins 3 and 4. In addition, 2-4, 6, 7, and 11 showed an interesting activity against V. cholerae, a key bacterium in the contaminated water; 2-4 were the most active. Coumarins were the most effective compounds against Gram-negative bacteria. The extract MeOH/CH2Cl2 (1: 4) M2 at 0.4 microg/disk inhibited the growth of E. coli and P. mirabilis (40%), K. pneumoniae (31.1%), Salmonella sp. (35.5%), and Shigella sp. (0%) at 72 h of culture. The dimethoxy compounds 6 and 7 showed a strong activity against fungal strains, especially T. mentagrophytes and R. solani (100% of inhibition at 125.0 and 250.0 microg/mL, respectively).
Inhibitory activity of polyhydroxycarboxylate chelators against recombinant NF-kappaB p50 protein-DNA binding.[Pubmed:15788163]
Bioorg Chem. 2005 Apr;33(2):67-81.
The inhibitory effect of 7,8-dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin (7,8-DHMC), 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin (5,7-DHMC), and gallic acid on the DNA binding of recombinant p50 protein and their interaction with zinc ion were studied. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) using p50 and biotin labeled DNA has shown that gallic acid is more effective than the dihydroxycoumarins in inhibiting the p50-DNA binding. Molecular modeling studies suggest an explanation for these observations. Effect of the addition of zinc after p50-DNA-binding inhibition by gallic acid was also studied. Chemical speciation and formation constant studies show that gallic acid forms a more stable 1:1 complex with zinc ion in comparison to the dihydroxycoumarins.
Crystal structure of 7,8-dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin.[Pubmed:12725413]
Anal Sci. 2003 Apr;19(4):647-8.
The structure of 7,8-dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin was determined by an X-ray diffraction method. The compound crystallized in the triclinic space group P1, Z = 2, with a = 7.631(2), b = 9.456(5), c = 7.075(3)A, alpha = 103.13(3), beta = 91.84(3), gamma= 68.21(3) degrees, and V= 460.9(3)A3. The X-ray crystal structure was also compared with those of 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin and 7-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin.
Pharmacological and biochemical actions of simple coumarins: natural products with therapeutic potential.[Pubmed:8853310]
Gen Pharmacol. 1996 Jun;27(4):713-22.
1. More than 300 coumarins have been identified from natural sources, especially green plants. The pharmacological and biochemical properties and therapeutic applications of simple coumarins depend upon the pattern of substitution. More complex related compounds based on the coumarin nucleus include the dicoumarol/warfarin anticoagulants, aflatoxins and the psoralens (photosensitizing agents). 2. Coumarin itself (1,2-benzopyrone) has long-established efficacy in slow-onset long-term reduction of lymphoedema in man, as confirmed in recent double-blind trials against elephantiasis and postmastectomy swelling of the arm. The mechanism of action is uncertain, but may involve macrophage-induced proteolysis of oedema protein. However, coumarin has low absolute bioavailability in man (< 5%), due to extensive first-pass hepatic conversion to 7-hydroxycoumarin followed by glucuronidation. It may, therefore, be a prodrug. 3. Scoparone (6,7-dimethoxycoumarin) has been purified from the hypolipidaemic Chinese herb Artemisia scoparia and shown to reduce the proliferative responses of human peripheral mononuclear cells, to relax smooth muscle, to reduce total cholesterol and triglycerides and to retard the characteristic pathomorphological changes in hypercholesterolaemic diabetic rabbits. Various properties of scoparone were suggested to account for these findings, including ability to scavenge reactive oxygen species, inhibition of tyrosine kinases and potentiation of prostaglandin generation. 4. Osthole (7-methoxy-8-[3-methylpent-2-enyl]coumarin) from Angelica pubescens, used also in Chinese medicine, causes hypotension in vivo, and inhibits platelet aggregation and smooth muscle contraction in vitro. It may interfere with calcium influx and with cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. 5. Cloricromene, a synthetic coumarin derivative, also possesses antithrombotic antiplatelet actions, inhibits PMN neutrophil function and causes vasodilatation. Some of these properties of cloricromene have been ascribed to inhibition of arachidonate release from membrane phospholipids. 6. Simple coumarins possessing ortho-dihydroxy functions, such as fraxetin and 4-methyldaphnetin, are potent inhibitors (low micromolar) of lipid peroxidation and scavengers of superoxide anion radicals and of aqueous alkylperoxyl radicals, but may be pro-oxidant (enhancing generation of hydroxyl radicals) in the presence of free iron ions. These coumarins also inhibit the proinflammatory 5-lipoxygenase enzyme at micromolar concentrations. Another related coumarin, 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin, is of special interest as it inhibits lipid peroxidation, and scavenges alkylperoxyl and superoxide radicals. Unlike most other simple coumarins studied, 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin also scavenges hypochlorous acid, and is a potent inhibitor of cyclo-oxygenase, but is not pro-oxidant. 7. 5,7- and 6,7-dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin both reduced the duration of ventricular fibrillation in postischaemic reperfused isolated perfused rat hearts (in which oxygen-derived free radicals are implicated), showing that these antioxidant coumarins possess beneficial properties in this pathophysiological model. 8. In view of the established low toxicity, relative cheapness, presence in the diet and occurrence in various herbal remedies of coumarins, it appears prudent to evaluate their properties and applications further.
Inhibitory activity of a series of coumarins on leukocyte eicosanoid generation.[Pubmed:7847183]
Agents Actions. 1994 Aug;42(1-2):44-9.
Sixteen plant-derived or synthetic coumarins with different patterns of substitution were tested for their capacity to modify A23187-induced synthesis of leukotriene B4 and thromboxane B2 via the 5-lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase pathways of arachidonate metabolism in rat peritoneal exudate leukocytes. Five of the 16 coumarins inhibited LTB4 production: all contain orthodihydroxy substitutions (approximate IC50 values 8-100 microM). The mechanism is likely to depend upon a combination of the coumarins' iron-chelating and iron ion-reducing abilities, properties which also confer beneficial activities of these compounds as scavengers of reactive oxygen species (Paya et al., Biochem. Pharmacol. 44, 205-214 (1992)). Inhibition of the cyclooxygenase pathway was only demonstrated by one compound, 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin, which did not inhibit 5-lipoxygenase, indicating that the cyclooxygenase inhibitory mechanism is different. Similar effects of the active coumarins were obtained using arachidonic acid as substrate for rat leukocyte eicosanoid generation, confirming that they act at the 5-lipoxygenase/cyclooxygenase level. The same profile of activity was also shown when the coumarins were tested against 5-lipoxygenase in human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Taken together, these antioxidant and anti-eicosanoid properties of coumarins could be exploited for the design of potentially valuable non-toxic anti-inflammatory agents for treating diseases in which eicosanoid generation and the production of reactive oxygen species are involved.
Interactions of a series of coumarins with reactive oxygen species. Scavenging of superoxide, hypochlorous acid and hydroxyl radicals.[Pubmed:1322662]
Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 22;44(2):205-14.
Sixteen plant-derived or synthetic coumarins with various hydroxyl and other substitutions were tested for their ability to inhibit lipid peroxidation and to scavenge hydroxyl radicals, superoxide radicals and hypochlorous acid. Seven unsubstituted or monosubstituted coumarins were essentially inactive in all tests except for ability to scavenge OH with rate constants approximately greater than 1 x 10(9) M-1. sec-1. Of the remaining nine, six containing dihydroxy substitutions were effective inhibitors of Fe3+-ascorbate-dependent microsomal lipid peroxidation (IC50 less than 20 microM), with ortho-dihydroxy + one additional substitution optimal (IC50 less than 10 microM). ortho-Dihydroxylated coumarins were pro-oxidant (enhanced OH generation) in the Fe3+-EDTA-H2O2 deoxyribose system but decreased OH' generation in the Fe3+-ascorbate-H2O2 deoxyribose system, indicating that these compounds can both chelate iron ions and also readily donate electrons for redox cycling of Fe3+. The meta-dihydroxycoumarin did not show this behaviour, but was an effective scavenger of hypochlorous acid, a property shared by only one other compound. Several other coumarins with one or more hydroxyl substituents were also capable of effectively removing superoxide anions (IC50 3.7-72 microM), although some could not be quantified due to direct rapid reduction of cytochrome c. We conclude that several compounds, notably 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin, possess beneficial biochemical profiles of interest in relation to pathophysiological processes dependent upon reactive oxygen species.
The sensitizing capacity of coumarins (III).[Pubmed:2529098]
Contact Dermatitis. 1989 Sep;21(3):141-7.
9 coumarins used as chemical reagents, laser dyes, in perfumery, cosmetics or occurring naturally, were investigated experimentally in guinea pigs to determine their contact sensitizing capacity. 5,7-dihydroxycoumarin, limettin and 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin were found to be moderate sensitizers, while scoparone, isoscopoletin and 4-hydroxycoumarin were weak. The 3 laser dyes were completely negative. The results indicate that substitution in the 6 and 7 or 5 and 7 positions with 2 hydroxy groups supports allergenic capability, while other substituents (e.g., methoxy groups) in the same positions, or an additional (third) substituent, diminish activity.


