Donepezil HClAChE inhibitor CAS# 120011-70-3 |
- Repaglinide
Catalog No.:BCC2504
CAS No.:135062-02-1
- Dronedarone
Catalog No.:BCN2176
CAS No.:141626-36-0
- NS309
Catalog No.:BCC1809
CAS No.:18711-16-5
- TRAM-34
Catalog No.:BCC1122
CAS No.:289905-88-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

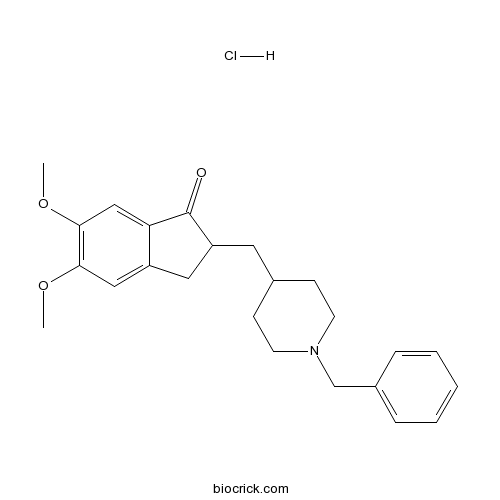
| Cas No. | 120011-70-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5741 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H30ClNO3 | M.Wt | 415.95 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | E 2020 | ||
| Solubility | H2O : 33.33 mg/mL (80.13 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMSO : 6.2 mg/mL (14.91 mM; Need warming) | ||
| Chemical Name | 2,3-Dihydro-5,6-dimethoxy-2-[[1-(ph | ||
| SMILES | [H+].[Cl-].COc1cc2CC(CC3CCN(CC3)Cc4ccccc4)C(=O)c2cc1OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XWAIAVWHZJNZQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H29NO3.ClH/c1-27-22-14-19-13-20(24(26)21(19)15-23(22)28-2)12-17-8-10-25(11-9-17)16-18-6-4-3-5-7-18;/h3-7,14-15,17,20H,8-13,16H2,1-2H3;1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (IC50 = 5.7 nM). Displays 1252-fold selectivity for AChE over BuChE (IC50 = 7138 nM for BuChE). Orally active. |

Donepezil HCl Dilution Calculator

Donepezil HCl Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4041 mL | 12.0207 mL | 24.0414 mL | 48.0827 mL | 60.1034 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4808 mL | 2.4041 mL | 4.8083 mL | 9.6165 mL | 12.0207 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2404 mL | 1.2021 mL | 2.4041 mL | 4.8083 mL | 6.0103 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0481 mL | 0.2404 mL | 0.4808 mL | 0.9617 mL | 1.2021 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.024 mL | 0.1202 mL | 0.2404 mL | 0.4808 mL | 0.601 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Donepezil Hydrochloride (Donepezil HCL) is a novel, potent and selective inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), an enzyme possibly involved in cognitive dysfunction of patients suffering Alzheimer’s disease (AD), with the half maximal inhibition concentration IC50 value of 6.7 nM [1].
Donepezil HCL is a piperidine-class AChE inhibitor containing an N-benzylpiperdine and an indanone moiety, which confers it a longer and more selective action against AchE as compared to BuChE (IC50: 7.4 μM) [1].
Donepezil HCL has been approved by FDA for the treatment of AD, in which it has improved cognitive function of mild to severe moderate AD patients and exhibited excellent tolerability without hepatotoxicity [1].
Reference
References:
[1] Sugimoto H, Ogura H, Arai Y, Limura Y, Yamanishi Y. Research and development of donepezil hydrochloride, a new type of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Jpn J Pharmacol. 2002 May;89(1):7-20.
- Dichlorphenamide
Catalog No.:BCC3761
CAS No.:120-97-8
- 1,2-Benzenediol
Catalog No.:BCN6103
CAS No.:120-80-9
- N,N'-Bis(salicylidene)-1,3-propanediamine
Catalog No.:BCC9063
CAS No.:120-70-7
- 2'-Methylacetanilide
Catalog No.:BCC8581
CAS No.:120-66-1
- Isosafrole
Catalog No.:BCC3976
CAS No.:120-58-1
- Benzyl benzoate
Catalog No.:BCN8521
CAS No.:120-51-4
- Ethylparaben
Catalog No.:BCN6094
CAS No.:120-47-8
- Desoxyanisoin
Catalog No.:BCN2264
CAS No.:120-44-5
- 3-Amino-4-methoxybenzanilide
Catalog No.:BCC8613
CAS No.:120-35-4
- Clorofene
Catalog No.:BCC8919
CAS No.:120-32-1
- Tropine benzilate
Catalog No.:BCN1921
CAS No.:3736-36-5
- Veratraldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN6089
CAS No.:120-14-9
- VCH-916
Catalog No.:BCC2031
CAS No.:1200133-34-1
- Edgeworin
Catalog No.:BCN6561
CAS No.:120028-43-5
- Meridinol
Catalog No.:BCN6087
CAS No.:120051-54-9
- Shizukanolide F
Catalog No.:BCN6411
CAS No.:120061-96-3
- CRF (6-33)
Catalog No.:BCC5791
CAS No.:120066-38-8
- Fmoc-D-Arg(Mtr)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3078
CAS No.:120075-24-3
- Flavanthrin
Catalog No.:BCN3687
CAS No.:120090-80-4
- IPI-145 (INK1197)
Catalog No.:BCC1104
CAS No.:1201438-56-3
- Crotaleschenine
Catalog No.:BCN2077
CAS No.:120154-95-2
- Vinflunine Tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4602
CAS No.:1201898-17-0
- MLN9708
Catalog No.:BCC2091
CAS No.:1201902-80-8
- TCS 2210
Catalog No.:BCC7798
CAS No.:1201916-31-5
Concurrent administration of donepezil HCl and levodopa/carbidopa in patients with Parkinson's disease: assessment of pharmacokinetic changes and safety following multiple oral doses.[Pubmed:15496222]
Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004 Nov;58 Suppl 1:41-9.
AIM: The use of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for the treatment of comorbid Alzheimer's disease in Parkinson's disease (PD) patients stabilized on a levodopa regimen may potentially disrupt cholinergic balance. This randomized, double-blind, crossover study investigated the safety of, and possible drug-drug interaction between, Donepezil HCl and levodopa/carbidopa. METHODS: Twenty-five patients with PD who were taking physician-optimized doses of levodopa/carbidopa (with daytime dosing intervals of 4-8 h) were administered once-daily doses of either Donepezil HCl (5 mg) or placebo for 15 days, in two treatment periods, separated by a washout of at least 2 weeks. Some patients took a second dose of levodopa/carbidopa after 4 h, therefore subanalysis of the levodopa/carbidopa data was conducted up to 4 h and 8 h after dosing. Twenty-six healthy matched controls received open-label Donepezil HCl only, for a single 15-day period. Blood samples were collected before, during and after the 15 doses of Donepezil HCl for pharmacokinetic (PK) assessments. Pharmacokinetic parameters included maximum attained plasma drug concentration (C(max)), time at which C(max) is attained (t(max)), plasma drug concentration at steady state (C(ss)), and area under the drug concentration-time curve over the dosing interval. Safety assessments included monitoring adverse events, and the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) motor examination. RESULTS: The mean age of all subjects was 72.6 +/- 1.3 years. Donepezil PK assessments of PD patients receiving levodopa/carbidopa were similar to the PK results from healthy controls who received Donepezil HCl only (mean AUC(0-12 h)= 281.6 +/- 17.6 and 268.6 +/- 19.9 ng.h ml(-1), respectively). Carbidopa PK were not significantly altered by the concomitant administration of multiple doses of Donepezil HCl, compared with when PD patients received placebo (mean AUC(0-8 h)= 921.8 +/- 160 and 821.8 +/- 113 ng.h ml(-1), respectively). Four hours after administration of Donepezil HCl in PD patients, AUC(0-4 h), C(max) and C(ss) of levodopa were higher than when PD patients received placebo (P < 0.05). Eight hours after Donepezil HCl, however, only C(max) and t(max) were observed to change compared with when PD patients received placebo (mean C(max) = 2652 +/- 429 and 2077 +/- 276 ng ml(-1), respectively; mean t(max) = 1.7 +/- 0.4 and 2.9 +/- 0.5 h, respectively; P< or = 0.05). The number of PD patients who experienced at least one adverse event during the study (13/25) was higher when they received Donepezil HCl than when they received placebo (5/25), but was the same as healthy subjects who received Donepezil HCl only (13/26). There were no significant differences in change from baseline on the UPDRS motor examination parameters in PD patients when they took Donepezil HCl and when they took placebo. CONCLUSIONS: No clinically significant drug-drug interactions between Donepezil HCl and levodopa/carbidopa were observed at steady state. The small changes in the pharmacokinetics of levodopa did not result in any change in motor symptoms. Co-administration of the two drugs led to a small increase in adverse events compared with administration of levodopa/carbidopa alone in PD patients. These adverse events, however, were consistent with donepezil's cholinomimetic effect, and their incidence was comparable to that observed following the administration of Donepezil HCl alone.
Electroanalytical determination of donepezil HCl in tablets and human serum by differential pulse and osteryoung square wave voltammetry at a glassy carbon electrode.[Pubmed:17020151]
Pharmazie. 2006 Sep;61(9):760-5.
Donepezil hydrochloride (DNP) is used for the treatment of mild to moderate dementia of the Alzheimer's type. The voltammetric behavior of DNP was studied at a glassy carbon electrode using cyclic, linear sweep, differential pulse (DPV) and square-wave (OSWV) voltammetric techniques. DNP exhibited irreversible anodic waves within the pH range 1.80 and 9.00 in different supporting electrolytes. The peak was characterized as being irreversible and diffusion-controlled. The possible mechanism of the oxidation process is discussed. The current-concentration plot was rectilinear over the range from 1 x 10(-6) to 1 x 10(-4) M in Britton-Robinson buffer at pH 7.0 with a correlation coefficient between 0.997 and 0.999 in supporting electrolyte and human serum samples using the DPV and SWV techniques. The repeatability and reproducibility of the methods for both media (supporting electrolyte and serum sample) were determined. Precision and accuracy of the developed methods were demonstrated by recovery studies. The standard addition method was used for the recovery studies. No electroactive interferences were found in biological fluids from endogenous substances or additives present in tablets. The methods developed were successfully applied to the determination of DNP in tablets and in spiked human serum.
Concurrent administration of donepezil HCl and risperidone in patients with schizophrenia: assessment of pharmacokinetic changes and safety following multiple oral doses.[Pubmed:15496223]
Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004 Nov;58 Suppl 1:50-7.
AIM: This open-label, multiple-dose trial investigated the effect of concurrent administration of Donepezil HCl with risperidone on the pharmacokinetics (PK) and safety profiles of both drugs. METHODS: Sixteen male patients with schizophrenia, who were receiving stable, physician-optimized risperidone (1-4 mg twice daily), and 15 healthy age- and weight-matched male controls, received Donepezil HCl 5 mg daily for 7 days. Patients with schizophrenia remained on their physician-optimized dose of risperidone throughout the study. Pharmacokinetic parameters (C(max), t(max) and AUC) were assessed from plasma drug concentrations measured in blood collected before, during and after administration (for 12 h after risperidone on days 0 and 7, and for 24 h after Donepezil HCl on day 7). RESULTS: The mean age of all the subjects was 38.5 years. Donepezil PK parameters were similar between patients taking Donepezil HCl + risperidone (AUC(0-24 h) = 329.0 +/- 17.2 ng x h ml(-1)) and controls taking Donepezil HCl alone (AUC(0-24 h) = 354.7 +/- 28.2 ng x h ml(-1)). Pharmacokinetic parameters for risperidone and 9-OH risperidone were not altered in patients with schizophrenia after 7 days of Donepezil HCl administration (AUC(0-12 h) standardized by dose: risperidone = 59.6 +/- 16.3 ng.h ml(-1) at day 0, 56.0 +/- 15.8 ng x h ml(-1) at day 7; 9-OH risperidone = 162.1 +/- 19.2 ng x h ml(-1) at day 0, 163.3 +/- 15.0 ng x h ml(-1) at day 7). The most common adverse event in both treatment groups was diarrhoea (6/16 risperidone + Donepezil HCl patients and 9/16 Donepezil HCl only subjects). There were no significant changes in physical examination, ECG, vital signs or treatment-emergent abnormal laboratory values associated with either of the treatment regimens. No subject developed extrapyramidal side-effects following donepezil administration. CONCLUSIONS: These results suggest that once-daily dosing of 5 mg Donepezil HCl does not alter the PK of risperidone in patients with schizophrenia. The combination of risperidone and Donepezil HCl was well tolerated.
Concurrent administration of donepezil HCl and sertraline HCl in healthy volunteers: assessment of pharmacokinetic changes and safety following single and multiple oral doses.[Pubmed:15496220]
Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004 Nov;58 Suppl 1:25-33.
AIM: This study evaluated the safety and pharmacokinetics (PK) of Donepezil HCl and sertraline HCl when administered separately and in combination. METHODS: This was a randomized, open-label, three-period crossover study. In consecutive dosing periods separated by washout periods of > or = 3 weeks, healthy volunteers received either oral donepezil HCI 5 mg once daily for 15 days, oral sertraline HCl 50 mg once daily for 5 days followed by 10 days of once-daily sertraline HCl 100 mg, or the simultaneous administration of oral Donepezil HCl and sertraline HCl. Plasma donepezil and sertraline concentrations were determined by high performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Safety was evaluated by physical and laboratory evaluations and the monitoring of adverse events (AEs). RESULTS: A total of 19 volunteers (16 male and three female) were enrolled. Three male subjects withdrew from the study prematurely due to AEs (one case of nausea/stomach cramps and one case of eosinophilia during combination treatment, and one upper respiratory tract infection during treatment with sertraline HCl alone). In subjects who completed all three treatment periods (n = 16), the concurrent administration of Donepezil HCl and sertraline HCl did not alter the steady-state (day 15) PK parameters of Donepezil HCl. A small (< 12%) but statistically significant (P = 0.02) increase in donepezil C(max) was seen after single doses of sertraline HCl and Donepezil HCl on day 1 but this was not thought to be clinically meaningful. No significant differences in the t(max) or AUC(0-24 h) of donepezil were observed between the Donepezil HCl only or Donepezil HCl plus sertraline HCl groups on day 1. No significant changes in sertraline PK parameters were observed either on day 1 (single dose) or on day 15 (steady state) when sertraline HCl was co-administered with Donepezil HCl. Generally, the concurrent administration of Donepezil HCl and sertraline HCl was well tolerated, with no serious AEs reported during the study. Some digestive system AEs tended to occur more frequently during combination treatment than with either treatment alone, but there was no statistically significant increase in the incidence of any individual AE. The most common AEs during the combination therapy were nausea and diarrhoea, which were rated as mild or moderate in severity. These AEs were also reported during the administration of each drug alone. CONCLUSIONS: The co-administration of once-daily oral Donepezil HCl 5 mg for 15 days and once-daily oral sertraline HCl (50 mg for 5 days increased to 100 mg for 10 days) did not result in any clinically meaningful pharmacokinetic interactions, and no unexpected AEs were observed.
Donepezil hydrochloride (E2020) and other acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.[Pubmed:10637367]
Curr Med Chem. 2000 Mar;7(3):303-39.
A wide range of evidence shows that acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors can interfere with the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The successful development of these compounds was based on a well-accepted theory that the decline in cognitive and mental functions associated with AD is related to the loss of cortical cholinergic neurotransmission. The earliest known AChE inhibitors, namely, physostigmine and tacrine, showed modest improvement in the cognitive function of Alzheimer's patients. However, clinical studies show that physostigmine has poor oral activity, brain penetration and pharmacokinetic parameters while tacrine has hepatotoxic liability. Studies were then focused on finding a new type of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor that would overcome the disadvantages of these two compounds. Donepezil hydrochloride inaugurates a new class of AChE inhibitors with longer and more selective action with manageable adverse effects. Currently, there are about 19 new Alzheimer's drugs in various phases of clinical development.
Structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with E2020 (Aricept): implications for the design of new anti-Alzheimer drugs.[Pubmed:10368299]
Structure. 1999 Mar 15;7(3):297-307.
BACKGROUND: Several cholinesterase inhibitors are either being utilized for symptomatic treatment of Alzheimer's disease or are in advanced clinical trials. E2020, marketed as Aricept, is a member of a large family of N-benzylpiperidine-based acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors developed, synthesized and evaluated by the Eisai Company in Japan. These inhibitors were designed on the basis of QSAR studies, prior to elucidation of the three-dimensional structure of Torpedo californica AChE (TcAChE). It significantly enhances performance in animal models of cholinergic hypofunction and has a high affinity for AChE, binding to both electric eel and mouse AChE in the nanomolar range. RESULTS: Our experimental structure of the E2020-TcAChE complex pinpoints specific interactions responsible for the high affinity and selectivity demonstrated previously. It shows that E2020 has a unique orientation along the active-site gorge, extending from the anionic subsite of the active site, at the bottom, to the peripheral anionic site, at the top, via aromatic stacking interactions with conserved aromatic acid residues. E2020 does not, however, interact directly with either the catalytic triad or the 'oxyanion hole', but only indirectly via solvent molecules. CONCLUSIONS: Our study shows, a posteriori, that the design of E2020 took advantage of several important features of the active-site gorge of AChE to produce a drug with both high affinity for AChE and a high degree of selectivity for AChE versus butyrylcholinesterase (BChE). It also delineates voids within the gorge that are not occupied by E2020 and could provide sites for potential modification of E2020 to produce drugs with improved pharmacological profiles.
Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: 1-benzyl-4-[(5,6-dimethoxy-1-oxoindan-2-yl)methyl]piperidine hydrochloride and related compounds.[Pubmed:7490731]
J Med Chem. 1995 Nov 24;38(24):4821-9.
Following the discovery of a new series of anti-acetylcholinesterase (anti-AChE) inhibitors such as 1-benzyl-4-[2-(N-benzoylamino)ethyl]piperidine (1), we reported that its rigid analogue, 1-benzyl-4-(2-isoindolin-2-ylethyl)piperidine (5), had more potent activity. We have extended the structure-activity relationship (SAR) study for the rigid analogue and found that the 2-isoindoline moiety in compound 5 can be replaced with a indanone moiety (8) without a major loss in potency. Among the indanone derivatives, 1-benzyl-4-[(5,6-dimethoxy-1-oxoindan-2-yl)methyl]piperidine (13e) (E2020) (IC50 = 5.7 nM) was found to be one of the most potent anti-AChE inhibitors. Compound 13e showed a selective affinity 1250 times greater for AChE than for butyrylcholinesterase. In vivo studies demonstrated that 13e has a longer duration of action than physostigmine at a dose of 5 mg/kg (po) and produced a marked and significant increase in acetylcholine content in rat cerebral cortex. We report the synthesis, SAR, and a proposed hypothetical binding site of 13e (E2020).


