TectoridinCAS# 611-40-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 611-40-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281810 | Appearance | White-pale yellow powder |
| Formula | C22H22O11 | M.Wt | 462.40 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Shekanin; Tectorigenin 7-glucoside; 4',5,7-Trihydroxy 6-methoxyisoflavone 7-glucoside | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in methan | ||
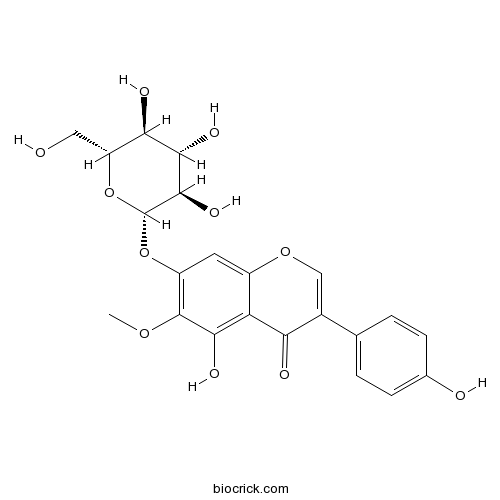
| Chemical Name | 5-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-6-methoxy-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C2C(=C1O)C(=O)C(=CO2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)O)OC4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CNOURESJATUGPN-UDEBZQQRSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H22O11/c1-30-21-13(32-22-20(29)19(28)17(26)14(7-23)33-22)6-12-15(18(21)27)16(25)11(8-31-12)9-2-4-10(24)5-3-9/h2-6,8,14,17,19-20,22-24,26-29H,7H2,1H3/t14-,17-,19+,20-,22-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Tectoridin, an lens aldose reductase inhibitor, has several pharmacological effects including hypoglycemic, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and hepatoprotectivy. It possesses a estrogenic and thyroid hormone-like agent by activating estrogen and thyroid hormone receptors, it also has inhibition on prostaglandin E2 production and cyclooxygenase-2 induction. |
| Targets | Estrogen receptor | COX | MEK | ERK | GPR | cAMP | PGE | Progestogen receptor |
| In vitro | Tectoridin from Maackia amurensis modulates both estrogen and thyroid receptors.[Pubmed: 24252334]Phytomedicine. 2014 Apr 15;21(5):602-6.The stem bark of Maackia amurensis has been used as folk medicine for the treatment of cancer, cholecystitis, arthritis, and hyperthyroidism in females. In this study we examined the effects of the ethyl acetate fraction obtained from the 70% ethanol extract of M. amurensis and Tectoridin, an active constituent isolated from the ethyl acetate fraction on thyroid and estrogen hormone activity.
Tectoridin, a poor ligand of estrogen receptor alpha, exerts its estrogenic effects via an ERK-dependent pathway.[Pubmed: 19326083 ]Mol Cells. 2009 Mar 31;27(3):351-7.Phytoestrogens are the natural compounds isolated from plants, which are structurally similar to animal estrogen, 17beta-estradiol. Tectoridin, a major isoflavone isolated from the rhizome of Belamcanda chinensis. Tectoridin is known as a phytoestrogen, however, the molecular mechanisms underlying its estrogenic effect are remained unclear.
|
| In vivo | Hepatoprotective effect of tectoridin and tectorigenin on tert-butyl hyperoxide-induced liver injury.[Pubmed: 15821336]J Pharmacol Sci. 2005 Apr;97(4):541-4.To clarify the hepatoprotective effects of Tectoridin and tectorigenin from Puerariae Flos, their effects on tert-butyl hyperoxide (t-BHP)-injured HepG2 cells and mice were investigated.
|
| Kinase Assay | Excretion of tectoridin metabolites in rat urine and bile orally administrated at different dosages and their inhibitory activity against aldose reductase.[Pubmed: 25256063]Fitoterapia. 2014 Dec;99:99-108.This study investigated the urinary and biliary excretion of Tectoridin, a major active isoflavonoid found in the flowers of Pueraria thomsonii Benth. and the rhizomes of Belamcanda chinensis (L.) DC.
|
| Cell Research | Inhibition by tectorigenin and tectoridin of prostaglandin E2 production and cyclooxygenase-2 induction in rat peritoneal macrophages.[Pubmed: 10366782]Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 Jun 10;1438(3):399-407.
|
| Structure Identification | Biol Pharm Bull. 1999 Dec;22(12):1314-8.Metabolism of 6"-O-xylosyltectoridin and tectoridin by human intestinal bacteria and their hypoglycemic and in vitro cytotoxic activities.[Pubmed: 10746163]6"-O-XylosylTectoridin and Tectoridin isolated from the flowers of Pueraria thunbergiana (Leguminosae), are metabolized to tectorigenin by human intestinal bacteria.
|

Tectoridin Dilution Calculator

Tectoridin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1626 mL | 10.8131 mL | 21.6263 mL | 43.2526 mL | 54.0657 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4325 mL | 2.1626 mL | 4.3253 mL | 8.6505 mL | 10.8131 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2163 mL | 1.0813 mL | 2.1626 mL | 4.3253 mL | 5.4066 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0433 mL | 0.2163 mL | 0.4325 mL | 0.8651 mL | 1.0813 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0216 mL | 0.1081 mL | 0.2163 mL | 0.4325 mL | 0.5407 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 4-Phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6769
CAS No.:6109-35-9
- Icotinib
Catalog No.:BCC4473
CAS No.:610798-31-7
- Isobonducellin
Catalog No.:BCN4130
CAS No.:610778-85-3
- Boc-His(Nτ-Me)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2684
CAS No.:61070-22-2
- L-Thyroxine sodium salt pentahydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4283
CAS No.:6106-07-6
- N-Desmethylclozapine
Catalog No.:BCC6887
CAS No.:6104-71-8
- Teicoplanin
Catalog No.:BCC4731
CAS No.:61036-62-2
- c-JUN peptide
Catalog No.:BCC8085
CAS No.:610273-01-3
- Ferulamide
Catalog No.:BCN4129
CAS No.:61012-31-5
- Succinylcholine Chloride Dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4564
CAS No.:6101-15-1
- Isoacetovanillone
Catalog No.:BCN7166
CAS No.:6100-74-9
- Tenuazonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1859
CAS No.:610-88-8
- (R)-Mandelic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8532
CAS No.:611-71-2
- Bromhexine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8898
CAS No.:611-75-6
- Epipterosin L 2'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4614
CAS No.:61117-89-3
- 3,9-Dihydroxypterocarpan
Catalog No.:BCN4131
CAS No.:61135-91-9
- 6alpha-Hydroxymedicarpin
Catalog No.:BCN3939
CAS No.:61135-92-0
- 4-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-2-butanone
Catalog No.:BCN4132
CAS No.:61152-62-3
- Grandifloroside
Catalog No.:BCN4133
CAS No.:61186-24-1
- Quinine HCl Dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4933
CAS No.:6119-47-7
- Uzarigenin digitaloside
Catalog No.:BCN4613
CAS No.:61217-80-9
- 6alpha-Hydroxymaackiain
Catalog No.:BCN3947
CAS No.:61218-44-8
- 11-Hydroxybisabola-1,3,5-trien-9-one
Catalog No.:BCN7530
CAS No.:61235-23-2
- Denudadione C
Catalog No.:BCN6608
CAS No.:61240-34-4
Hepatoprotective effect of tectoridin and tectorigenin on tert-butyl hyperoxide-induced liver injury.[Pubmed:15821336]
J Pharmacol Sci. 2005 Apr;97(4):541-4. Epub 2005 Apr 9.
To clarify the hepatoprotective effects of Tectoridin and tectorigenin from Puerariae Flos, their effects on tert-butyl hyperoxide (t-BHP)-injured HepG2 cells and mice were investigated. When tectorigenin at a dose of 50 mg/kg was intraperitoneally administered to mice injured by t-BHP, it significantly inhibited the increase the activities of plasma ALT and AST by 39% and 41%, respectively, in the t-BHP-treated group. The inhibitory effect of tectorigenin is much more potent than that of a commercially available dimethyl diphenyl bicarboxylate. Orally administered Tectoridin showed hepatoprotective activity. However, when Tectoridin was intraperitoneally administrated to mice, no hepatoprotective activity was observed. Tectorigenin also protected against the cytotoxicity of HepG2 cells induced by t-BHP. This protection may have originated from the inhibition of apoptosis. Tectorigenin may be hepatoprotective and Tectoridin should be a prodrug that is transformed to tectorigenin.
Metabolism of 6"-O-xylosyltectoridin and tectoridin by human intestinal bacteria and their hypoglycemic and in vitro cytotoxic activities.[Pubmed:10746163]
Biol Pharm Bull. 1999 Dec;22(12):1314-8.
6"-O-XylosylTectoridin and Tectoridin isolated from the flowers of Pueraria thunbergiana (Leguminosae), are metabolized to tectorigenin by human intestinal bacteria. Although Tectoridin is metabolized to tectorigenin by most intestinal bacteria, 6"-O-xylosylTectoridin is metabolized to tectorigenin via Tectoridin by only a few intestinal bacteria, such as Bifidobacterium breve K-110 and Eubacterium A-44. The metabolite, tectorigenin, had more potent hypoglycemic activity as well as in vitro cytotoxic activity against tumor cell lines than 6"-O-xylosylTectoridin and Tectoridin. These results suggest that 6"-O-xylosylTectoridin and Tectoridin are prodrugs which can be transformed to the active agents by human intestinal bacteria.
Excretion of tectoridin metabolites in rat urine and bile orally administrated at different dosages and their inhibitory activity against aldose reductase.[Pubmed:25256063]
Fitoterapia. 2014 Dec;99:99-108.
This study investigated the urinary and biliary excretion of Tectoridin, a major active isoflavonoid found in the flowers of Pueraria thomsonii Benth. and the rhizomes of Belamcanda chinensis (L.) DC. Using UHPLC/Q-TOFMS, seven glucuronides and/or sulfated metabolites and four Phase I metabolites were simultaneously quantified in rat urine after oral administration of Tectoridin at 100 and 200 mg/kg. Over a 72-h period, 14.2% and 14.7% of the Tectoridin were excreted as eleven metabolites in urine, among which, two major metabolites tectorigenin-7-O-beta-D-glucuronide (Te-7G) and tectorigenin accounted for 5.5-5.5% and 4.3-4.4%. Furthermore, the cumulative excretion of four glucuronides and sulfated metabolites in bile accounted for 7.3% and 3.9% of the dose within 60 h, among which, Te-7G and tectorigenin-7-O-glucuronide-4'-O-sulfate (Te-7G-4'S) accounted for 2.3-3.0% and 1.4-3.9%, respectively. The results indicate that the urine was the primary elimination route, and glucuronidation after deglycosylation at C-7 position was the major metabolic pathway of Tectoridin in vivo. Moreover, the inhibitory activities of Tectoridin and its five metabolites on rat lens aldose reductase were confirmed (IC(5)(0): 1.4-15.5 muM), whereas irisolidone-7-O-glucuronide (Ir-7G) and irisolidone showed little activity.
Pharmacokinetics of conjugated metabolites in rat plasma after oral administration of tectoridin.[Pubmed:22771104]
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2012 Aug 1;902:61-9.
Tectoridin is a major isoflavone found in the flowers of Pueraria thomsonii Benth. It possesses estrogenic, hypoglycemic, anti-oxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities. In the present study, we evaluated the plasma pharmacokinetic profile of Tectoridin in rats. We isolated a new metabolite, tectorigenin-7-O-glucuronide-4'-O-sulfate (Te-7G-4'S), from the bile of rats treated orally with Tectoridin and determined its chemical structure by spectral analysis. Furthermore, we developed a selective and accurate method for the simultaneous quantification of Tectoridin metabolites, including Te-7G-4'S, tectorigenin-7-O-glucuronide (Te-7G), tectorigenin-7-O-sulfate (Te-7S), and tectorigenin in rat plasma, and measured their plasma concentrations in rats orally administered Tectoridin (200mg/kg). Plasma concentrations of Te-7G-4'S, Te-7G, Te-7S, and tectorigenin reached maximal values of 21.4+/-13.8 mumol at 3.50+/-1.87 h, 20.5+/-9.7 mumol at 3.17+/-1.81 h, 14.3+/-3.3 mumol at 5.58+/-3.07 h, and 8.67+/-3.07 mumol at 4.92+/-2.87 h, respectively. Enterohepatic recirculation resulted in double peaks or a flat concentration curve/time profile of the metabolites. Since plasma concentrations of tectorigenin conjugated metabolites were higher than those of the tectorigenin aglycone, it can be concluded that extensive phase II metabolism plays an important role in the pharmacokinetics of Tectoridin and tectorigenin in vivo.
Inhibition by tectorigenin and tectoridin of prostaglandin E2 production and cyclooxygenase-2 induction in rat peritoneal macrophages.[Pubmed:10366782]
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 Jun 10;1438(3):399-407.
Tectorigenin and Tectoridin, isolated from the rhizomes of Korean Belamcanda chinensis (Iridaceae) which are used as Chinese traditional medicine for the treatment of inflammation, suppressed prostaglandin E2 production by rat peritoneal macrophages stimulated by the protein kinase C activator, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA), or the endomembrane Ca2+-ATPase inhibitor, thapsigargin. Tectorigenin inhibited prostaglandin E2 production more potently than Tectoridin. Neither compound inhibited the release of radioactivity from [3H]arachidonic acid-labeled macrophages stimulated by TPA or thapsigargin. In addition, activities of isolated cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and COX-2 were not inhibited by the two compounds. Western blot analysis revealed that the induction of COX-2 by TPA or thapsigargin was inhibited by the two compounds in parallel with the inhibition of prostaglandin E2 production. These findings suggest that one of the mechanisms of the anti-inflammatory activities of the rhizomes of Belamcanda chinensis is the inhibition of prostaglandin E2 production by tectorigenin and Tectoridin due to the inhibition of the induction of COX-2 in the inflammatory cells.
Tectoridin from Maackia amurensis modulates both estrogen and thyroid receptors.[Pubmed:24252334]
Phytomedicine. 2014 Apr 15;21(5):602-6.
AIM: The stem bark of Maackia amurensis has been used as folk medicine for the treatment of cancer, cholecystitis, arthritis, and hyperthyroidism in females. In this study we examined the effects of the ethyl acetate fraction obtained from the 70% ethanol extract of M. amurensis and Tectoridin, an active constituent isolated from the ethyl acetate fraction on thyroid and estrogen hormone activity. METHODS: The effect of the ethanolic extract of M. amurensis stem bark on thyroid hormone activity was evaluated using thyroid hormone responsive-luciferase assay. We isolated Tectoridin from the ethyl acetate fraction using a recrystallization method. T-screen assays were used to confirm thyroid hormone activity. The estrogenic activity of the ethyl acetate fraction of M. amurensis and Tectoridin was evaluated by estrogen responsive-luciferase assay and estrogen receptor alpha regulation as compared to 17beta-estradiol. RESULTS: Both the ethyl acetate fraction and Tectoridin activated thyroid-responsive reporters and increased thyroid hormone-dependent proliferation of rat pituitary GH3 cells, indicating modulation of thyroid hormone receptors. In parallel, the estrogenic activity of the fraction and Tectoridin were characterized in a transient transfection system using estrogen-responsive luciferase plasmids in MCF-7 cells. The ethyl acetate fraction and Tectoridin activated reporter gene expression and decreased the estrogen receptor protein level. CONCLUSIONS: These data indicate that Tectoridin acts as a weak phytoestrogen as well as a thyroid hormone-like agent by activating both estrogen and thyroid hormone receptors.
Tectoridin, a poor ligand of estrogen receptor alpha, exerts its estrogenic effects via an ERK-dependent pathway.[Pubmed:19326083]
Mol Cells. 2009 Mar 31;27(3):351-7.
Phytoestrogens are the natural compounds isolated from plants, which are structurally similar to animal estrogen, 17beta-estradiol. Tectoridin, a major isoflavone isolated from the rhizome of Belamcanda chinensis. Tectoridin is known as a phytoestrogen, however, the molecular mechanisms underlying its estrogenic effect are remained unclear. In this study we investigated the estrogenic signaling triggered by Tectoridin as compared to a famous phytoestrogen, genistein in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Tectoridin scarcely binds to ER alpha as compared to 17beta-estradiol and genistein. Despite poor binding to ER alpha, Tectoridin induced potent estrogenic effects, namely recovery of the population of cells in the S-phase after serum starvation, transactivation of the estrogen response element, and induction of MCF-7 cell proliferation. The Tectoridin-induced estrogenic effect was severely abrogated by treatment with U0126, a specific MEK1/2 inhibitor. Tectoridin promoted phosphorylation of ERK1/2, but did not affect phosphorylation of ER alpha at Ser(118). It also increased cellular accumulation of cAMP, a hallmark of GPR30-mediated estrogen signaling. These data imply that Tectoridin exerts its estrogenic effect mainly via the GPR30 and ERK-mediated rapid nongenomic estrogen signaling pathway. This property of Tectoridin sets it aside from genistein where it exerts the estrogenic effects via both an ER-dependent genomic pathway and a GPR30-dependent nongenomic pathway.


