Tenuazonic acidCAS# 610-88-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 610-88-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 54683011 | Appearance | Powder |
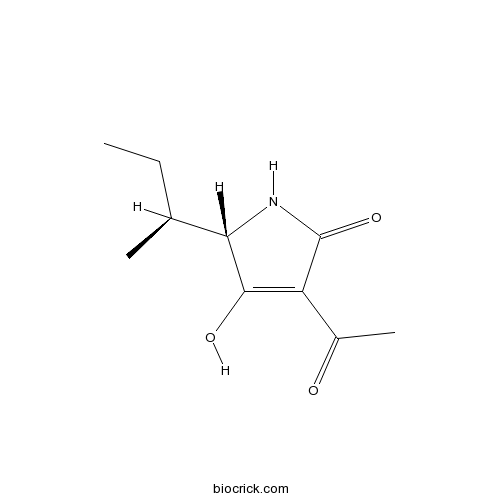
| Formula | C10H15NO3 | M.Wt | 197.23 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-4-acetyl-2-[(2S)-butan-2-yl]-3-hydroxy-1,2-dihydropyrrol-5-one | ||
| SMILES | CCC(C)C1C(=C(C(=O)N1)C(=O)C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CEIZFXOZIQNICU-XNCJUZBTSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H15NO3/c1-4-5(2)8-9(13)7(6(3)12)10(14)11-8/h5,8,13H,4H2,1-3H3,(H,11,14)/t5-,8-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Tenuazonic acid, an active component in the A. alternata toxin. 2. Tenuazonic acid exhibits a strong inhibition in photosystem II (PSII) activity. 3. Tenuazonic acid causes cell necrosis of host-plants by oxidative damage from chloroplast-mediated ROS eruption, and enhances the plant's resistances against rose aphids. |
| Targets | ATPase | ROS |

Tenuazonic acid Dilution Calculator

Tenuazonic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.0702 mL | 25.3511 mL | 50.7022 mL | 101.4045 mL | 126.7556 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.014 mL | 5.0702 mL | 10.1404 mL | 20.2809 mL | 25.3511 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.507 mL | 2.5351 mL | 5.0702 mL | 10.1404 mL | 12.6756 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1014 mL | 0.507 mL | 1.014 mL | 2.0281 mL | 2.5351 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0507 mL | 0.2535 mL | 0.507 mL | 1.014 mL | 1.2676 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- H-Leu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2968
CAS No.:61-90-5
- Zoxazolamine
Catalog No.:BCC4751
CAS No.:61-80-3
- 4-Aminohippuric Acid
Catalog No.:BCC4753
CAS No.:61-78-9
- Phenylephrine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4335
CAS No.:61-76-7
- Mefenamic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC4433
CAS No.:61-68-7
- Papaverine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8348
CAS No.:61-25-6
- Adenosine 5'-monophosphate
Catalog No.:BCC8809
CAS No.:61-19-8
- Dibucaine (Cinchocaine) HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3760
CAS No.:61-12-1
- 2-Methoxycinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5038
CAS No.:6099-03-2
- Geraniin
Catalog No.:BCN2402
CAS No.:60976-49-0
- Bz-Glu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2922
CAS No.:6094-36-6
- YZ9
Catalog No.:BCC8001
CAS No.:6093-71-6
- Isoacetovanillone
Catalog No.:BCN7166
CAS No.:6100-74-9
- Succinylcholine Chloride Dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4564
CAS No.:6101-15-1
- Ferulamide
Catalog No.:BCN4129
CAS No.:61012-31-5
- c-JUN peptide
Catalog No.:BCC8085
CAS No.:610273-01-3
- Teicoplanin
Catalog No.:BCC4731
CAS No.:61036-62-2
- N-Desmethylclozapine
Catalog No.:BCC6887
CAS No.:6104-71-8
- L-Thyroxine sodium salt pentahydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4283
CAS No.:6106-07-6
- Boc-His(Nτ-Me)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2684
CAS No.:61070-22-2
- Isobonducellin
Catalog No.:BCN4130
CAS No.:610778-85-3
- Icotinib
Catalog No.:BCC4473
CAS No.:610798-31-7
- 4-Phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6769
CAS No.:6109-35-9
- Tectoridin
Catalog No.:BCN1020
CAS No.:611-40-5
Chloroplastic oxidative burst induced by tenuazonic acid, a natural photosynthesis inhibitor, triggers cell necrosis in Eupatorium adenophorum Spreng.[Pubmed:20026008]
Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Mar;1797(3):391-405.
Tenuazonic acid (TeA), a nonhost-specific phytotoxin produced by Alternaria alternata, was determined to be a novel natural photosynthesis inhibitor owning several action sites in chloroplasts. To further elucidate the mode of its action, studies were conducted to assess the production and involvement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the toxic activity of TeA. A series of experiments indicated that TeA treatment can induce chloroplast-derived ROS generation including not only (1)O(2) but also superoxide radical, H(2)O(2) and hydroxyl radicals in Eupatorium adenophorum mesophyll cells, resulting from electron leakage and charge recombination in PSII as well as thylakoid overenergization due to inhibition of the PSII electron transport beyond Q(A) and the reduction of end acceptors on the PSI acceptor side and chloroplast ATPase activity. The initial production of TeA-induced ROS was restricted to chloroplasts and accompanied with a certain degree of chloroplast damage. Subsequently, abundant ROS were quickly dispersed throughout whole cell and cellular compartments, causing a series of irreversible cellular harm such as chlorophyll breakdown, lipid peroxidation, plasma membrane rupture, chromatin condensation, DNA cleavage, and organelle disintegration, and finally resulting in rapid cell destruction and leaf necrosis. These results show that TeA causing cell necrosis of host-plants is a result of direct oxidative damage from chloroplast-mediated ROS eruption.
In vivo assessment of effect of phytotoxin tenuazonic acid on PSII reaction centers.[Pubmed:25240106]
Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014 Nov;84:10-21.
Tenuazonic acid (TeA), a phytotoxin produced by the fungus Alternaria alternata isolated from diseased croftonweed (Ageratina adenophora), exhibits a strong inhibition in photosystem II (PSII) activity. In vivo chlorophyll fluorescence transients of the host plant croftonweed, show that the dominant effect of TeA is not on the primary photochemical reaction but on the biochemical reaction after QA. The most important action site of TeA is the QB site on the PSII electron-acceptor side, blocking electron transport beyond QA(-) by occupying the QB site in the D1 protein. However, TeA does not affect the antenna pigments, the energy transfer from antenna pigment molecules to reaction centers (RCs), and the oxygen-evolving complex (OEC) at the donor side of PSII. TeA severely inactivated PSII RCs. The fraction of non-QA reducing centers and non-QB reducing centers show a time- and concentration-dependent linear increase. Conversely, the amount of active QA or QB reducing centers declined sharply in a linear way. The fraction of non-QB reducing centers calculated from data of fluorescence transients is close to the number of PSII RCs with their QB site filled by TeA. An increase of the step-J level (VJ) in the OJIP fluorescence transients attributed to QA(-) accumulation due to TeA bound to the QB site is a typical characteristic response of the plants leaf with respect to TeA penetration.
Determination of tenuazonic acid in human urine by means of a stable isotope dilution assay.[Pubmed:23397093]
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013 May;405(12):4149-58.
The content of Tenuazonic acid in human urine was determined by a stable isotope dilution assay (SIDA) that was recently developed for the analysis of food commodities and extensively re-validated for urine matrix in this study. Linearity of the response curve was proven between molar ratios n(labeled standard)/n(analyte) of 0.02-100. The limits of detection and determination were 0.2 and 0.6 mug/L, respectively. The mean recovery of the stable isotope dilution assay was 102 +/- 3 % in the range between 1.0 and 100 mug/L. Interassay precision was 6.7 % (relative standard deviation of three triplicate analyses of a human urine sample during 3 weeks). The method was applied to two studies dealing with urinary excretion of Tenuazonic acid: In the first study, Tenuazonic acid was quantified in the 24-h urine of six volunteers from Germany (three female, three male) in a concentration range of 1.3-17.3 mug/L or 2.3-10.3 ng/mg(-1) creatinine, respectively. In the second study, two volunteers (one female, one male) ingested 30 mug Tenuazonic acid by consumption of naturally contaminated whole meal sorghum infant cereals and tomato juice, respectively. The urinary excretion of the ingested Tenuazonic acid was 54-81 % after 6 h, depending on matrix and volunteer. After 24 h, 87-93 % of the ingested amount of Tenuazonic acid was excreted, but the fate of the remaining about 10 % is open. Thus, it is not possible to exclude potential health hazards for the consumer, completely.
Alternaria toxin-induced resistance in rose plants against rose aphid (Macrosiphum rosivorum): effect of tenuazonic acid.[Pubmed:25845360]
J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2015 Apr;16(4):264-74.
Many different types of toxins are produced by the fungus, Alternaria alternata (Fr.) Keissler. Little is known, however, regarding the influence of these toxins on insects. In this study, we investigated the toxin-induced inhibitory effects of the toxin produced by A. alternata on the rose aphid, Macrosiphum rosivorum, when the toxin was applied to leaves of the rose, Rosa chinensis. The results demonstrated that the purified crude toxin was non-harmful to rose plants and rose aphids, but had an intensive inhibitory effect on the multiplication of aphids. The inhibitory index against rose aphids reached 87.99% when rose plants were sprayed with the toxin solution at a low concentration. Further results from bioassays with aphids and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analyses demonstrated that Tenuazonic acid (TeA) was one of the most important resistance-related active components in the crude toxin. The content of TeA was 0.1199% in the crude toxin under the HPLC method. Similar to the crude toxin, the inhibitory index of pure TeA reached 83.60% 15 d after the rose plants were sprayed with pure TeA solution at the lower concentration of 0.060 mug/ml, while the contents of residual TeA on the surface and in the inner portion of the rose plants were only 0.04 and 0.00 ng/g fresh weight of TeA-treated rose twigs, respectively, 7 d after the treatment. Our results show that TeA, an active component in the A. alternata toxin, can induce the indirect plant-mediated responses in rose plants to intensively enhance the plant's resistances against rose aphids, and the results are very helpful to understand the plant-mediated interaction between fungi and insects on their shared host plants.


