ScutellarinCAS# 27740-01-8 |
- Breviscapine
Catalog No.:BCX0873
CAS No.:116122-36-2
Quality Control & MSDS
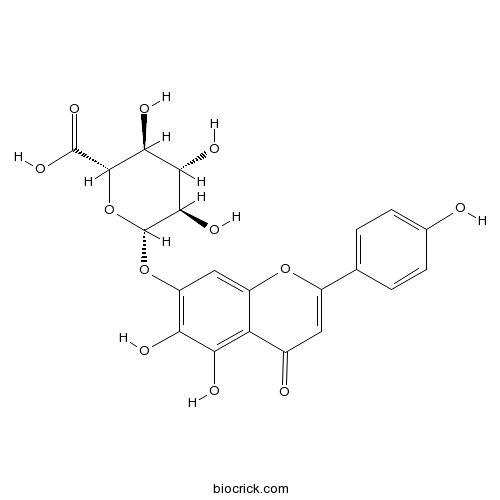
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 27740-01-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 185617 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C21H18O12 | M.Wt | 462.37 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Breviscapin;Scutellarein-7-glucuronide;Scutellarein-7beta-D-glucuronide;116122-36-2 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (216.28 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S,3S,4S,5R,6S)-6-[5,6-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxochromen-7-yl]oxy-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C2=CC(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3O2)OC4C(C(C(C(O4)C(=O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DJSISFGPUUYILV-ZFORQUDYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H18O12/c22-8-3-1-7(2-4-8)10-5-9(23)13-11(31-10)6-12(14(24)15(13)25)32-21-18(28)16(26)17(27)19(33-21)20(29)30/h1-6,16-19,21-22,24-28H,(H,29,30)/t16-,17-,18+,19-,21+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Breviscapine can treat coronary disease . 2. Breviscapine inhibits the increased levels of 4-HNE and 8-OHdG, and enhances the antioxidant capacity of cortex tissue. 3. Breviscapine can reduce the inflammatory response, protect the lungs from inflammatory cascade responses by inhibiting the expression of IL-18 and ICAM-1. 4. Breviscapine injection significantly ameliorates neurologic deficit, reduces infarct volume and water content, and suppresses the levels of NSE in a time-dependent manner, may the mechanism is by up-regulating the expression of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway .5.Scutellarin has many pharmacological effects, such as antioxidant, antitumor, antiviral, neuroprotection and antiinflammatory activities. It down-regulates the STAT3/Girdin/Akt signaling in HCC cells, and inhibits RANKL-mediated MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway in osteoclasts. |
| Targets | P450 (e.g. CYP17) | MMP(e.g.TIMP) | ROS | Calcium Channel | TGF-β/Smad | IL Receptor | TNF-α | p38MAPK | ERK | NOS | ROCK | PDE | Nrf2 | HO-1 |
| In vitro | Protection against hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells by scutellarin.[Pubmed: 15051420 ]Life Sci. 2004 Apr 30;74(24):2959-73.The present study investigated the protective actions of the antioxidant Scutellarin against the cytotoxicity produced by exposure to H2O2 in PC12 cells. This was done by assaying for MTT (3,(4,5-dimethylthiazole-2-yl)2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide) reduction and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release.
|
| In vivo | Scutellarin alleviates interstitial fibrosis and cardiac dysfunction of infarct rats by inhibiting TGFβ1 expression and activation of p38-MAPK and ERK1/2.[Pubmed: 20942814]Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Feb;162(3):688-700.Interstitial fibrosis plays a causal role in the development of heart failure after chronic myocardial infarction (MI), and anti-fibrotic therapy represents a promising strategy to mitigate this pathological process. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of long-term administration of Scutellarin (Scu) on cardiac interstitial fibrosis of myocardial infarct rats and the underlying mechanisms.
|
| Kinase Assay | In vivo effects of scutellarin on the activities of CYP1A2, CYP2C11, CYP2D1, and CYP3A1/2 by cocktail probe drugs in rats.[Pubmed: 25073400]Biological evaluation and molecular docking of baicalin and scutellarin as Helicobacter pylori urease inhibitors.[Pubmed: 25557028]J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Mar 13;162:69-78.
Pharmazie. 2014 Jul;69(7):537-41.
|
| Cell Research | Effect of scutellarin on nitric oxide production in early stages of neuron damage induced by hydrogen peroxide.[Pubmed: 15661569 ]Pharmacol Res. 2005 Mar;51(3):205-10.The aims of the present study were to investigate the regulatory function of Scutellarin on production of nitric oxide (NO) as well as activities of constitutive NO synthase (cNOS) and inducible NO synthase (iNOS) in early stages of neuron damage induced by hydrogen peroxide.
|
| Animal Research | Anti-fibrosis effect of scutellarin via inhibition of endothelial-mesenchymal transition on isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis in rats.[Pubmed: 25268717]Molecules. 2014 Sep 29;19(10):15611-23.Scutellarin (SCU) is the major active component of breviscapine and has been reported to be capable of decreasing myocardial fibrosis. The aim of the present study is to investigate whether SCU treatment attenuates isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis and the mechanisms of its action.
|

Scutellarin Dilution Calculator

Scutellarin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1628 mL | 10.8139 mL | 21.6277 mL | 43.2554 mL | 54.0693 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4326 mL | 2.1628 mL | 4.3255 mL | 8.6511 mL | 10.8139 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2163 mL | 1.0814 mL | 2.1628 mL | 4.3255 mL | 5.4069 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0433 mL | 0.2163 mL | 0.4326 mL | 0.8651 mL | 1.0814 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0216 mL | 0.1081 mL | 0.2163 mL | 0.4326 mL | 0.5407 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Scutellarin, an active flavone isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis, can down-regulates the STAT3/Girdin/Akt signaling in HCC cells, and inhibits RANKL-mediated MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway in osteoclasts.
In Vitro:Scutellarin treatment significantly reduces HepG2 cell viability in a dose-dependent manner, and inhibits migration and invasion of HCC cells in vitro. Scutellarin treatment significantly reduces STAT3 and Girders of actin filaments (Girdin) expression, STAT3 and Akt phosphorylation in HCC cells. Introduction of STAT3 overexpression restores the scutellarin-downregulated Girdin expression, Akt activation, migration and invasion of HCC cells. Furthermore, induction of Girdin overexpression completely abrogates the inhibition of scutellarin on the Akt phosphorylation, migration and invasion of HCC cells. Scutellarin can inhibit HCC cell metastasis in vivo, and migration and invasion in vitro by down-regulating the STAT3/Girdin/Akt signaling[1]. Scutellarin selectively enhances Akt phosphorylation[2]. Scutellarin is a putative therapeutic agent as it has been found to not only suppress microglial activation thus ameliorating neuroinflammation, but also enhance astrocytic reaction. Acutellarin amplifies the astrocytic reaction by upregulating the expression of neurotrophic factors among others thus indicating its neuroprotective role. Remarkably, the effects of scutellarin on reactive astrocytes are mediated by activated microglia supporting a functional cross-talk between the two glial types[3]. Scutellarin can suppress RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis, the function of osteoclast bone resorption, and the expression levels of osteoclast-specific genes (tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), cathepsin K, c-Fos, NFATc1). Further investigation indicates that Scutellarin can inhibit RANKL-mediated MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway, including JNK1/2, p38, ERK1/2, and IκBα phosphorylation[5].
In Vivo:Scutellarin (50 mg/kg/day) significantly mitigates the lung and intrahepatic metastasis of HCC tumors in vivo. The numbers of the lung and intrahepatic metastatic tumors in the scutellarin-treated group are significantly less than that in the controls[1]. The rats treated with Scutellarin display a significant alleviation in neurobehavioral deficits compared to the SAH group. Scutellarin enhanced eNOS expression compared with SAH rats[4].
References:
[1]. Ke Y, et al. Scutellarin suppresses migration and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting the STAT3/Girdin/Akt activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Dec 18. pii: S0006-291X(16)32174-X.
[2]. Yang LL, et al. Differential regulation of baicalin and scutellarin on AMPK and Akt in promoting adipose cell glucose disposal. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Nov 27 1863(2):598-606.
[3]. Wu CY, et al. Scutellarin attenuates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and promotes astrogliosis in cerebral ischemia - a therapeutic consideration. Curr Med Chem. 2016 Nov 18. [Epub ahead of print]
[4]. Li Q, et al. Scutellarin attenuates vasospasm through the Erk5-KLF2-eNOS pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. J Clin Neurosci. 2016 Dec 34:264-270.
[5]. Zhao S, et al. Scutellarin inhibits RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis and titanium particle-induced osteolysis via suppression of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Nov 40:458-465.
- 2,4-Bis(α,α-dimethylbenzyl)phenol
Catalog No.:BCC8498
CAS No.:2772-45-4
- 7-Megastigmene-3,5,6,9-tetraol
Catalog No.:BCN5168
CAS No.:276870-26-9
- Cryptomoscatone D2
Catalog No.:BCN7203
CAS No.:276856-55-4
- WAY 161503 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7179
CAS No.:276695-22-8
- Akt/SKG Substrate Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC5748
CAS No.:276680-69-4
- Leucoside
Catalog No.:BCN5167
CAS No.:27661-51-4
- Cyanidin-3-O-galactoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3022
CAS No.:27661-36-5
- Boc-Ser-OMe
Catalog No.:BCC3441
CAS No.:2766-43-0
- 5-Isoquinolinesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8749
CAS No.:27655-40-9
- 15-Nonacosanol
Catalog No.:BCC8439
CAS No.:2764-81-0
- Muscimol
Catalog No.:BCC6593
CAS No.:2763-96-4
- Rhodexin B
Catalog No.:BCC8246
CAS No.:2763-20-4
- Erysotrine
Catalog No.:BCN5170
CAS No.:27740-43-8
- Geniposidic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5171
CAS No.:27741-01-1
- Pahutoxin
Catalog No.:BCN1811
CAS No.:27742-14-9
- 5-Hydroxy-1-methoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN6575
CAS No.:27770-13-4
- Ervamycine
Catalog No.:BCN5172
CAS No.:27773-39-3
- 9-Angeloylretronecine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN2037
CAS No.:27773-86-0
- Uncarinic acid E
Catalog No.:BCN6774
CAS No.:277751-61-8
- Loroquine
Catalog No.:BCN2008
CAS No.:27792-82-1
- UDP disodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7570
CAS No.:27821-45-0
- Sunset yellow
Catalog No.:BCN2222
CAS No.:2783-94-0
- Serratenediol diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN5173
CAS No.:27832-84-4
- Loxapine Succinate
Catalog No.:BCC4674
CAS No.:27833-64-3
Protection against hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells by scutellarin.[Pubmed:15051420]
Life Sci. 2004 Apr 30;74(24):2959-73.
The present study investigated the protective actions of the antioxidant Scutellarin against the cytotoxicity produced by exposure to H2O2 in PC12 cells. This was done by assaying for MTT (3,(4,5-dimethylthiazole-2-yl)2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide) reduction and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and Ca2+ in cells were evaluated by fluorescent microplate reader using DCFH and Fura 2-AM, respectively, as probes. Lipid peroxidation was quantified using thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS). Mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) was assessed by the retention of rhodamine123 (Rh123), a specific fluorescent cationic dye that is readily sequestered by active mitochondria, depending on their transmembrane potential. The DNA content and percentage of apoptosis were monitored with flow cytometry. Vitamin E, a potent antioxidant, was employed as a comparative agent. Preincubation of PC12 cells with Scutellarin prevented cytotoxicity induced by H2O2. Intracellular accumulation of ROS, Ca2+ and products of lipid peroxidation, resulting from H2O2 were significantly reduced by Scutellarin. Incubation of cells with H2O2 caused a marked decrease in MMP, which was significantly inhibited by Scutellarin. PC12 cells treated with H2O2 underwent apoptotic death as determined by flow cytometric assay. The percentage of this H2O2-induced apoptosis in the cells was decreased in the presence of different concentrations of Scutellarin. Scutellarin exhibited significantly higher potency compared to the antioxidant vitamin E. The present findings showed that Scutellarin attenuated H2O2-induced cytotoxicity, intracellular accumulation of ROS and Ca2+, lipid peroxidation, and loss of MMP and DNA, which may represent the cellular mechanisms for its neuroprotective action.
Scutellarin alleviates interstitial fibrosis and cardiac dysfunction of infarct rats by inhibiting TGFbeta1 expression and activation of p38-MAPK and ERK1/2.[Pubmed:20942814]
Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Feb;162(3):688-700.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Interstitial fibrosis plays a causal role in the development of heart failure after chronic myocardial infarction (MI), and anti-fibrotic therapy represents a promising strategy to mitigate this pathological process. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of long-term administration of Scutellarin (Scu) on cardiac interstitial fibrosis of myocardial infarct rats and the underlying mechanisms. EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH: Scu was administered to rats that were subjected to coronary artery ligation. Eight weeks later, its effects on cardiac fibrosis were assessed by examining cardiac function and histology. The number and collagen content of cultured cardiac fibroblasts exposed to angiotensin II (Ang II) were determined after the administration of Scu in vitro. Protein expression was detected by Western blot technique, and mRNA levels by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. KEY RESULTS: The echocardiographic and haemodynamic measurements showed that Scu improved the impaired cardiac function of infarct rats and decreased interstitial fibrosis. Scu inhibited the expression of FN1 and TGFbeta1, but produced no effects on inflammatory cytokines (TNFalpha, IL-1beta and IL-6) in the 8 week infarct hearts. Scu inhibited the proliferation and collagen production of cardiac fibroblasts (CFs) and the up-regulation of FN1 and TGFbeta1 induced by Ang II. The enhanced phosphorylation of p38-MAPK and ERK1/2 in both infarct cardiac tissue and cultured CFs challenged by Ang II were suppressed by Scu. CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS: Long-term administration of Scu improved the cardiac function of MI rats by inhibiting interstitial fibrosis, and the mechanisms may involve the suppression of pro-fibrotic cytokine TGFbeta1 expression and inhibition of p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 phosphorylation.
Icariin combined with breviscapine improves the erectile function of spontaneously hypertensive rats.[Pubmed:24912989]
J Sex Med. 2014 Sep;11(9):2143-52.
INTRODUCTION: The impaired erectile response in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) is caused by increased signaling of RhoA/Rho-kinase and decreased signaling of nitric oxide (NO). Icariin improves erectile function via upregulating multitargets in NO/cyclic guanosine monophosphate (NO/cGMP) pathway, which breviscapine accomplishes by downregulating RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway. AIM: To investigate the effect and mechanism of icariin combined with breviscapine on the erectile function of SHR. METHODS: Five 12-week-old male Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats and 20 age-matched male SHR were evenly randomized into WKY rats control group, SHR control group, icariin-treated group, breviscapine-treated group, and combined treatment group treated by vehicle, icariin, breviscapine, and icariin plus breviscapine, respectively, by gavage for four successive weeks. Maximum intracavernosal pressure/mean arterial pressure (ICPmax/MAP) and the expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5), and Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1 and 2 (ROCK1 and ROCK2) in the cavernous tissues were determined. RESULTS: The ICPmax/MAP in the combined treatment group was significantly increased compared with SHR control group, icariin-treated group, and breviscapine-treated group. The expression of eNOS and nNOS was significantly higher in the combined treatment group than in SHR control group, icariin-treated group, and breviscapine-treated group (P < 0.05). The expression of PDE5 was significantly lower in the icariin-treated group than in SHR control group (P < 0.05). The expression of ROCK1 was significantly lower in the combined treatment group than in other groups (P < 0.05). The expression of ROCK2 was significantly higher in SHR control group than in WKY rats control group, icariin-treated group, and combined treatment group (P < 0.05). Among these groups, the expression of eNOS and nNOS was the strongest, and ROCK1 was the lowest in WKY rats control group. CONCLUSION: Icariin combined with breviscapine has synergistic effects on erectile function of SHR through different signal pathways.
Breviscapine Injection Improves the Therapeutic Effect of Western Medicine on Angina Pectoris Patients.[Pubmed:26052709]
PLoS One. 2015 Jun 8;10(6):e0129969.
To evaluate the beneficial and adverse effects of breviscapine injection in combination with Western medicine on the treatment of patients with angina pectoris. The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Medline, Science Citation Index, EMBASE, the China National Knowledge Infrastructure, the Wanfang Database, the Chongqing VIP Information Database and the China Biomedical Database were searched to identify randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that evaluated the effects of Western medicine compared to breviscapine injection plus Western medicine on angina pectoris patients. The included studies were analyzed using RevMan 5.1.0 software. The literature search yielded 460 studies, wherein 16 studies matched the selection criteria. The results showed that combined therapy using Breviscapine plus Western medicine was superior to Western medicine alone for improving angina pectoris symptoms (OR=3.77, 95% Cl: 2.76~5.15) and also resulted in increased electrocardiogram (ECG) improvement (OR=2.77, 95% Cl: 2.16~3.53). The current evidence suggests that Breviscapine plus Western medicine achieved a superior therapeutic effect compared to Western medicine alone.
Improved oral bioavailability of breviscapine via a Pluronic P85-modified liposomal delivery system.[Pubmed:24697705]
J Pharm Pharmacol. 2014 Jul;66(7):903-11.
OBJECTIVES: Breviscapine, a hydrophobic drug used for treating cardiovascular disease, was encapsulated in liposomes to improve its pharmaceutical characteristics. This study describes a novel liposome composition approach to specifically inhibit the P-glycoprotein efflux system. METHODS: Breviscapine-loaded Pluronic P85-coated liposomes were prepared by the thin film hydration technique. The particle size, zeta potential and encapsulation efficiency of the formulations were characterized. In-vitro drug release and permeability of Caco-2 cells were investigated. In-vitro characteristics and pharmacokinetics of the liposomes were evaluated in rat studies. KEY FINDINGS: The Pluronic P85-modified liposomes dispersed individually and had an approximate diameter of 118.8 +/- 4.9 nm and a zeta potential of -35.4 +/- 1.5 mV. Encapsulation efficiency was more than 90%. The use of the P85-coated liposomes resulted in significantly (P<0.05) increased absorption of breviscapine in Caco-2 cells and in 5.6-fold enhancement in its oral bioavailability in rats. CONCLUSION: The P85-modified liposomes for the oral delivery of breviscapine were prepared using l-alpha-phosphatidylcholine (soy-hydrogenated) and cholesterol with a narrow size distribution. This method seems to effectively enhance the bioavailability of breviscapine in rats.
In vivo effects of scutellarin on the activities of CYP1A2, CYP2C11, CYP2D1, and CYP3A1/2 by cocktail probe drugs in rats.[Pubmed:25073400]
Pharmazie. 2014 Jul;69(7):537-41.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the influence of Scutellarin on the activities of CYP1A2, CYP2C11, CYP2D1, and CYP3A1/2 in rats in vivo. METHODS: Scutellarin and saline were intravenously administered to male Wistar rats via the caudal vein for 7 days consecutively. On the 8th day, the rats were treated with probe drugs of caffeine (10 mg/kg), tolbutamide (10 mg/kg), metoprolol (20 mg/kg), dapsone (10 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection, and the blood samples were collected at different times. The probe drugs in the blood samples were measured by ultra performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometer (UPLC-MS/MS) and the changes of the pharmacokinetics parameters of the drugs were observed to evaluate the effects of Scutellarin on the four CYP450 isoforms in rats. RESULTS: The activity of CYP1A2 in rats was inhibited significantly after treatment with Scutellarin by increased caffeine t1/2 (21.76%, P < 0.05), T(max) (43.05%, P < 0.05), C(max) (43.92%, P < 0.01) and AUC(0-infinity) (50.88%, P < 0.01) in the Scutellarin-treated group compared with those of the blank control. The activity of CYP2C11 in rats was inhibited significantly after treatment with Scutellarin by increased tolbutamide t1/2 (16.74%, P < 0.01), T(max) (116.87%, P < 0.05), C(max) (63.78%, P < 0.01) and AUC(0-infinity) (70.61%, P < 0.01) in the Scutellarin-treated group compared with those of the blank control. The activity of CYP3A1/2 in rats was inhibited significantly after treatment with Scutellarin by increased dapsone t1/2 (45.28%, P < 0.05), T(max) (81.55%, P < 0.05), C(max) (155.58%, P < 0.01)and AUC(0-infinity) (176.35%, P < 0.01) in the Scutellarin-treated group compared with those of the blank control. The pharmacokinetic parameters of metoprolol were not significantly changed in the Scutellarin-treated group compared with those of the blank control. CONCLUSION: Scutellarin could significantly inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2C11 and CYP3A1/2 activities in rats in vivo, but had no effects on the activity of CYP2D1.
Breviscapine reduces acute lung injury induced by left heart ischemic reperfusion in rats by inhibiting the expression of ICAM-1 and IL-18.[Pubmed:24223666]
Exp Ther Med. 2013 Nov;6(5):1322-1326.
It has been demonstrated that breviscapine is able to treat coronary disease and reduce the inflammatory response; however, there are no relevant reports concerning its effects on the expression of inflammatory factors in acute lung injury induced by left heart ischemic reperfusion and the underlying mechanisms. In this study, we created a left heart ischemia-reperfusion model in rats to investigate the effects of breviscapine on the expression of interleukin 18 (IL-18) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), as well as to determine the possible mechanisms involved in the protective effects of breviscapine on respiratory function. The left heart ischemia-reperfusion model was created by ligating the anterior descending branch of the coronary artery for 30 mins followed by reperfusion. Rats in the treatment group (TG) were treated with breviscapine (10 mg/kg) and the rats in the control group (CG) received normal saline. Ten rats in the two groups were sacrificed at three points: 30 min after ligating (T1), 30 min after reperfusion (T2) and 60 min after reperfusion (T3). A respiration curve was produced and the arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) was measured for all rats. Additionally, the expression levels of IL-18 and ICAM-1 were determined and the correlation between IL-18 and ICAM-1 expression in lung tissue was analyzed. The level of IL-18 in peripheral blood and bronchialalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was also measured. The respiration amplitude was lower and the duration time was shorter in the TG rats than in the CG rats at T1, T2 and T3. The expression levels of IL-18 and ICAM-1 in the TG group were clearly reduced. The level of IL-18 in the peripheral blood and BALF was downregulated following the administration of breviscapine. These results demonstrate that breviscapine inhibits the expression of IL-18 and ICAM-1, thereby protecting the lungs from inflammatory cascade responses.
Therapeutic time window and underlying therapeutic mechanism of breviscapine injection against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats.[Pubmed:24291152]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151(1):660-6.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Breviscapine injection is a Chinese herbal medicine standardized product extracted from Erigeron breviscapus (Vant.) Hand.-Mazz. It has been widely used for treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. However, the therapeutic time window and the action mechanism of breviscapine are still unclear. The present study was designed to investigate the therapeutic time window and underlying therapeutic mechanism of breviscapine injection against cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion for 2h followed by 24h of reperfusion. Experiment part 1 was used to investigate the therapeutic time window of breviscapine. Rats were injected intravenously with 50mg/kg breviscapine at different time-points of reperfusion. After 24h of reperfusion, neurologic score, infarct volume, brain water content and serum level of neuron specific enolase (NSE) were measured in a masked fashion. Part 2 was used to explore the therapeutic mechanism of breviscapine. 4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE), 8-hydroxyl-2'- deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) and the antioxidant capacity of ischemia cortex were measured by ELISA and ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay, respectively. Immunofluorescence and western blot analysis were used to analyze the expression of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1). RESULTS: Part 1: breviscapine injection significantly ameliorated neurologic deficit, reduced infarct volume and water content, and suppressed the levels of NSE in a time-dependent manner. Part 2: breviscapine inhibited the increased levels of 4-HNE and 8-OHdG, and enhanced the antioxidant capacity of cortex tissue. Moreover, breviscapine obviously raised the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 proteins after 24h of reperfusion. CONCLUSION: The therapeutic time window of breviscapine injection for cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury seemed to be within 5h after reperfusion. By up-regulating the expression of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway might be involved in the therapeutic mechanism of breviscapine injection.
Biological evaluation and molecular docking of baicalin and scutellarin as Helicobacter pylori urease inhibitors.[Pubmed:25557028]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Mar 13;162:69-78.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Baicalin and Scutellarin are the principal bioactive components of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi which has extensively been incorporated into heat-clearing and detoxification formulas for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori-related gastrointestinal disorders in traditional Chinese medicine. However, the mechanism of action remained to be defined. AIM OF THE STUDY: To explore the inhibitory effect, kinetics and mechanism of Helicobacter pylori urease (the vital pathogenetic factor for Helicobacter pylori infection) inhibition by baicalin and Scutellarin, for their therapeutic potential. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The ammonia formations, indicator of urease activity, were examined using modified spectrophotometric Berthelot (phenol-hypochlorite) method. The inhibitory effect of baicalin and Scutellarin was characterized with IC50 values, compared to acetohydroxamic acid (AHA), a well known Helicobacter pylori urease inhibitor. Lineweaver-Burk and Dixon plots for the Helicobacter pylori urease inhibition of baicalin and Scutellarin was constructed from the kinetic data. SH-blocking reagents and competitive active site Ni(2+) binding inhibitors were employed for mechanism study. Molecular docking technique was used to provide some information on binding conformations as well as confirm the inhibition mode. Moreover, cytotoxicity experiment using Gastric Epithelial Cells (GES-1) was evaluated. RESULTS: Baicalin and Scutellarin effectively suppressed Helicobacter pylori urease in dose-dependent and time-independent manner with IC50 of 0.82+/-0.07 mM and 0.47+/-0.04 mM, respectively, compared to AHA (IC50=0.14+/-0.05 mM). Structure-activity relationship disclosed 4'-hydroxyl gave flavones an advantage to binding with Helicobacter pylori urease. Kinetic analysis revealed that the types of inhibition were non-competitive and reversible with inhibition constant Ki of 0.14+/-0.01 mM and 0.18+/-0.02 mM for baicalin and Scutellarin, respectively. The mechanism of urease inhibition was considered to be blockage of the SH groups of Helicobacter pylori urease, since thiol reagents (L,D-dithiothreitol, L-cysteine and glutathione) abolished the inhibitory action and competitive active site Ni(2+) binding inhibitors (boric acid and sodium fluoride) carried invalid effect. Molecular docking study further supported the structure-activity analysis and indicated that baicalin and Scutellarin interacted with the key residues Cys321 located on the mobile flap through S-H.pi interaction, but did not interact with active site Ni(2+). Moreover, Baicalin (at 0.59-1.05 mM concentrations) and Scutellarin (at 0.23-0.71 mM concentrations) did not exhibit significant cytotoxicity to GES-1. CONCLUSIONS: Baicalin and Scutellarin were non-competitive inhibitors targeting sulfhydryl groups especially Cys321 around the active site of Helicobacter pylori urease, representing potential to be good candidate for future research as urease inhibitor for treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Furthermore, our work gave additional scientific support to the use of Scutellaria baicalensis in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) to treat gastrointestinal disorders.
Anti-fibrosis effect of scutellarin via inhibition of endothelial-mesenchymal transition on isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis in rats.[Pubmed:25268717]
Molecules. 2014 Sep 29;19(10):15611-23.
Scutellarin (SCU) is the major active component of breviscapine and has been reported to be capable of decreasing myocardial fibrosis. The aim of the present study is to investigate whether SCU treatment attenuates isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis and the mechanisms of its action. Rats were injected subcutaneously with isoprenaline (Iso) to induce myocardial fibrosis and rats in the SCU treatment groups were intraperitoneally infused with SCU (10 mg.kg-1.d-1 or 20 mg.kg-1.d-1, for 14 days). Post-treatment, cardiac functional measurements and the left and right ventricular weight indices (LVWI and RVWI, respectively) were analysed. Pathological alteration, expression of type I and III collagen, Von Willebrand factor, alpha-smooth muscle actin, cluster of differentiation-31 (CD31), and the Notch signalling proteins (Notch1, Jagged1 and Hes1) were examined. The administration of SCU resulted in a significant improvement in cardiac function and decrease in the cardiac weight indices; reduced fibrous tissue proliferation; reduced levels of type I and III collagen; increased microvascular density; and decreased expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin and increased expression of CD31, Notch1, Jagged1 and Hes1 in isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis in rats. Our results suggest that SCU prevents isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis via inhibition of cardiac endothelial-mesenchymal transition potentially, which may be associated with the Notch pathway.


