Geniposidic acidCAS# 27741-01-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 27741-01-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 443354 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C16H22O10 | M.Wt | 374.3 |
| Type of Compound | Iridoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (267.14 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
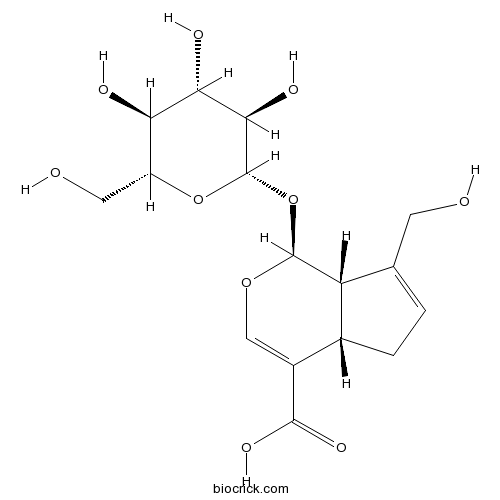
| Chemical Name | (1S,4aS,7aS)-7-(hydroxymethyl)-1-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-1,4a,5,7a-tetrahydrocyclopenta[c]pyran-4-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1C=C(C2C1C(=COC2OC3C(C(C(C(O3)CO)O)O)O)C(=O)O)CO | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZJDOESGVOWAULF-OGJQONSISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H22O10/c17-3-6-1-2-7-8(14(22)23)5-24-15(10(6)7)26-16-13(21)12(20)11(19)9(4-18)25-16/h1,5,7,9-13,15-21H,2-4H2,(H,22,23)/t7-,9-,10-,11-,12+,13-,15+,16+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Geniposidic acid is an effective anticancer and radioprotection agent, used to treat inflammation, jaundice and hepatic disorders. It has anti-atherosclerotic effects, can protect vascular endothelium and reverse plaque formation in an atherosclerotic model. Geniposidic acid has effects on the expression of MRP2 and BSEP in BRL-3A cells after FXR gene silencing mediated by si RNA. |
| Targets | HO-1 | IL Receptor | Caspase | FXR | MRP2 | BSEP |
| In vitro | Effects of geniposidic acid on the expression of MRP2 and BSEP in BRL-3A cells after FXR gene silencing mediated by si RNA[Reference: WebLink]China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine & Pharmacy, 2016,5.To investigate the effects of Geniposidic acid(GPA) on the protein expression of multidrug resistance protein 2(MRP2) and bile salt export pump(BSEP) in BRL-3A cells, which was mediated by small interfering RNA(si RNA) farnesoid X receptor(FXR) gene silencing. |
| In vivo | Comparisons of geniposidic acid and geniposide on antitumor and radioprotection after sublethal irradiation.[Pubmed: 9065798]Cancer Lett. 1997 Feb 26;113(1-2):31-7.The antitumor effects of two iridoid compounds, Geniposidic acid (GA) and geniposide (GP), were investigated in mice along with their possible effects on radioprotection after sublethal X-irradiation.
Geniposidic acid protects against D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatic failure in mice.[Pubmed: 23298456]J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Mar 7;146(1):271-7.Geniposidic acid (GA) is an iridoid glucoside isolated from Gardeniae jasminoides Ellis (Rubiaceae) that has long been used to treat inflammation, jaundice and hepatic disorders.
This study examined the cytoprotective properties of GA against D-galactosamine (GalN)/lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced fulminant hepatic failure.
|
| Animal Research | Geniposidic acid protected against ANIT-induced hepatotoxity and acute intrahepatic cholestasis, due to Fxr-mediated regulation of Bsep and Mrp2.[Pubmed: 26723467]Anti-atherosclerotic effect of geniposidic acid in a rabbit model and related cellular mechanisms.[Pubmed: 24963945]Pharm Biol. 2015 Feb;53(2):280-5.Geniposidic acid, one of the main active ingredients in Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis (Rubiaceae), may also possess important pharmacological activities for cardiovascular disorders similar to other derivatives, such as geniposide.
To evaluate its anti-atherosclerosis (anti-AS) effect, the related pharmacological activities and possible cellular mechanisms were studied.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 17;179:197-207.Geniposidic acid (GPA) is the main constituent of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis (Rubiaceae), which has long been used to treat inflammation, jaundice and hepatic disorders. The cholagogic effect of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis (Rubiaceae) and GPA have been widely reported, but the underlying occurrence mechanism remains unclear.
This investigation was designed to evaluate the hepatoprotection effect and potential mechanisms of GPA derived from Gardenia jasminoides Ellis (Rubiaceae) on fighting against α-naphthylisothiocyanate (ANIT) caused liver injury with acute intrahepatic cholestasis.
|

Geniposidic acid Dilution Calculator

Geniposidic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6717 mL | 13.3583 mL | 26.7165 mL | 53.4331 mL | 66.7913 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5343 mL | 2.6717 mL | 5.3433 mL | 10.6866 mL | 13.3583 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2672 mL | 1.3358 mL | 2.6717 mL | 5.3433 mL | 6.6791 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0534 mL | 0.2672 mL | 0.5343 mL | 1.0687 mL | 1.3358 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0267 mL | 0.1336 mL | 0.2672 mL | 0.5343 mL | 0.6679 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Geniposidic acid is an effective anticancer and radioprotection agent. Target: Others Mice were given an intraperitoneal injection of Geniposidic acid (GA) (12.5, 25, 50 mg/kg) 1 h before receiving GA against d-galactosamine (GalN) (800 mg/kg)/LPS (40 μg/kg). Liver and blood samples were collected 1 and 8 h after GalN/LPS injection. The survival rate of the GA group was significantly higher than the control. GalN/LPS increased serum aminotransferase activity, serum tumor necrosis factor-α level and hepatic lipid peroxidation and decreased hepatic glutathione content [1]. GA enhanced significantly the postirradiation responses of splenic blastogenesis by PHA. In addition, GA is a potent tumor growth inhibitor when combined with the X-irradiation, though there was no significant synergetic effect on their combined antitumor activity. The preliminary results of GA on hematological and blastogenic observations in this study suggested that it may very well, partially, play a role in an effective anticancer product with the ability to decrease undesirable radiation damage to the hematologic tissue after high dose irradiation [2].
References:
[1]. Kim, S.J., et al., Geniposidic acid protects against D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatic failure in mice. J Ethnopharmacol, 2013. 146(1): p. 271-7.
[2]. Hsu, H.Y., et al., Comparisons of geniposidic acid and geniposide on antitumor and radioprotection after sublethal irradiation. Cancer Lett, 1997. 113(1-2): p. 31-7.
- Erysotrine
Catalog No.:BCN5170
CAS No.:27740-43-8
- Scutellarin
Catalog No.:BCN5902
CAS No.:27740-01-8
- 2,4-Bis(α,α-dimethylbenzyl)phenol
Catalog No.:BCC8498
CAS No.:2772-45-4
- 7-Megastigmene-3,5,6,9-tetraol
Catalog No.:BCN5168
CAS No.:276870-26-9
- Cryptomoscatone D2
Catalog No.:BCN7203
CAS No.:276856-55-4
- WAY 161503 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7179
CAS No.:276695-22-8
- Akt/SKG Substrate Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC5748
CAS No.:276680-69-4
- Leucoside
Catalog No.:BCN5167
CAS No.:27661-51-4
- Cyanidin-3-O-galactoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3022
CAS No.:27661-36-5
- Boc-Ser-OMe
Catalog No.:BCC3441
CAS No.:2766-43-0
- 5-Isoquinolinesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8749
CAS No.:27655-40-9
- 15-Nonacosanol
Catalog No.:BCC8439
CAS No.:2764-81-0
- Pahutoxin
Catalog No.:BCN1811
CAS No.:27742-14-9
- 5-Hydroxy-1-methoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN6575
CAS No.:27770-13-4
- Ervamycine
Catalog No.:BCN5172
CAS No.:27773-39-3
- 9-Angeloylretronecine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN2037
CAS No.:27773-86-0
- Uncarinic acid E
Catalog No.:BCN6774
CAS No.:277751-61-8
- Loroquine
Catalog No.:BCN2008
CAS No.:27792-82-1
- UDP disodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7570
CAS No.:27821-45-0
- Sunset yellow
Catalog No.:BCN2222
CAS No.:2783-94-0
- Serratenediol diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN5173
CAS No.:27832-84-4
- Loxapine Succinate
Catalog No.:BCC4674
CAS No.:27833-64-3
- Macrophylline
Catalog No.:BCN1987
CAS No.:27841-97-0
- Nicergoline
Catalog No.:BCC5214
CAS No.:27848-84-6
Geniposidic acid protects against D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatic failure in mice.[Pubmed:23298456]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Mar 7;146(1):271-7.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Geniposidic acid (GA) is an iridoid glucoside isolated from Gardeniae jasminoides Ellis (Rubiaceae) that has long been used to treat inflammation, jaundice and hepatic disorders. AIMS OF THE STUDY: This study examined the cytoprotective properties of GA against D-galactosamine (GalN)/lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced fulminant hepatic failure. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Mice were given an intraperitoneal injection of GA (12.5, 25, 50 mg/kg) 1h before receiving GalN (800 mg/kg)/LPS (40 mug/kg). Liver and blood samples were collected 1 and 8 h after GalN/LPS injection. RESULTS: The survival rate of the GA group was significantly higher than the control. GalN/LPS increased serum aminotransferase activity, serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha level and hepatic lipid peroxidation and decreased hepatic glutathione content. These changes were attenuated by GA. GA augmented increases in serum interleukin-6 level, heme oxygenase-1 and NF-E2-related factor 2 protein expression. Mice treated with GA decreased cleaved caspase-8 and caspase-3 protein expression and showed significantly fewer apoptotic cells. GA increased Bcl-xL protein expression and decreased Bax protein expression. Moreover, GA treatment enhanced phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. CONCLUSION: Our findings suggest that Geniposidic acid alleviates GalN/LPS-induced liver injury by enhancing antioxidative defense system and reducing apoptotic signaling pathways.
Anti-atherosclerotic effect of geniposidic acid in a rabbit model and related cellular mechanisms.[Pubmed:24963945]
Pharm Biol. 2015 Feb;53(2):280-5.
CONTEXT: Geniposidic acid, one of the main active ingredients in Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis (Rubiaceae), may also possess important pharmacological activities for cardiovascular disorders similar to other derivatives, such as geniposide. OBJECTIVE: To evaluate its anti-atherosclerosis (anti-AS) effect, the related pharmacological activities and possible cellular mechanisms were studied. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Thirty rabbits were randomly divided into normal control group, model control group, and Geniposidic acid subgroups. In the AS model, its effects on the intima/media thickness ratio and aortic morphology were observed. In the study of primary cultured endothelial cells (ECs) and human umbilical artery smooth muscle cells (HUASMCs), its activities on both ECs and HUASMCs proliferation, HUASMCs' migration were also studied. RESULTS: Compared with the model control group, the plaque area, intima/media thickness ratio, and intimal foam cells number in Geniposidic acid (80, 160, and 240 mg/kg) subgroups were significantly improved (p < 0.05). By HE staining, the activities of Geniposidic acid on relieving ECs shedding and improving aortic morphology disorders were also demonstrated. From the results of CCK-8 testing, only 100 mug/ml Geniposidic acid performed significant inhibition on SMC proliferation. The relative IC50 of Geniposidic acid on SMC inhibition was 87.73 mug/ml. Geniposide acid also showed promotion effect on ECs proliferation, and the related ED50 of Geniposidic acid was 86.05 mug/ml. Besides, only 50 and 100 mug/ml Geniposidic acid showed obvious inhibition on SMC migration from the upper chamber (p < 0.05). DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: The effects of Geniposidic acid on protecting vascular endothelium and reversing plaque formation in an atherosclerotic model were demonstrated.
Geniposidic acid protected against ANIT-induced hepatotoxity and acute intrahepatic cholestasis, due to Fxr-mediated regulation of Bsep and Mrp2.[Pubmed:26723467]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 17;179:197-207.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Geniposidic acid (GPA) is the main constituent of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis (Rubiaceae), which has long been used to treat inflammation, jaundice and hepatic disorders. The cholagogic effect of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis (Rubiaceae) and GPA have been widely reported, but the underlying occurrence mechanism remains unclear. AIM OF THE STUDY: This investigation was designed to evaluate the hepatoprotection effect and potential mechanisms of GPA derived from Gardenia jasminoides Ellis (Rubiaceae) on fighting against alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate (ANIT) caused liver injury with acute intrahepatic cholestasis. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were intragastrically (i.g.) administered with the GPA (100, 50 and 25mg/kg B.W. every 24h) for seven consecutive days, and then they were treated with ANIT (i.g. 65mg/kg once in the 5th day) which induced liver injury with acute intrahepatic cholestasis. Serum and bile biochemical analysis, bile flow rate and liver histopathology were measured to evaluate the protective effect of GPA fight against ANIT treatment. The protein and mRNA expression levels of farnesoid X receptor (Fxr), bile-salt export pump (Bsep), multidrug resistance associated protein2 (Mrp2), were evaluated to study the effect of liver protection about GPA against ANIT induced hepatotoxicity and underlying mechanisms. RESULTS: Some abnormalities were observed on ANIT treated rats including weight loss, reduced food intake and hair turned yellow. Obtained results demonstrated that at dose 100 and 50mg/kg B.W. (P<0.01) and 25mg/kg B.W. (P<0.05) of GPA pretreated dramatically prevented ANIT induced decreased in bile flow rate. Compared with ANIT treated group, the results of bile biochemical parameters about total bile acid (TBA) was increased by GPA at groups with any dose (P<0.01), glutathione (GSH) was increased significantly at high dose (P<0.01) and medium dose (P<0.05), total bilirubin (TB) was increased at high and medium dose (P<0.05), direct bilirubin (DB) was only increased at high dose (P<0.01). Serum levels of glutamic-Oxalacetic transaminase (GOT), glutamic pyruvic transaminase (GPT), gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase (gamma-GT), TB, DB and TBA in comparison with ANIT treated group (P<0.01) were reduced by GPA (between 100 and 50mg/kg B.W.) pretreatment. Histopathology of the liver tissue showed that pathological damages and hepatic portal area filled with bile were relieved after GPA pretreatment compared with ANIT treated group. The protein and mRNA expression of Fxr, Bsep and Mrp2 were decreased in ANIT treated group. On the contrary, the protein and mRNA of Fxr, Bsep and Mrp2 were up regulated significantly pretreatment by GPA at dose of high and medium groups. On protein level of Bsep and Mrp2 the result shown no statistical difference in GPA (25mg/kg B.W.), but it was not same shown in mRNA level. CONCLUSION: The results of this investigation have demonstrated that the GPA exerts a dose dependent hepatoprotection effect on ANIT induced liver damage with acute intrahepatic cholestasis in rats, which may due to Fxr mediated regulation of bile transporters like Bsep and Mrp2.
Comparisons of geniposidic acid and geniposide on antitumor and radioprotection after sublethal irradiation.[Pubmed:9065798]
Cancer Lett. 1997 Feb 26;113(1-2):31-7.
The antitumor effects of two iridoid compounds, Geniposidic acid (GA) and geniposide (GP), were investigated in mice along with their possible effects on radioprotection after sublethal X-irradiation. Decreases in the growth of the implanted tumor by ascitic cells were a result of intraperitoneal administration of GA and GP at high concentrated levels. This result was achieved by exerting the levels of dosage in a dose-dependent manner. Except on the 12th day after treatment by the dosage of 500 mg/kg, reduced radiation effects of mice treated with the drugs in the 30 min preirradiated period by GA and GP on peripheral leukocytes were not observed significantly by the sublethal whole-body X-irradiation. And except on the 7th day after treatment, when these two compounds were administered i.p. to mice 30 min before 4 Gy irradiation, neither GA nor GP enhanced significantly the postirradiation responses of splenic blastogenesis by PHA. In addition, GA might be a more potent tumor growth inhibitor than GP when combined with the X-irradiation, though there was no significant synergetic effect on their combined antitumor activity. The preliminary results of GA and GP on hematological and blastogenic observations in this study suggested that they may very well, partially, play a role in an effective anticancer product with the ability to decrease undesirable radiation damage to the hematologic tissue after high dose irradiation.


