PD 166793MMP inhibitor CAS# 199850-67-4 |
- Calpain Inhibitor I, ALLN
Catalog No.:BCC1233
CAS No.:110044-82-1
- Calpeptin
Catalog No.:BCC2351
CAS No.:117591-20-5
- Acetyl-Calpastatin (184-210) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC2350
CAS No.:123714-50-1
- Calpain Inhibitor II, ALLM
Catalog No.:BCC1234
CAS No.:136632-32-1
- MDL 28170
Catalog No.:BCC2352
CAS No.:88191-84-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 199850-67-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9887870 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H18BrNO4S | M.Wt | 412.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 100 mM in ethanol | ||
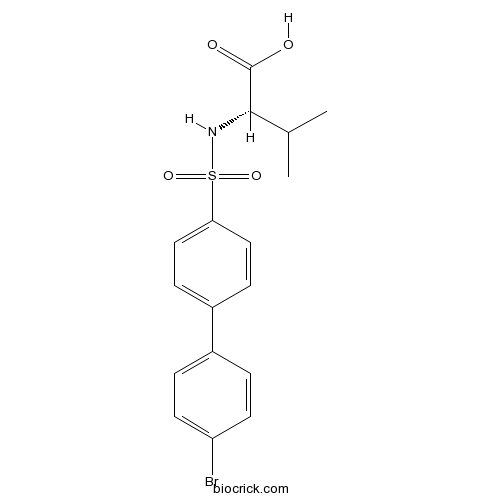
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-[[4-(4-bromophenyl)phenyl]sulfonylamino]-3-methylbutanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C(C(=O)O)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)Br | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GJOCABIDMCKCEG-INIZCTEOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H18BrNO4S/c1-11(2)16(17(20)21)19-24(22,23)15-9-5-13(6-10-15)12-3-7-14(18)8-4-12/h3-11,16,19H,1-2H3,(H,20,21)/t16-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Broad spectrum MMP inhibitor. Displays high affinity for MMP-2, -3 and -13 (IC50 values are 4, 7 and 8 nM respectively) and exhibits > 750-fold selectivity over MMP-1, -7 and -9. Attenuates left ventricular remodelling and dysfunction in rat model of heart failure. |

PD 166793 Dilution Calculator

PD 166793 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4254 mL | 12.1271 mL | 24.2542 mL | 48.5084 mL | 60.6355 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4851 mL | 2.4254 mL | 4.8508 mL | 9.7017 mL | 12.1271 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2425 mL | 1.2127 mL | 2.4254 mL | 4.8508 mL | 6.0635 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0485 mL | 0.2425 mL | 0.4851 mL | 0.9702 mL | 1.2127 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0243 mL | 0.1213 mL | 0.2425 mL | 0.4851 mL | 0.6064 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Broad spectrum MMP inhibitor. Displays high affinity for MMP-2, -3 and -13 (IC50 values are 4, 7 and 8 nM respectively) and exhibits > 750-fold selectivity over MMP-1, -7 and -9. Attenuates left ventricular remodelling and dysfunction in rat model of heart failure.
- Stattic
Catalog No.:BCC1176
CAS No.:19983-44-9
- 1-Actamido-3,5-dimethyladmantane
Catalog No.:BCC8449
CAS No.:19982-07-1
- Liguiritigenin-7-O-D-apiosyl-4'-O-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN2840
CAS No.:199796-12-8
- LY 334370 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7559
CAS No.:199673-74-0
- Ro 61-8048
Catalog No.:BCC7619
CAS No.:199666-03-0
- CP 465022 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7520
CAS No.:199655-36-2
- JIB-04
Catalog No.:BCC4548
CAS No.:199596-05-9
- Methyllucidone
Catalog No.:BCN4877
CAS No.:19956-54-8
- Lucidone
Catalog No.:BCN4876
CAS No.:19956-53-7
- NNC 26-9100
Catalog No.:BCC7361
CAS No.:199522-35-5
- 2-Amino-4-chlorobenzothiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8529
CAS No.:19952-47-7
- Veraguensin
Catalog No.:BCN2163
CAS No.:19950-55-1
- Isocudraniaxanthone B
Catalog No.:BCN6887
CAS No.:199851-52-0
- RS 127445
Catalog No.:BCC1909
CAS No.:199864-87-4
- DL-Alanyl-DL-Methionine
Catalog No.:BCC8950
CAS No.:1999-43-5
- Chrysoeriol-7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN3796
CAS No.:19993-32-9
- UCL 1684
Catalog No.:BCC7016
CAS No.:199934-16-2
- CVT-313
Catalog No.:BCC1503
CAS No.:199986-75-9
- ALX 5407 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7168
CAS No.:200006-08-2
- Benzyl 4-bromophenyl ketone
Catalog No.:BCC8868
CAS No.:2001-29-8
- Valinomycin
Catalog No.:BCC7671
CAS No.:2001-95-8
- H-Arg(Pbf)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2866
CAS No.:200115-86-2
- H-D-Arg(Pbf)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2872
CAS No.:200116-81-0
- SKF 38393 hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC6848
CAS No.:20012-10-6
Inhibiting metalloproteases with PD 166793 in heart failure: impact on cardiac remodeling and beyond.[Pubmed:18466418]
Cardiovasc Ther. 2008 Spring;26(1):24-37.
Metalloproteinases (MMPs, also called matrixins) are extracellular proteolytic enzymes involved in the degradation of both matrix and nonmatrix proteins. Currently, 25 MMPs have been identified in humans, and the overexpression of one or more MMPs has been implicated in several pathologies, spanning from cancer to rheumathoid arthritis to cardiovascular disease. While research over the past 20 years has focused on understanding MMP biology and selectively inhibiting MMP activity, key issues that remain to be addressed include MMP roles in the context of normal versus pathological conditions and whether globally inhibiting MMPs improves or deteriorates overall organ function. In terms of cardiovascular disease, increased MMP expression has been demonstrated in the setting of myocardial ischemia, reperfusion injury, and during the progression to congestive heart failure. MMPs are also major contributors to the progression of atherosclerotic lesions. In this review, we focus on cardiovascular effects produced by PD 166793, a wide-broad spectrum MMP inhibitor, originally developed by Parke-Davis (now Pfizer). We will briefly review its structure, mechanism of action, and inhibitory capacity. Finally, we will illustrate the cardiac contexts, both in vivo and in vitro, in which PD166793 administration has proven beneficial.
Effects of matrix metalloproteinase inhibition on ventricular remodeling due to volume overload.[Pubmed:11997287]
Circulation. 2002 Apr 23;105(16):1983-8.
BACKGROUND: Left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy and dilatation are important compensatory responses to chronic volume overload. Although LV function is initially preserved by these responses, the continued structural remodeling of the myocardium ultimately becomes maladaptive, leading to the development of heart failure. We have shown previously that increased myocardial matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activity precedes LV dilatation induced by a chronic volume overload. Accordingly, this study focused on the effects of MMP inhibition therapy (PD 166793, 1 mg x kg(-1) x d(-1)) on LV size and function in a rat model of volume overload-induced heart failure. METHODS AND RESULTS: Rats were divided into the following groups: treated and untreated infrarenal abdominal aortocaval fistula and treated and untreated sham-operated (control). LV weights of both fistula groups were increased above that of the control group (868+/-79 mg; P< or =0.001); LV weights in the treated fistula group, however, were lower than in the untreated fistula group at 8 weeks (1447+/-186 versus 1715+/-279 mg, respectively; P< or =0.012). The marked ventricular dilatation seen in the untreated fistula group was significantly diminished in the treated fistula group, although the increase in LV compliance was similar in both treated and untreated fistula hearts. CONCLUSIONS: MMP inhibition significantly attenuates the myocardial remodeling associated with chronic volume overload, as evidenced by prevention of dilatation, a marked reduction in LV hypertrophy, and preservation of ventricular function.
Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition attenuates left ventricular remodeling and dysfunction in a rat model of progressive heart failure.[Pubmed:11342481]
Circulation. 2001 May 8;103(18):2303-9.
BACKGROUND: Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activation contributes to tissue remodeling in several disease states, and increased MMP activity has been observed in left ventricular (LV) failure. The present study tested the hypothesis that MMP inhibition would influence LV remodeling and function in developing LV failure. METHODS AND RESULTS: LV size and function were measured in 5 groups of rats: (1) obese male spontaneously hypertensive heart failure rats (SHHF) at 9 months (n=10), (2) SHHF at 13 months (n=12), (3) SHHF rats treated with an MMP inhibitor during months 9 to 13 (PD166793 5 mg. kg(-1). d(-1) PO; n=14), (4) normotensive Wistar-Furth rats (WF) at 9 months (n=12), and (5) WF at 13 months (n=12). Plasma concentrations of the MMP inhibitor (116+/-11 micromol/L) reduced in vitro LV myocardial MMP-2 activity by approximately 100%. LV function and geometry were similar in WF rats at 9 and 13 months. LV peak +dP/dt was unchanged at 9 months in SHHF but by 13 months was reduced in the SHHF group compared with WF (3578+/-477 versus 5983+/-109 mm Hg/s, P
Structure-activity relationships and pharmacokinetic analysis for a series of potent, systemically available biphenylsulfonamide matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors.[Pubmed:10649971]
J Med Chem. 2000 Jan 27;43(2):156-66.
A series of biphenylsulfonamide derivatives of (S)-2-(biphenyl-4-sulfonylamino)-3-methylbutyric acid (5) were prepared and evaluated for their ability to inhibit matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). For this series of compounds, our objective was to systematically replace substituents appended to the biphenyl and alpha-position of 5 with structurally diverse functionalities to assess the effects these changes have on biological and pharmacokinetic activity. The ensuing structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies showed that biphenylsulfonamides substituted with bromine in the 4'-position (11c) significantly improved in vitro activity and exhibited superior pharmacokinetics (C(max), t(1/2), AUCs), relative to compound 5. Varying the lipophilicity of the alpha-position by replacing the isopropyl group of 11c with a variety of substituents, in general, maintained potency versus MMP-2, -3, and -13 but decreased the oral systemic availability. Subsequent evaluation of its enantiomer, 11c', showed that both compounds were equally effective MMP inhibitors. In contrast, the corresponding hydroxamic acid enantiomeric pair, 16a (S-isomer) and 16a' (R-isomer), stereoselectivity inhibited MMPs. For the first time in this series, 16a' provided nanomolar potency against MMP-1, -7, and -9 (IC(50)'s = 110, 140, and 18 nM, respectively), whereas 16a was less potent against these MMPs (IC(50)'s = 24, 78, and 84 microM, respectively). However, unlike 11c, compound 16a' afforded very low plasma concentrations following a single 5 mg/kg oral dose in rat. Subsequent X-ray crystal structures of the catalytic domain of stromelysin (MMP-3CD) complexed with inhibitors from closely related series established the differences in the binding mode of carboxylic acid-based inhibitors (11c,c') relative to the corresponding hydroxamic acids (16a,a').


