NNC 26-9100Selective sst4 agonist CAS# 199522-35-5 |
- DBeQ
Catalog No.:BCC3916
CAS No.:177355-84-9
- Xanthohumol
Catalog No.:BCN5768
CAS No.:569-83-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 199522-35-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9893924 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H25N6Cl2SBr | M.Wt | 556.35 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in DMSO and to 50 mM in ethanol | ||
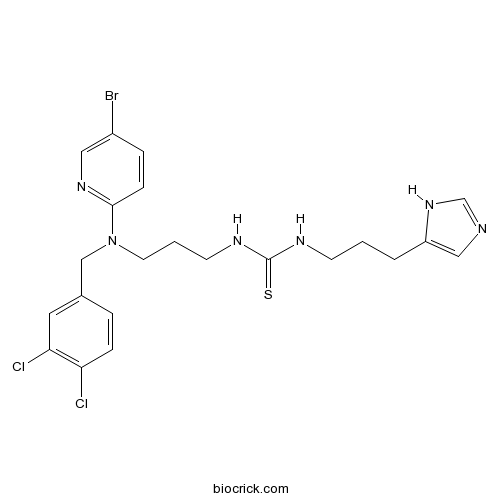
| Chemical Name | 1-[3-[(5-bromopyridin-2-yl)-[(3,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl]amino]propyl]-3-[3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propyl]thiourea | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C=C1CN(CCCNC(=S)NCCCC2=CN=CN2)C3=NC=C(C=C3)Br)Cl)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UREJDUPKGMFJRU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H25BrCl2N6S/c23-17-5-7-21(29-12-17)31(14-16-4-6-19(24)20(25)11-16)10-2-9-28-22(32)27-8-1-3-18-13-26-15-30-18/h4-7,11-13,15H,1-3,8-10,14H2,(H,26,30)(H2,27,28,32) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Somatostatin sst4 receptor agonist that displays > 100-fold selectivity over sst2 receptors (Ki values are 6 and 621 nM for sst4 and sst2 receptors respectively). Potently inhibits forskolin-induced cAMP accumulation (EC50 = 26 nM). |

NNC 26-9100 Dilution Calculator

NNC 26-9100 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7974 mL | 8.9871 mL | 17.9743 mL | 35.9486 mL | 44.9357 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3595 mL | 1.7974 mL | 3.5949 mL | 7.1897 mL | 8.9871 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1797 mL | 0.8987 mL | 1.7974 mL | 3.5949 mL | 4.4936 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0359 mL | 0.1797 mL | 0.3595 mL | 0.719 mL | 0.8987 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.018 mL | 0.0899 mL | 0.1797 mL | 0.3595 mL | 0.4494 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 2-Amino-4-chlorobenzothiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8529
CAS No.:19952-47-7
- Veraguensin
Catalog No.:BCN2163
CAS No.:19950-55-1
- Y-33075
Catalog No.:BCC2064
CAS No.:199433-58-4
- 3-Epicabraleadiol
Catalog No.:BCN4875
CAS No.:19942-04-2
- Gymnestrogenin
Catalog No.:BCN7846
CAS No.:19942-02-0
- Kolavenol
Catalog No.:BCN4680
CAS No.:19941-83-4
- Crocatone
Catalog No.:BCN3532
CAS No.:19937-86-1
- Glyurallin A
Catalog No.:BCN7538
CAS No.:199331-36-7
- Dehydroglyasperin C
Catalog No.:BCN6790
CAS No.:199331-35-6
- O6-Benzylguanine
Catalog No.:BCC6485
CAS No.:19916-73-5
- Boc-D-N-Me-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3211
CAS No.:19914-38-6
- Enniatin B1
Catalog No.:BCN4853
CAS No.:19914-20-6
- Lucidone
Catalog No.:BCN4876
CAS No.:19956-53-7
- Methyllucidone
Catalog No.:BCN4877
CAS No.:19956-54-8
- JIB-04
Catalog No.:BCC4548
CAS No.:199596-05-9
- CP 465022 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7520
CAS No.:199655-36-2
- Ro 61-8048
Catalog No.:BCC7619
CAS No.:199666-03-0
- LY 334370 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7559
CAS No.:199673-74-0
- Liguiritigenin-7-O-D-apiosyl-4'-O-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN2840
CAS No.:199796-12-8
- 1-Actamido-3,5-dimethyladmantane
Catalog No.:BCC8449
CAS No.:19982-07-1
- Stattic
Catalog No.:BCC1176
CAS No.:19983-44-9
- PD 166793
Catalog No.:BCC2376
CAS No.:199850-67-4
- Isocudraniaxanthone B
Catalog No.:BCN6887
CAS No.:199851-52-0
- RS 127445
Catalog No.:BCC1909
CAS No.:199864-87-4
Somatostatin receptor subtype-4 agonist NNC 26-9100 mitigates the effect of soluble Abeta(42) oligomers via a metalloproteinase-dependent mechanism.[Pubmed:23669069]
Brain Res. 2013 Jul 3;1520:145-56.
Soluble amyloid-beta peptide (Abeta) oligomers have been hypothesized to be primary mediators of Alzheimer's disease progression. In this regard, reduction of soluble Abeta-oligomers levels within the brain may provide a viable means in which to treat the disease. Somatostatin receptor subtype-4 (SSTR4) agonists have been proposed to reduce Abeta levels in the brain via enhancement of enzymatic degradation. Herein we evaluated the effect of selective SSTR4 agonist NNC 26-9100 on the changes in learning and soluble Abeta42 oligomer brain content with and without co-administration of the M13-metalloproteinase family enzyme-inhibitor phosphoramidon, using the senescence-accelerated mouse prone-8 (SAMP8) model. NNC 26-9100 treatment (0.2 microg i.c.v. in 2 microL) improved learning, which was blocked by phosphoramidon (1 and 10mM, respectively). NNC 26-9100 decreased total soluble Abeta42, an effect which was blocked by phosphoramidon (10mM). Extracellular, intracellular, and membrane fractions were then isolated from cortical tissue and assessed for soluble oligomer alterations. NNC 26-9100 decreased the Abeta42 trimeric (12 kDa) form within the extracellular and intracellular fractions, and produced a band-split effect of the Abeta42 hexameric (25 kDa) form within the extracellular fraction. These effects were also blocked by phosphoramdon (1 and 10mM, respectively). Subsequent evaluation of NNC 26-9100 in APPswe Tg2576 transgenic mice showed a similar learning improvement and corresponding reduction in soluble Abeta42 oligomers within extracellular, intracellular, and membrane fractions. These data support the hypothesis that NNC 26-9100 reduces soluble Abeta42 oligomers and enhances learning through a phosphoramidon-sensitive metalloproteinase-dependent mechanism.
Somatostatin receptor subtype-4 agonist NNC 26-9100 decreases extracellular and intracellular Abeta(1)(-)(4)(2) trimers.[Pubmed:22449380]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 May 15;683(1-3):116-24.
Soluble amyloid beta-protein (Abeta) oligomers are primary mediators of synaptic dysfunction associated with the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Such Abeta oligomers exist dependent on their rates of aggregation and metabolism. Use of selective somatostatin receptor-subtype agonists have been identified as a potential means to mitigate Abeta accumulation in the brain, via regulation of the enzyme neprilysin. Herein, we first evaluated the impact of the somatostatin receptor subtype-4 agonist 1-[3-[N-(5-Bromopyridin-2-yl)-N-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)amino]propyl]-3-[3-(1H-imidaz ol-4-yl)propyl]thiourea (NNC 26-9100) on learning and memory in 12-month SAMP8 mice (i.c.v. injection). NNC 26-9100 (0.2 mug-dose) was shown to enhance both learning (T-maze) and memory (object recognition) compared to vehicle controls. Cortical and hippocampal tissues were evaluated subsequent to NNC 26-9100 (0.2 mug) or vehicle administration for changes in neprilysin activity, along with protein expression of amyloid-precursor protein (APP), neprilysin, and Abeta(1)(-)(4)(2) oligomers within respective cellular fractions (extracellular, intracellular and membrane). NNC 26-9100 increased neprilysin activity in cortical tissue, with an associated protein expression increase in the extracellular fraction and decreased in the intracellular fraction. A decrease in intracellular APP expression was found with treatment in both cortical and hippocampal tissues. NNC 26-9100 also significantly decreased expression of Abeta(1)(-)(4)(2) trimers within both the extracellular and intracellular cortical fractions. No expression changes were found in membrane fractions for any protein. These finding suggest the potential use of selective SSTR4 agonists to mitigate toxic oligomeric forms of Abeta(1)(-)(4)(2) in critical regions of the brain identified with learning and memory decline.
Chronic peripheral administration of somatostatin receptor subtype-4 agonist NNC 26-9100 enhances learning and memory in SAMP8 mice.[Pubmed:21185826]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Mar 1;654(1):53-9.
Selective somatostatin receptor subtype agonists have been proposed as a means to mitigate learning and memory loss associated with Alzheimer's disease. The first aim of this study evaluated blood-to-brain transport and regional brain distribution of NNC 26-9100, a selective somatostatin subtype-4 (sst4) receptor agonist. The entry rate of (131)I-NNC 26-9100 was K(i)=0.25 mul/g min, with an ~93% association with the parenchymal component. The second goal of this study was to evaluate the effect of chronic NNC 26-9100 administration (i.p.) on learning and memory, brain Abeta(x-42) levels, and protein expression of sst4 receptor and amyloid precursor protein (APP) in the senescence-accelerated mouse p8 (SAMP8) model of Alzheimer's disease. Mice chronically treated with NNC 26-9100 showed improved learning (day 21) and memory (day 28) using the T-maze paradigm (20 and 200 mug). Ex vivo tissue analyses showed a decline in Abeta(x-42) levels at the 20 mug dose, while no alterations were observed in sst4 receptor or APP protein expression compared to vehicle controls. These findings indicate NNC 26-9100 is taken up into key brain regions associated with learning and memory. Furthermore, chronic administration of NNC 26-9100 improved learning and memory and decreased Abeta(x-42) brain levels. These results suggest sst4 receptor agonists may provide a viable therapy in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other forms of cognitive impairment.
Inhibitory effect of somatostatin receptor subtype-4 agonist NNC 26-9100 on micturition reflex in rats.[Pubmed:22951005]
Urology. 2012 Dec;80(6):1391.e9-13.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the effects of activation of somatostatin subtype 4 (SST4) on the micturition reflex in rats. METHODS: Continuous cystometrograms (0.04 mL/min infusion rate) were performed in female Sprague-Dawley rats (242-265 g) under urethane anesthesia. After stable micturition cycles were established, a selective SST4 receptor agonist, NNC 26-9100, was administered intravenously in normal rats or rats pretreated with capsaicin 4 days before the experiments. The micturition parameters were recorded and compared before and after drug administration. RESULTS: Intravenous administration of NNC 26-9100 (10-300 mug/kg) significantly increased the intercontraction interval in a dose-dependent fashion. Intravenous administration of NNC 26-9100 (10-300 mug/kg) also significantly increased the pressure threshold in a dose-dependent fashion. No significant changes were seen in the baseline pressure, maximum voiding pressure, or postvoid residual urine volume. However, NNC 26-9100-induced increases in the intercontraction intervals and pressure threshold were not seen in rats with C-fiber desensitization induced by capsaicin pretreatment. CONCLUSION: These results indicate that in urethane-anesthetized rats, activation of the SST4 receptor can inhibit the micturition reflex by suppression of capsaicin-sensitive C-fiber afferent pathways. Thus, the SST4 receptor could be a potential target for the treatment of C-fiber afferent-mediated bladder dysfunction.
2-pyridylthioureas: novel nonpeptide somatostatin agonists with SST4 selectivity.[Pubmed:10101224]
Curr Pharm Des. 1999 Apr;5(4):255-63.
Somatostatin [somatotropin release-inhibiting factor (SRIF)] is a cyclic tetradecapeptide that is a potent inhibitor of growth hormone (GH) secretion from the anterior pituitary. In addition to the inhibitory effects on GH-release, SRIF-14 and SRIF-28, a 28-amino acid form of SRIF extended from the N-terminal end, inhibit the release of a variety of other peptides including glucagon, insulin, and gastrin, and both peptides act as neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in the central nervous system and the periphery. SRIF exerts its potent inhibitory effects following binding to high affinity SRIF receptors (ssts) that have been identified on target tissues. The recent cloning of five ssts has confirmed that the effects of SRIF are mediated by a family of G protein-coupled receptors (sst1-5). Based on structural and pharmacological properties sst2, sst3, and sst5 belong to the SRIF1 receptor subclass, and the sst1 and sst4 subtypes comprise the SRIF2 subclass. The major difference between these two subclasses is that SRIF1 receptors bind octapeptide and hexapeptide SRIF-14 analogs with high affinity, while SRIF2 receptors bind these analogs with drastically reduced affinity. A screening program was initiated to identify a lead nonpeptide with affinity for sst1-5 receptors. The search focused on a scaffold with the following attachments: (1) a heteroaromatic nucleus to mimic the Trp8 residue, (2) a nonheteroaromatic nucleus to mimic Phe7, and (3) a primary amine or other basic group to mimic the Lys9 residue of SRIF-14. Using these criteria, a novel thiourea (NNC 26-9100, 17) was discovered as a structural lead. The key fragments in this compound are a heteroaromatic moiety (pyridine), an aromatic group, and a basic imidazole group connected through a thiourea scaffold. Compound 17 exhibited a Ki = 6 nM at sst4 receptors with a 100-fold sst4/sst2 selectivity and was shown to be a full agonist at this receptor subtype. This article will review the literature on the design and development of nonpeptide somatostatin receptor ligands and the therapeutic potential of these agents. Furthermore, our work on the development of 2-pyridylthioureas as sst4 receptor agonists will be described.
Nonpeptide somatostatin agonists with sst4 selectivity: synthesis and structure-activity relationships of thioureas.[Pubmed:9822540]
J Med Chem. 1998 Nov 19;41(24):4693-705.
Utilizing NNC 26-9100 (11) as a structural lead, a variety of nonpeptide derivatives of somatostatin were synthesized and evaluated for sst2 and sst4 receptor binding affinity. A novel thiourea scaffold was utilized to attach (1) a heteroaromatic nucleus to mimic the Trp8 residue, (2) a nonheteroaromatic nucleus to mimic Phe7, and (3) a primary amine or other basic group to mimic the Lys9 residue of somatostatin. Displacement studies were carried out using membranes from cell lines expressing ssts [BHK cells (sst4) and HEK 293 cells (sst2)] utilizing [125I]Tyr11-SRIF as the radioligand. Several thioureas (11, 38, 39, 41, and 42) and the urea 66 exhibited Ki values of less than 100 nM. The thioureas 11 (Ki = 6 nM) and 41 (Ki = 16 nM) and the urea 66 (Ki = 14 nM) are believed to be the most potent nonpeptide sst4 agonists known. Since the thiourea 11 and the urea 66 exhibit high sst4 selectivity, these novel nonpeptide derivatives may be useful tools for studying the sst4 receptor. Studies are currently in progress to evaluate the therapeutic potential of NNC 26-9100 (11) in the treatment of glaucoma.


