LapacholCAS# 84-79-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 84-79-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3884 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
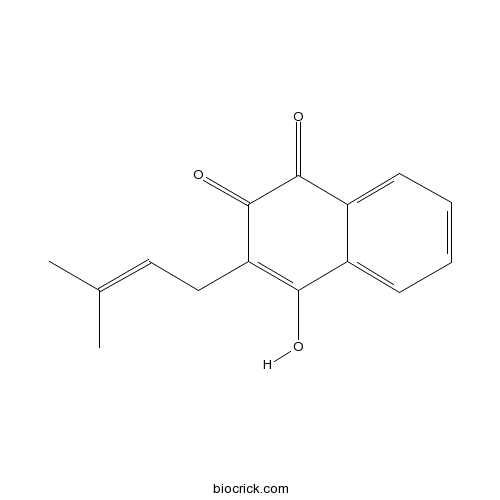
| Formula | C15H14O3 | M.Wt | 242.3 |
| Type of Compound | Quinones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol and methanol; sparingly soluble in hot water | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-hydroxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)naphthalene-1,2-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CCC1=C(C2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)C1=O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CWPGNVFCJOPXFB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H14O3/c1-9(2)7-8-12-13(16)10-5-3-4-6-11(10)14(17)15(12)18/h3-7,16H,8H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Lapachol shows both antimicrobial, trypanocidal and antiviral activities, it also shows antimalarial activity against Plasmodium falciparum in vitro and Plasmodium berghei in vivo. Probiotics are capable of converting Lapachol into the most effective cytotoxic compound against a breast cancer cell line. |
| Targets | Antifection |
| In vitro | Cytotoxicity of lapachol metabolites produced by probiotics.[Pubmed: 24635204]Lett Appl Microbiol. 2014 Jul;59(1):108-14.Probiotics are currently added to a variety of functional foods to provide health benefits to the host and are commonly used by patients with gastrointestinal complaints or diseases. The therapeutic effects of Lapachol continue to inspire studies to obtain derivatives with improved bioactivity and lower unwanted effects. Therefore, the general goal of this study was to show that probiotics are able to convert Lapachol and are important to assess the effects of bacterial metabolism on drug performance and toxicity.
Trypanosoma cruzi: activities of lapachol and alpha- and beta-lapachone derivatives against epimastigote and trypomastigote forms.[Pubmed: 18029184 ]Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Jan 15;16(2):668-74.
Antimalarial activity of phenazines from lapachol, beta-lapachone and its derivatives against Plasmodium falciparum in vitro and Plasmodium berghei in vivo.[Pubmed: 14980653]Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Mar 8;14(5):1145-9.
|
| Cell Research | Demonstration of the lapachol as a potential drug for reducing cancer metastasis.[Pubmed: 15643520]Oncol Rep. 2005 Feb;13(2):329-33.Metastasis is the major process responsible for the death in cancer patients. In the search for more effective antineoplasic drugs, many substances are under investigation, among them Lapachol. This study aims to examine the molecular and morphological alterations caused by Lapachol treatment, as well as its effects on the intrinsic tissue invasive property of this cell line. |
| Structure Identification | J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Jan 1;944:128-35.Structural elucidation of the metabolites of lapachol in rats by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 24316523]Lapachol is a natural naphthoquinone compound derived from Bignoniaceae (Tabebuia sp.) that possesses a range of significant biological activities. |

Lapachol Dilution Calculator

Lapachol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.1271 mL | 20.6356 mL | 41.2712 mL | 82.5423 mL | 103.1779 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8254 mL | 4.1271 mL | 8.2542 mL | 16.5085 mL | 20.6356 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4127 mL | 2.0636 mL | 4.1271 mL | 8.2542 mL | 10.3178 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0825 mL | 0.4127 mL | 0.8254 mL | 1.6508 mL | 2.0636 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0413 mL | 0.2064 mL | 0.4127 mL | 0.8254 mL | 1.0318 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Dibutyl Phthalate
Catalog No.:BCC8411
CAS No.:84-74-2
- Diisobutyl phthalate
Catalog No.:BCN7148
CAS No.:84-69-5
- Anthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCC8832
CAS No.:84-65-1
- Anthraflavic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8831
CAS No.:84-60-6
- Tectoquinone
Catalog No.:BCN3481
CAS No.:84-54-8
- Stylopine
Catalog No.:BCN3715
CAS No.:84-39-9
- Syrosingopine
Catalog No.:BCN5365
CAS No.:84-36-6
- Ophiohayatone C
Catalog No.:BCN3608
CAS No.:84-33-3
- Rutaecarpine
Catalog No.:BCN4385
CAS No.:84-26-4
- Hexestrol
Catalog No.:BCC4484
CAS No.:84-16-2
- Cariprazine
Catalog No.:BCC1453
CAS No.:839712-12-8
- 2,7-Dimethyl-1,4-dihydroxynaphthalene 1-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7611
CAS No.:839711-70-5
- Vitamin K1
Catalog No.:BCN2209
CAS No.:84-80-0
- Xanthoxyletin
Catalog No.:BCN6579
CAS No.:84-99-1
- Fmoc-N-Me-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3210
CAS No.:84000-07-7
- Fmoc-N-Me-Val-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3358
CAS No.:84000-11-3
- Helioxanthin 8-1
Catalog No.:BCC5415
CAS No.:840529-13-7
- Lamotrigine
Catalog No.:BCC5051
CAS No.:84057-84-1
- Roquinimex
Catalog No.:BCC5355
CAS No.:84088-42-6
- 1-Benzhydrylpiperazine
Catalog No.:BCC8453
CAS No.:841-77-0
- Wilforlide A
Catalog No.:BCN4383
CAS No.:84104-71-2
- Wilforlide A acetate
Catalog No.:BCN4384
CAS No.:84104-80-3
- Triptotriterpenic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN6780
CAS No.:84108-17-8
- R406 (free base)
Catalog No.:BCC2553
CAS No.:841290-80-0
Demonstration of the lapachol as a potential drug for reducing cancer metastasis.[Pubmed:15643520]
Oncol Rep. 2005 Feb;13(2):329-33.
Metastasis is the major process responsible for the death in cancer patients. In the search for more effective antineoplasic drugs, many substances are under investigation, among them Lapachol. This study aims to examine the molecular and morphological alterations caused by Lapachol treatment, as well as its effects on the intrinsic tissue invasive property of this cell line. HeLa cells were exposed to different concentrations of Lapachol, and the resulting alterations on cellular protein profile, morphology and invasiveness property were studied. At 400 microg/ml, cellular viability remains unchanged, but Lapachol induces alterations in the protein profile and inhibits the invasiveness of HeLa cells in CAM model. With these results, we can conclude that Lapachol has a great potential of application in fighting metastasis.
Antimalarial activity of phenazines from lapachol, beta-lapachone and its derivatives against Plasmodium falciparum in vitro and Plasmodium berghei in vivo.[Pubmed:14980653]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Mar 8;14(5):1145-9.
The antimalarial activity of benzo[a]phenazines synthesized from 1,2-naphthoquinone, Lapachol, beta-lapachone and several derivatives have been tested against Plasmodium falciparum in vitro using isolates of parasites with various susceptibilities to chloroquine and/or mefloquine. Parasite growth in the presence of the test drugs was measured by incorporation of [(3)H]-hipoxanthine in comparison to controls with no drugs, always testing in parallel chloroquine, a standard antimalarial. Among seven benzophenazines tested, four had significant in vitro activities; important, the parasites resistant to chloroquine were more susceptible to the active phenazines in vitro. The doses of phenazines causing 50% inhibition of parasite growth varied from 1.67 to 9.44 microM. The two most active ones were also tested in vivo against Plasmodium berghei in mice, in parallel with Lapachol and beta-lapachone. The 3-sulfonic acid-beta-lapachone-derived phenazine was the most active causing up to 98% inhibition of parasitaemia in long term treatment (7 doses) subcutaneously, whereas the phenazine from 3-bromo-beta-lapachone was inactive. Thus, these simple phenazines, containing polar (-Br,-I) and ionizable (-SO(3)H, -OH) groups, easily synthesized from cheap, natural or synthetic precursors (Lapachol and beta-lapachone), at rather low cost, provide prototypes for development of new antimalarials aiming the chloroquine resistant parasites.
Cytotoxicity of lapachol metabolites produced by probiotics.[Pubmed:24635204]
Lett Appl Microbiol. 2014 Jul;59(1):108-14.
UNLABELLED: Probiotics are currently added to a variety of functional foods to provide health benefits to the host and are commonly used by patients with gastrointestinal complaints or diseases. The therapeutic effects of Lapachol continue to inspire studies to obtain derivatives with improved bioactivity and lower unwanted effects. Therefore, the general goal of this study was to show that probiotics are able to convert Lapachol and are important to assess the effects of bacterial metabolism on drug performance and toxicity. The microbial transformations of Lapachol were carried out by Bifidobacterium sp. and Lactobacillus acidophilus and different metabolites were produced in mixed and isolated cultures. The cytotoxic activities against breast cancer and normal fibroblast cell lines of the isolated metabolites (4alpha-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-5-oxo-2,3,4,4alpha,5,9beta-hexahydroindeno[1,2-beta] pyran-9beta-carboxilic acid, a new metabolite produced by mixed culture and dehydro-alpha-lapachone produced by isolated cultures) were assessed and compared with those of Lapachol. The new metabolite displayed a lower activity against a breast cancer cell line (IC50 = 532.7 mumol l(-1) ) than Lapachol (IC50 = 72.3 mumol l(-1) ), while dehydro-alpha-lapachone (IC50 = 10.4 mumol l(-1) ) displayed a higher activity than Lapachol. The present study is the first to demonstrate that probiotics are capable of converting Lapachol into the most effective cytotoxic compound against a breast cancer cell line. SIGNIFICANCE AND IMPACT OF THE STUDY: Probiotics have been used in dairy products to promote human health and have the ability to metabolize drugs and other xenobiotics. Naphthoquinones, such as Lapachol, are considered privileged scaffolds due to their high propensity to interact with biological targets. The present study is the first to demonstrate that probiotics are capable of converting Lapachol into the most effective cytotoxic compound against a breast cancer cell line. The developed approach highlights the importance of probiotics to assess the effects of bacterial metabolism on drug performance and toxicity.
Trypanosoma cruzi: activities of lapachol and alpha- and beta-lapachone derivatives against epimastigote and trypomastigote forms.[Pubmed:18029184]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Jan 15;16(2):668-74.
Derivatives of natural quinones with biological activities, such as Lapachol, alpha- and beta-lapachones, have been synthesized and their trypanocidal activity evaluated in vitro in Trypanosoma cruzi cells. All tested compounds inhibited epimastigote growth and trypomastigote viability. Several compounds showed similar or higher activity as compared with current trypanocidal drugs, nifurtimox and benznidazole. The results presented here show that the anti-T. cruzi activity of the alpha-lapachone derivatives can be increased by the replacement of the benzene ring by a pyridine moiety. Free radical production and consequently oxidative stress through redox cycling or production of electrophilic metabolites are the potential biological mechanism of action for these synthetic quinones.
Structural elucidation of the metabolites of lapachol in rats by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:24316523]
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Jan 1;944:128-35.
Lapachol is a natural naphthoquinone compound derived from Bignoniaceae (Tabebuia sp.) that possesses a range of significant biological activities. Nine phase I and four phase II metabolites of Lapachol in rat bile were firstly elucidated and identified using a sensitive LC-ESI-MS(n) method. The molecular structures of the metabolites have been presented on the basis of the characteristics of their precursor and product ions, as well as their fragmentation mechanisms and chromatographic retention times. The results indicated that the phase I metabolites were predominantly biotransformed by the hydroxylation, semiquinone hydrogenation at the oxygen position or a side chain rearrangement. The phase II metabolites were identified as the glucuronidated conjugates which showed a characteristic neutral loss of 176Da. Based on the results of this research, we have proposed the metabolic pathways for Lapachol in rats. This work has provided novel information for the in vivo Lapachol metabolism which could be used to develop a novel drug candidate, as well as a better understanding of the safety and efficacy of the drug.


