KawainCAS# 500-64-1 |
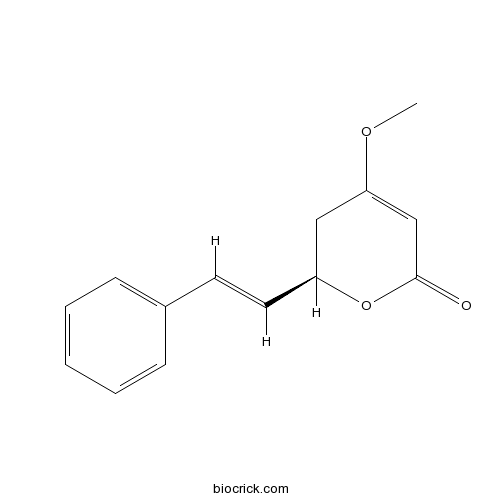
- Kavain
Catalog No.:BCN8295
CAS No.:3155-48-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 500-64-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281565 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H14O3 | M.Wt | 230.3 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 125 mg/mL (542.86 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2R)-4-methoxy-2-[(E)-2-phenylethenyl]-2,3-dihydropyran-6-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=O)OC(C1)C=CC2=CC=CC=C2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XEAQIWGXBXCYFX-GUOLPTJISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H14O3/c1-16-13-9-12(17-14(15)10-13)8-7-11-5-3-2-4-6-11/h2-8,10,12H,9H2,1H3/b8-7+/t12-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Kavain has anticonvulsive properties, attenuating vascular smooth muscle contraction through interactions with voltage-dependent Na+ and Ca2+ channels. Kawain is advanced glycation endproduct inhibitors, can increase the mean life span of Caenorhabditis elegans exposed to high glucose. |
| Targets | NMDAR |
| In vitro | Effects of kawain and dihydromethysticin on field potential changes in the hippocampus.[Pubmed: 9194150]Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1997 May;21(4):697-706.1. The kava-pyrones Kawain and dihydromethysticin are constituents of Piper methysticum which exert anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties. |
| In vivo | Pharmacokinetics and disposition of the kavalactone kawain: interaction with kava extract and kavalactones in vivo and in vitro.[Pubmed: 16033948]Drug Metab Dispos. 2005 Oct;33(10):1555-63.
|
| Kinase Assay | Kavalactones, a novel class of protein glycation and lipid peroxidation inhibitors.[Pubmed: 25098935]Planta Med. 2014 Aug;80(12):1001-8.Kawain, methysticin, and dihydromethysticin, all belonging to the group of kavalactones, were identified as advanced glycation endproduct inhibitors. |

Kawain Dilution Calculator

Kawain Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.3422 mL | 21.7108 mL | 43.4216 mL | 86.8432 mL | 108.5541 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8684 mL | 4.3422 mL | 8.6843 mL | 17.3686 mL | 21.7108 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4342 mL | 2.1711 mL | 4.3422 mL | 8.6843 mL | 10.8554 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0868 mL | 0.4342 mL | 0.8684 mL | 1.7369 mL | 2.1711 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0434 mL | 0.2171 mL | 0.4342 mL | 0.8684 mL | 1.0855 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Yangonin
Catalog No.:BCN3565
CAS No.:500-62-9
- Convolamine
Catalog No.:BCN1905
CAS No.:500-56-1
- Apoatropine
Catalog No.:BCN1869
CAS No.:500-55-0
- L-Mimosine
Catalog No.:BCC5450
CAS No.:500-44-7
- Nordihydroguaiaretic acid
Catalog No.:BCC1805
CAS No.:500-38-9
- D-(+)-Glucose
Catalog No.:BCN1259
CAS No.:50-99-7
- Ephedrine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8322
CAS No.:50-98-6
- Floxuridine
Catalog No.:BCC1187
CAS No.:50-91-9
- Thymidine
Catalog No.:BCN5622
CAS No.:50-89-5
- Ascorbic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2207
CAS No.:50-81-7
- Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic acid)
Catalog No.:BCC2097
CAS No.:50-78-2
- Actinomycin D
Catalog No.:BCC2385
CAS No.:50-76-0
- Rhapontigenin
Catalog No.:BCN3515
CAS No.:500-65-2
- Olivetol
Catalog No.:BCN4629
CAS No.:500-66-3
- 3,5-Dimethoxyphenol
Catalog No.:BCN7198
CAS No.:500-99-2
- Rilpivirine
Catalog No.:BCC1897
CAS No.:500287-72-9
- GANT61
Catalog No.:BCC1090
CAS No.:500579-04-4
- Securinol A
Catalog No.:BCN6987
CAS No.:5008-48-0
- Trans-caffeic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3462
CAS No.:501-16-6
- Cardanol (C15:1)
Catalog No.:BCN3751
CAS No.:501-26-8
- Kojic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6543
CAS No.:501-30-4
- 8-Azabicyclo-3.2.1-octan-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1888
CAS No.:501-33-7
- Resveratrol
Catalog No.:BCN5607
CAS No.:501-36-0
- Hydrocinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4057
CAS No.:501-52-0
Effects of kawain and dihydromethysticin on field potential changes in the hippocampus.[Pubmed:9194150]
Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1997 May;21(4):697-706.
1. The kava-pyrones Kawain and dihydromethysticin are constituents of Piper methysticum which exert anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties. 2. In the present study the effect of these kava-pyrones were tested on field potential changes (fp) induced by omission of the extracellular Mg2+, recorded from the area CA1 and CA3 of the hippocampal slice preparation of guinea pigs. These fp are generated by an activation of NMDA receptors and voltage dependent calcium channels. 3. Kawain and dihydromethysticin reduced reversibly the frequency of occurrence of fp in a concentration range from 5 to 40 mumol/l and 10 to 40 mumol/l, respectively. 4. Reduction of the fp frequency after addition of subthreshold concentrations of 5 mumol/l Kawain and 10 mumol/l dihydromethysticin indicated additive actions of both drugs. 5. Since the serotonin-1A agonist ipsapirone also exerts anxiolytic effects, subthreshold concentrations of Kawain or dihydromethysticin were combined with a subthreshold concentration of ipsapirone in another set of experiments. Combining Kawain and ipsapirone or dihydromethysticin and ipsapirone caused a reduction of the rate of fp to 0.76 and 0.81 of the baseline value, respectively. 6. The findings suggest that (i) single constituents of Piper methysticum may have additive actions, (ii) that the two components Kawain and dihydromethysticin may enhance the effects of the anxiolytic serotonin-1A agonist ipsapirone and (iii) that activation of NMDA receptors and/or voltage dependent calcium channels may be involved in the elementary mechanism of action of some kava-pyrones.
Pharmacokinetics and disposition of the kavalactone kawain: interaction with kava extract and kavalactones in vivo and in vitro.[Pubmed:16033948]
Drug Metab Dispos. 2005 Oct;33(10):1555-63.
Reported adverse drug interactions with the popular herb kava have spurred investigation of the mechanisms by which kava could mediate these effects. In vivo and in vitro experiments were conducted to examine the effects of kava extract and individual kavalactones on cytochrome P450 (P450) and P-glycoprotein activity. The oral pharmacokinetics of the kavalactone, Kawain (100 mg/kg), were determined in rats with and without coadministration of kava extract (256 mg/kg) to study the effect of the extract on drug disposition. Kawain was well absorbed, with >90% of the dose eliminated within 72 h, chiefly in urine. Compared with Kawain alone, coadministration with kava extract caused a tripling of Kawain AUC(0-8 h) and a doubling of C(max). However, a 7-day pretreatment with kava extract (256 mg /kg/day) had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of Kawain administered on day 8. The 7-day pretreatment with kava extract only modestly induced hepatic P450 activities. The human hepatic microsomal P450s most strongly inhibited by kava extract (CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4) were inhibited to the same degree by a "composite" kava formulation composed of the six major kavalactones contained in the extract. K(i) values for the inhibition of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 activities by methysticin, dihydromethysticin, and desmethoxyyangonin ranged from 5 to 10 microM. Kava extract and kavalactones (< or =9 microM) modestly stimulated P-glycoprotein ATPase activities. Taken together, the data indicate that kava can cause adverse drug reactions via inhibition of drug metabolism.
Kavalactones, a novel class of protein glycation and lipid peroxidation inhibitors.[Pubmed:25098935]
Planta Med. 2014 Aug;80(12):1001-8.
Both advanced glycation endproducts and advanced lipoxidation endproducts are implicated in many age-related chronic diseases and in protein ageing. In this study, Kawain, methysticin, and dihydromethysticin, all belonging to the group of kavalactones, were identified as advanced glycation endproduct inhibitors. With IC50 values of 43.5 +/- 1.2 microM and 45.0 +/- 1.3 microM for Kawain and methysticin, respectively, the compounds inhibited the in vitro protein glycation significantly better than aminoguanidine (IC50 = 231.0 +/- 11.5 microM; p = 0.01), an established reference compound. Kawain and methysticin also inhibited the formation of dicarbonyl compounds, which are intermediates in the process of advanced glycation endproduct formation. Similarly, Kawain and aminoguanidine prevented the formation of thiobarbituric reactive substances in both low-density lipoprotein and linoleic acid oxidation. Moreover, Kawain and aminoguanidine prevented advanced glycation endproduct formation by chelating Fe(3+) and Cu(2+) two to three times better than aminoguanidine. Furthermore, Kawain increased the mean life span of Caenorhabditis elegans exposed to high glucose. With glycation inhibiting, lipid peroxidation inhibiting, metal chelating properties, and life span extending ability, kavalactones show a high potential as advanced glycation endproducts and advanced lipoxidation endproduct inhibitors.


