Cardanol (C15:1)CAS# 501-26-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 501-26-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281854 | Appearance | Powder |
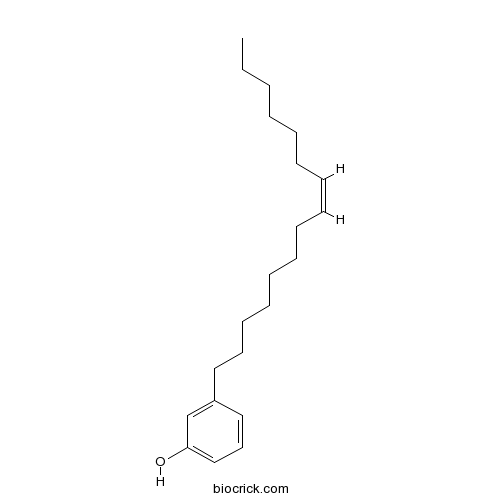
| Formula | C21H34O | M.Wt | 302.3 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 3-[(Z)-pentadec-8-enyl]phenol | ||
| SMILES | CCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC1=CC(=CC=C1)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YLKVIMNNMLKUGJ-FPLPWBNLSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H34O/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-16-20-17-15-18-21(22)19-20/h7-8,15,17-19,22H,2-6,9-14,16H2,1H3/b8-7- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Cardanol (C15:1) possesses the same side chain as anacardic acid (C15:1), acted neither as a substrate nor as an inhibitor of lipoxygenase-1. |
| In vitro | Lipoxygenase inhibitory activity of anacardic acids.[Pubmed: 15913294 ]J Agric Food Chem. 2005 Jun 1;53(11):4350-4.
|
| Structure Identification | Journal of the Science of Food & Agriculture, 2010 , 52 (1) :71-83.Long chain phenols--the thermal and oxidative deterioration of phenolic lipids from the cashew (Anacardium occidentale) nut shell.[Reference: WebLink]
|

Cardanol (C15:1) Dilution Calculator

Cardanol (C15:1) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.308 mL | 16.5399 mL | 33.0797 mL | 66.1594 mL | 82.6993 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6616 mL | 3.308 mL | 6.6159 mL | 13.2319 mL | 16.5399 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3308 mL | 1.654 mL | 3.308 mL | 6.6159 mL | 8.2699 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0662 mL | 0.3308 mL | 0.6616 mL | 1.3232 mL | 1.654 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0331 mL | 0.1654 mL | 0.3308 mL | 0.6616 mL | 0.827 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Trans-caffeic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3462
CAS No.:501-16-6
- Securinol A
Catalog No.:BCN6987
CAS No.:5008-48-0
- GANT61
Catalog No.:BCC1090
CAS No.:500579-04-4
- Rilpivirine
Catalog No.:BCC1897
CAS No.:500287-72-9
- 3,5-Dimethoxyphenol
Catalog No.:BCN7198
CAS No.:500-99-2
- Olivetol
Catalog No.:BCN4629
CAS No.:500-66-3
- Rhapontigenin
Catalog No.:BCN3515
CAS No.:500-65-2
- Kawain
Catalog No.:BCN3564
CAS No.:500-64-1
- Yangonin
Catalog No.:BCN3565
CAS No.:500-62-9
- Convolamine
Catalog No.:BCN1905
CAS No.:500-56-1
- Apoatropine
Catalog No.:BCN1869
CAS No.:500-55-0
- L-Mimosine
Catalog No.:BCC5450
CAS No.:500-44-7
- Kojic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6543
CAS No.:501-30-4
- 8-Azabicyclo-3.2.1-octan-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1888
CAS No.:501-33-7
- Resveratrol
Catalog No.:BCN5607
CAS No.:501-36-0
- Hydrocinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4057
CAS No.:501-52-0
- 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethanol
Catalog No.:BCN5608
CAS No.:501-94-0
- Rhododendrol
Catalog No.:BCN5609
CAS No.:501-96-2
- Phloretic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2950
CAS No.:501-97-3
- 2,3-Di-O-methylthiomethyleuscaphic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5610
CAS No.:
- Pilosol A
Catalog No.:BCC9121
CAS No.:501086-15-3
- 5,6,7,4'-Tetrahydroxyflavanone 6,7-diglucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1434
CAS No.:501434-65-7
- BI-D1870
Catalog No.:BCC5030
CAS No.:501437-28-1
- NS 1738
Catalog No.:BCC7535
CAS No.:501684-93-1
Lipoxygenase inhibitory activity of anacardic acids.[Pubmed:15913294]
J Agric Food Chem. 2005 Jun 1;53(11):4350-4.
6[8'(Z)-pentadecenyl]salicylic acid, otherwise known as anacardic acid (C15:1), inhibited the linoleic acid peroxidation catalyzed by soybean lipoxygenase-1 (EC 1.13.11.12, type 1) with an IC50 of 6.8 microM. The inhibition of the enzyme by anacardic acid (C15:1) is a slow and reversible reaction without residual activity. The inhibition kinetics analyzed by Dixon plots indicates that anacardic acid (C15:1) is a competitive inhibitor and the inhibition constant, KI, was obtained as 2.8 microM. Although anacardic acid (C15:1) inhibited the linoleic acid peroxidation without being oxidized, 6[8'(Z),11'(Z)-pentadecadienyl]salicylic acid, otherwise known as anacardic acid (C15:2), was dioxygenated at low concentrations as a substrate. In addition, anacardic acid (C15:2) was also found to exhibit time-dependent inhibition of lipoxygenase-1. The alk(en)yl side chain of anacardic acids is essential to elicit the inhibitory activity. However, the hydrophobic interaction alone is not enough because Cardanol (C15:1), which possesses the same side chain as anacardic acid (C15:1), acted neither as a substrate nor as an inhibitor.


