YangoninCAS# 500-62-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 500-62-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281575 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
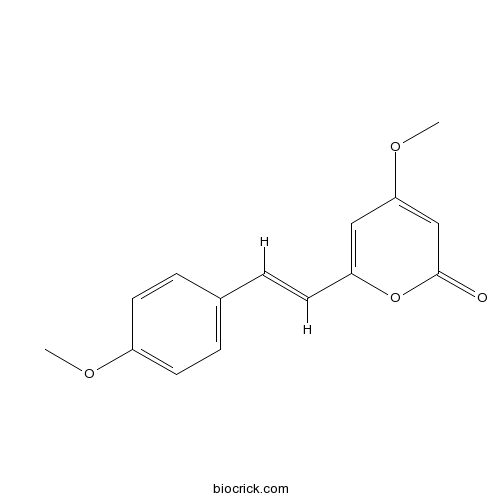
| Formula | C15H14O4 | M.Wt | 258.3 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Freely soluble in dioxane and methanol; slightly soluble in water | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-methoxy-6-[(E)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethenyl]pyran-2-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC=C(C=C1)C=CC2=CC(=CC(=O)O2)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XLHIYUYCSMZCCC-VMPITWQZSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H14O4/c1-17-12-6-3-11(4-7-12)5-8-13-9-14(18-2)10-15(16)19-13/h3-10H,1-2H3/b8-5+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Yangonin is a novel CB₁ receptor ligand, it exhibits affinity for the human recombinant CB₁ receptor, it is also an effective inhibitor of EV-A71 infection in the low-micromolar. Yangonin could be a valuable candidate for the intervention of NF-κB-dependent pathological conditions such as inflammation.Yangonin induces autophagy and sensitizes bladder cancer cells to flavokawain A and docetaxel via inhibition of the mTOR pathway. |
| Targets | TNF-α | p65 | NF-kB | IkB | ERK | p38MAPK | COX | IL Receptor | JNK | IKK | CB₁ receptor |
| In vitro | Yangonin blocks tumor necrosis factor-α-induced nuclear factor-κB-dependent transcription by inhibiting the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65 subunit.[Pubmed: 22510965]J Pharmacol Sci. 2012;118(4):447-54.The nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) transcription factors control many physiological processes including inflammation, immunity, and apoptosis. In our search for NF-κB inhibitors from natural resources, we identified Yangonin from Piper methysticum as an inhibitor of NF-κB activation. Characterization of three small molecule inhibitors of enterovirus 71 identified from screening of a library of natural products.[Pubmed: 28412182 ]Antiviral Res. 2017 Jul;143:85-96.Enterovirus 71 (EV-A71) is a major cause of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). Infection with EV-A71 is more often associated with neurological complications in children and is responsible for the majority of fatalities, but currently there is no approved antiviral therapy for treatment. |
| Kinase Assay | Kavalactone yangonin induces autophagy and sensitizes bladder cancer cells to flavokawain A and docetaxel via inhibition of the mTOR pathway.[Pubmed: 28630390]Kavalactones and the endocannabinoid system: the plant-derived yangonin is a novel CB₁ receptor ligand.[Pubmed: 22525682]Pharmacol Res. 2012 Aug;66(2):163-9.
J Biomed Res. 2017 Jun 20.Consumption of kava (Piper methysticum Forst) has been linked to reduced cancer risk in the South Pacific Islands. Kavalactones are major bioactive components in kava root extracts, which have recently demonstrated anti-cancer activities. However, molecular mechanisms of kavalactones' anti-cancer action remain largely unknown. |

Yangonin Dilution Calculator

Yangonin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.8715 mL | 19.3573 mL | 38.7147 mL | 77.4293 mL | 96.7867 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7743 mL | 3.8715 mL | 7.7429 mL | 15.4859 mL | 19.3573 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3871 mL | 1.9357 mL | 3.8715 mL | 7.7429 mL | 9.6787 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0774 mL | 0.3871 mL | 0.7743 mL | 1.5486 mL | 1.9357 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0387 mL | 0.1936 mL | 0.3871 mL | 0.7743 mL | 0.9679 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Yangonin exhibits affinity for the human recombinant cannabinoid CB1 receptor with an IC50 and a Ki of 1.79 ± 0.53 μM and 0.72±0.21 μM, respectively.
In Vitro:Yangonin is one of the six major kavalactones found in Piper methysticum.Yangonin potently inhibits NF-κB activation through suppression of the transcriptional activity of the RelA/p65 subunit of NF-κB. Yangonin significantly inhibits the induced expression of the NF-κB-reporter gene. However, Yangonin does not interfere with TNF-α-induced inhibitor of κBα (IκBα) degradation, p65 nuclear translocation, and DNA-binding activity of NF-κB. Yangonin inhibits not only the induced NF-κB activation by overexpression of RelA/p65, but also transactivation activity of RelA/p65. Yangonin does not inhibit TNF-α-induced activation of p38, but it significantly impairs activation of ERK 1/2 and stress-activated protein kinase/JNK[2].
References:
[1]. Ligresti A, et al. Kavalactones and the endocannabinoid system: the plant-derived yangonin is a novel CB1 receptor ligand. Pharmacol Res. 2012 Aug;66(2):163-9.
[2]. Ma J, et al. Yangonin blocks tumor necrosis factor-α-induced nuclear factor-κB-dependent transcription by inhibiting the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65 subunit. J Pharmacol Sci. 2012;118(4):447-54.
[3]. Wruck CJ, et al. Kavalactones protect neural cells against amyloid beta peptide-induced neurotoxicity via extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2-dependent nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 activation. Mol Pharmacol. 2008 Jun;73(6):1785-95.
- Convolamine
Catalog No.:BCN1905
CAS No.:500-56-1
- Apoatropine
Catalog No.:BCN1869
CAS No.:500-55-0
- L-Mimosine
Catalog No.:BCC5450
CAS No.:500-44-7
- Nordihydroguaiaretic acid
Catalog No.:BCC1805
CAS No.:500-38-9
- D-(+)-Glucose
Catalog No.:BCN1259
CAS No.:50-99-7
- Ephedrine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8322
CAS No.:50-98-6
- Floxuridine
Catalog No.:BCC1187
CAS No.:50-91-9
- Thymidine
Catalog No.:BCN5622
CAS No.:50-89-5
- Ascorbic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2207
CAS No.:50-81-7
- Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic acid)
Catalog No.:BCC2097
CAS No.:50-78-2
- Actinomycin D
Catalog No.:BCC2385
CAS No.:50-76-0
- 1,3:2,4-Di-p-methylbenyliedene sorbitol
Catalog No.:BCC4847
CAS No.:54686-97-4
- Kawain
Catalog No.:BCN3564
CAS No.:500-64-1
- Rhapontigenin
Catalog No.:BCN3515
CAS No.:500-65-2
- Olivetol
Catalog No.:BCN4629
CAS No.:500-66-3
- 3,5-Dimethoxyphenol
Catalog No.:BCN7198
CAS No.:500-99-2
- Rilpivirine
Catalog No.:BCC1897
CAS No.:500287-72-9
- GANT61
Catalog No.:BCC1090
CAS No.:500579-04-4
- Securinol A
Catalog No.:BCN6987
CAS No.:5008-48-0
- Trans-caffeic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3462
CAS No.:501-16-6
- Cardanol (C15:1)
Catalog No.:BCN3751
CAS No.:501-26-8
- Kojic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6543
CAS No.:501-30-4
- 8-Azabicyclo-3.2.1-octan-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1888
CAS No.:501-33-7
- Resveratrol
Catalog No.:BCN5607
CAS No.:501-36-0
Yangonin blocks tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent transcription by inhibiting the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65 subunit.[Pubmed:22510965]
J Pharmacol Sci. 2012;118(4):447-54.
The nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) transcription factors control many physiological processes including inflammation, immunity, and apoptosis. In our search for NF-kappaB inhibitors from natural resources, we identified Yangonin from Piper methysticum as an inhibitor of NF-kappaB activation. In the present study, we demonstrate that Yangonin potently inhibits NF-kappaB activation through suppression of the transcriptional activity of the RelA/p65 subunit of NF-kappaB. This compound significantly inhibited the induced expression of the NF-kappaB-reporter gene. However, this compound did not interfere with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha)-induced inhibitor of kappaBalpha (IkappaBalpha) degradation, p65 nuclear translocation, and DNA-binding activity of NF-kappaB. Further analysis revealed that Yangonin inhibited not only the induced NF-kappaB activation by overexpression of RelA/p65, but also transactivation activity of RelA/p65. Moreover, Yangonin did not inhibit TNF-alpha-induced activation of p38, but it significantly impaired activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase. We also demonstrated that pretreatment of cells with this compound prevented TNF-alpha-induced expression of NF-kappaB target genes, such as interleukin 6, interleukin 8, monocyte chemotactic protein 1, cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide. Taken together, Yangonin could be a valuable candidate for the intervention of NF-kappaB-dependent pathological conditions such as inflammation.
Characterization of three small molecule inhibitors of enterovirus 71 identified from screening of a library of natural products.[Pubmed:28412182]
Antiviral Res. 2017 Jul;143:85-96.
Enterovirus 71 (EV-A71) is a major cause of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). Infection with EV-A71 is more often associated with neurological complications in children and is responsible for the majority of fatalities, but currently there is no approved antiviral therapy for treatment. Here, we identified auraptene, formononetin, and Yangonin as effective inhibitors of EV-A71 infection in the low-micromolar range from screening of a natural product library. Among them, formononetin and Yangonin selectively inhibited EV-A71 while auraptene could inhibit viruses within the enterovirus species A. Time of addition studies showed that all the three inhibitors inhibit both attachment and postattachment step of entry. We found mutations conferring the resistance to these inhibitors in the VP1 and VP4 capsid proteins and confirmed the target residues using a reverse genetic approach. Interestingly, auraptene- and formononetin-resistant viruses exhibit cross-resistance to other inhibitors while Yangonin-resistant virus still remains susceptible to auraptene and formononetin. Moreover, auraptene and formononetin, but not Yangonin protected EV-A71 against thermal inactivation, indicating a direct stabilizing effect of both compounds on virion capsid conformation. Finally, neither biochanin A (an analog of formononetin) nor DL-Kavain (an analog of Yangonin) exhibited anti-EV-A71 activity, suggesting the structural elements required for anti-EV-A71 activity. Taken together, these compounds could become potential lead compounds for anti-EV-A71 drug development and also serve as tool compounds for studying virus entry.
Kavalactones and the endocannabinoid system: the plant-derived yangonin is a novel CB(1) receptor ligand.[Pubmed:22525682]
Pharmacol Res. 2012 Aug;66(2):163-9.
To investigate the possible interactions between kavalactone-based molecules and proteins of the endocannabinoid system and provide novel and synthetically accessible structural scaffolds for the design of cannabinoid receptor ligands sharing pharmacological properties with kavapyrones, a preliminary SAR analysis was performed on five commercially available natural kavalactones and nine kavalactone-analogues properly synthesized. These compounds were investigated for assessing their cannabinoid receptor binding affinity and capability of inhibiting the activity of the two major metabolic enzymes of the endocannabinoid system, fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL). Among the molecules tested, only Yangonin exhibited affinity for the human recombinant CB(1) receptor with a K(i)=0.72 muM and selectivity vs. the CB(2) receptor (K(i)>10 muM). None of the compounds exhibited strong inhibitory effects on the two enzymes analyzed. The CB(1) receptor affinity of Yangonin suggests that the endocannabinoid system might contribute to the complex human psychopharmacology of the traditional kava drink and the anxiolytic preparations obtained from the kava plant.


