HistamineCAS# 51-45-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 51-45-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 774 | Appearance | Powder |
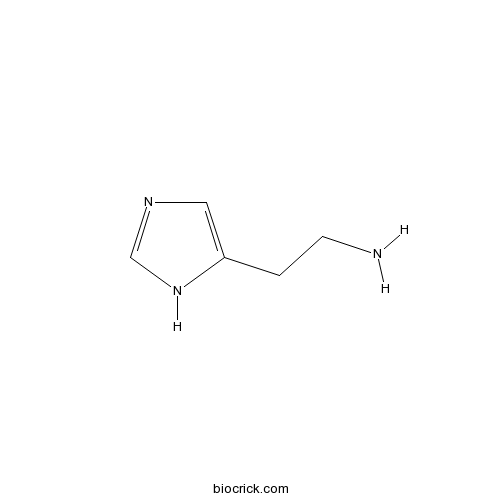
| Formula | C5H9N3 | M.Wt | 111.15 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Ergamine | ||
| Solubility | H2O : ≥ 34 mg/mL (305.89 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)ethanamine | ||
| SMILES | C1=C(NC=N1)CCN | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NTYJJOPFIAHURM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C5H9N3/c6-2-1-5-3-7-4-8-5/h3-4H,1-2,6H2,(H,7,8) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Histamine, an organic nitrogenous compound, is involved in local immune responses regulating physiological function in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. It is a potent H1 and H2 receptor agonist. Histamine increases Nav1.8 expression in primary afferent neurons via H2 receptor-mediated pathway and thereby contributes to neuropathic pain, H2 receptor antagonists may potentially be used as analgesics for patients with neuropathic pain. |
| Targets | IL Receptor | Histamine Receptor | Nav1.8 |
| In vivo | Modulation of ConA-induced inflammatory ascites by histamine - short communication.[Pubmed: 25823456]Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2015 Mar;62(1):87-91.The early phase of the ConA-induced inflammatory ascites was studied, with special reference to Histamine. The histamine H4 -receptor (H4 R) regulates eosinophilic inflammation in ovalbumin-induced experimental allergic asthma in mice.[Pubmed: 25501767]Eur J Immunol. 2015 Apr;45(4):1129-40.Via the Histamine H4 -receptor (H4 R), Histamine promotes the pathogenesis of experimental allergic asthma in mice. Application of H4 R antagonists during sensitization as well as during provocation reduces the severity of the disease. However, the specific cell types functionally expressing H4 R in experimental allergic asthma have not been well characterized in vivo. |
| Animal Research | Histamine upregulates Nav1.8 expression in primary afferent neurons via H2 receptors: involvement in neuropathic pain.[Pubmed: 24990156]CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014 Oct;20(10):883-92.The upregulation of Nav1.8 in primary afferents plays a critical role in the development and persistence of neuropathic pain. The mechanisms underlying the upregulation are not fully understood. |

Histamine Dilution Calculator

Histamine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 8.9969 mL | 44.9843 mL | 89.9685 mL | 179.937 mL | 224.9213 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.7994 mL | 8.9969 mL | 17.9937 mL | 35.9874 mL | 44.9843 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.8997 mL | 4.4984 mL | 8.9969 mL | 17.9937 mL | 22.4921 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1799 mL | 0.8997 mL | 1.7994 mL | 3.5987 mL | 4.4984 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.09 mL | 0.4498 mL | 0.8997 mL | 1.7994 mL | 2.2492 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses as well as regulating physiological function in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter.
- Adrenaline
Catalog No.:BCN2191
CAS No.:51-43-4
- Epinephrine Bitartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4348
CAS No.:51-42-3
- Norepinephrine
Catalog No.:BCN2206
CAS No.:51-41-2
- H-Hyp-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3250
CAS No.:51-35-4
- Scopolamine
Catalog No.:BCN5045
CAS No.:51-34-3
- Isoprenaline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4328
CAS No.:51-30-9
- Tiratricol
Catalog No.:BCC4738
CAS No.:51-24-1
- Fluorouracil (Adrucil)
Catalog No.:BCC2135
CAS No.:51-21-8
- Benzimidazole
Catalog No.:BCC8847
CAS No.:51-17-2
- Procaine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5072
CAS No.:51-05-8
- Pronethalol hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5678
CAS No.:51-02-5
- 7ACC1
Catalog No.:BCC5553
CAS No.:50995-74-9
- L-Thyroxine
Catalog No.:BCC4917
CAS No.:51-48-9
- Propylthiouracil
Catalog No.:BCC4931
CAS No.:51-52-5
- Atropine
Catalog No.:BCN5639
CAS No.:51-55-8
- Homatropine Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC4570
CAS No.:51-56-9
- D-Amphetamine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC5942
CAS No.:51-63-8
- 4'-Methoxyacetanilide
Catalog No.:BCC8711
CAS No.:51-66-1
- Tyramine
Catalog No.:BCN6776
CAS No.:51-67-2
- Carbamoylcholine chloride
Catalog No.:BCC7492
CAS No.:51-83-2
- (2-Acetoxyethyl)trimethylammonium
Catalog No.:BCN1743
CAS No.:51-84-3
- Tetramethylammonium
Catalog No.:BCN1816
CAS No.:51-92-3
- Trachelanthine
Catalog No.:BCN2042
CAS No.:510-19-0
- Voacangine
Catalog No.:BCN3224
CAS No.:510-22-5
The histamine H4 -receptor (H4 R) regulates eosinophilic inflammation in ovalbumin-induced experimental allergic asthma in mice.[Pubmed:25501767]
Eur J Immunol. 2015 Apr;45(4):1129-40.
Via the Histamine H4 -receptor (H4 R), Histamine promotes the pathogenesis of experimental allergic asthma in mice. Application of H4 R antagonists during sensitization as well as during provocation reduces the severity of the disease. However, the specific cell types functionally expressing H4 R in experimental allergic asthma have not been well characterized in vivo. In this study, we identified the cell type(s) responsible for H4 R activity in experimental asthma and related physiological mechanisms. Using H4 R-deficient mice, we studied the role of H4 R in the sensitization and effector phase. DCs lacking H4 R expression during the in vitro sensitization reaction resulted in effector T cells unable to induce an entire eosinophilic inflammation in the lung upon adoptive transfer in vivo. Recipient mice lacking H4 R expression, which were adoptively transferred with H4 R(+/+) T cells polarized in the presence of H4 R(+/+) DCs, showed reduced signs of inflammation and ameliorated lung function. Here, we provide in vivo evidence that in experimental asthma in mice the H4 R specifically regulates activation of DCs during sensitization, while in the effector phase the H4 R is active in cells involved in the activation of eosinophils, and possibly other cells. A putative therapy targeting the H4 R may be an option for asthma patients developing IL-5-dependent eosinophilia.
Modulation of ConA-induced inflammatory ascites by histamine - short communication.[Pubmed:25823456]
Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2015 Mar;62(1):87-91.
The early phase of the ConA-induced inflammatory ascites was studied, with special reference to Histamine. Concanavalin A (ConA), a cell-surface binding lectin was injected i.p. (25 mg/kg bw) to mice. After 1 h the animals were killed, the ascitic fluid collected and measured. Other agents were injected s.c., 10 min before the ConA-challenge. Exogenous Histamine markedly inhibited the ConA-induced ascites. Release of endogenous vasoactive agents from the mast cells by Compound 48/80 had a similar, but slight effect. Cromolyn, a mast cell stabilizing agent, and chloropyramine, a Histamine H1 receptor antagonist was ineffective. Although Histamine increases endothelial permeability, it did not enhance the formation of ascitic fluid, on the contrary, it inhibited the ConA-induced ascites, presumably due to its known hypotonic effect. It is concluded that ConA-induced ascites is not mediated by mast cell Histamine.
Histamine upregulates Nav1.8 expression in primary afferent neurons via H2 receptors: involvement in neuropathic pain.[Pubmed:24990156]
CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014 Oct;20(10):883-92.
INTRODUCTION: The upregulation of Nav1.8 in primary afferents plays a critical role in the development and persistence of neuropathic pain. The mechanisms underlying the upregulation are not fully understood. AIMS: The present study aims to investigate the regulatory effect of Histamine on the expression of Nav1.8 in primary afferent neurons and its involvement in neuropathic pain. RESULTS: Histamine at 10(-8) M increased the expression of Nav1.8 in cultured DRG neurons. This effect could be blocked by H2 receptor antagonist cimetidine or famotidine, but not by H1 receptor antagonist pyrilamine or dual H3 /H4 antagonist thioperamide. Peri-sciatic administration of Histamine increased Nav1.8 expression in the sciatic nerve and L4/L5 DRG neurons in a dose-dependent manner, accompanied with remarkable mechanical allodynia and heat hyperalgesia in the ipsilateral hindpaw. Famotidine but not pyrilamine or thioperamide inhibited Nav1.8 upregulation and pain hypersensitivity. In addition, famotidine (40 mg/kg, i.p.) not only suppressed autotomy behavior in the rat neuroma model of neuropathic pain but also attenuated mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia following partial sciatic nerve ligation. Moreover, famotidine inhibited Nav1.8 upregulation in the neuroma and ligated sciatic nerve. CONCLUSIONS: Our findings indicate that Histamine increases Nav1.8 expression in primary afferent neurons via H2 receptor-mediated pathway and thereby contributes to neuropathic pain. H2 receptor antagonists may potentially be used as analgesics for patients with neuropathic pain.


